Updated March 8, 2023
Introduction to SQL pivot
Pivot is the situation where we require that the results of the table or query are rotated in the sense that would lead to the data that is present in columns to be displayed in a horizontal manner and the data which is present in the rows of the table to be represented in the vertical format. This rotation of the data representation is called the pivot or a pivot table. There are many ways using which we can display the data in the pivot format in SQL. In this article, we will see how we can transpose the data that rotate the data to display in pivot format using a simple case statement and then by using the pivot statement in SQL.
Pivoting Data in SQL
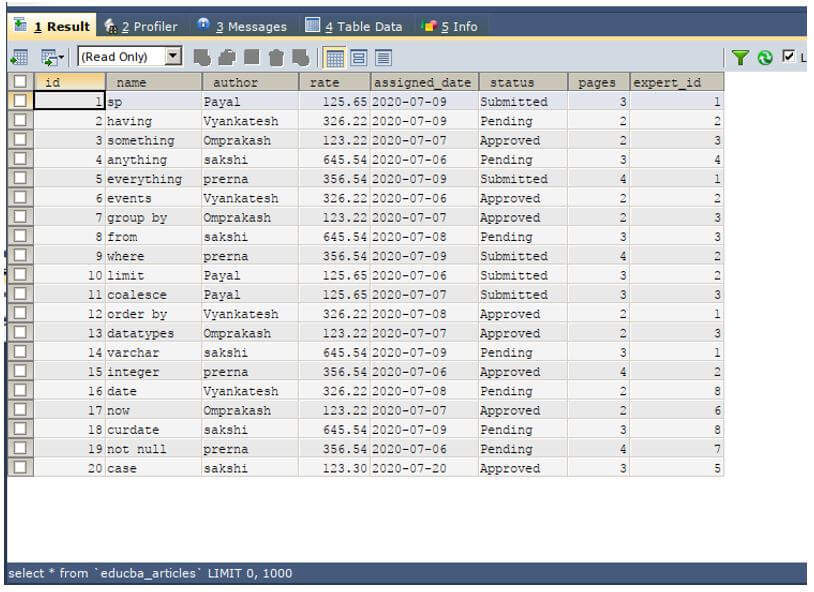
To know the pivoting let us consider one simple example, where we have on existing tables named educba_articles in the database named educba which stores the datewise articles of each date and has columns maintained in the table which includes the status, author, and rate of that article.
The contents of the tables are as shown in the output of the below query statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM educba_articles;The execution of the above query statement gives an output which is as shown below where we have data up to of different dates and articles and the table contains a total of 20 records in it.
Output:
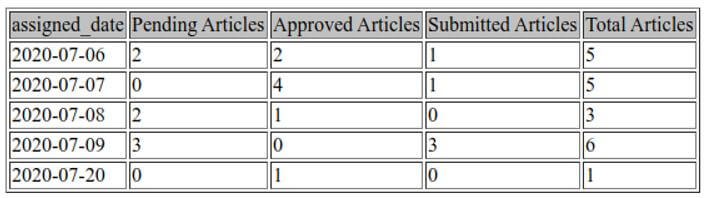
Now, what we have to do is calculate the total article count of each assigned date and display the assigned date values and article count values in the horizontal manner such that the assigned date and their respective article details are shown further after the assigned date column and the last column should include the total column that will show the total count of articles as shown in the below format.
Output:
Now, we will see how we can display the data in the pivot format as shown above by both of the ways that include the use of the case statement and secondly the use of pivot statement.
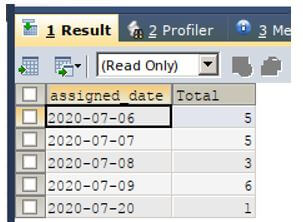
Let us first calculate the total of each articles and display all the assigned date values that are present in the table. For this, we will make the use of a simple query that will group the result based on the assigned date and order the result set on assigned date column value and use the count aggregate function to calculate the total articles of each assigned date.
Code:
SELECT assigned_date,
COUNT(id) AS Total
FROM educba_articles
GROUP BY assigned_date
ORDER BY assigned_date;Output:
Standard ANSI-SQL pivot
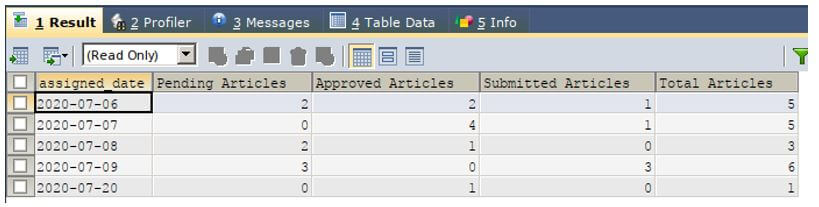
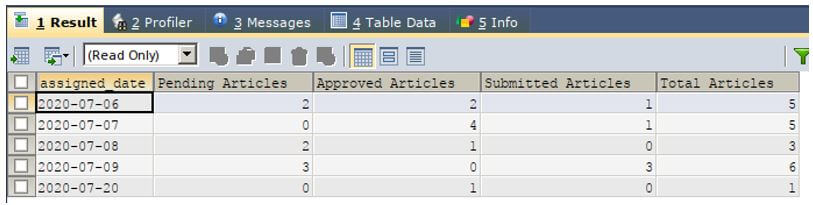
The standard SQL supports the usage of case statements that can be used to revert the row values to column values and vice versa. Now, let us try implementing the pivot functionality using case statement to achieve the resultset as shown in the above figure.
Our query statement will be as follows having a CASE statement in it.
Code:
SELECT
`assigned_date` , COUNT(
CASE
WHEN `status` = "Pending"
THEN `id`
END
) AS "Pending Articles",
COUNT(
CASE
WHEN `status` = "Approved"
THEN `id`
END
) AS "Approved Articles",
COUNT(
CASE
WHEN `status` = "Submitted"
THEN `id`
END
) AS "Submitted Articles",
COUNT(`id`) AS "Total Articles"
FROM
`educba_articles`
GROUP BY `assigned_date` ;Output:
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 pivot
Microsoft SQL Server 2005 introduced the support of pivot statement to get the functionality of pivot and implement the same. Let us consider the same above example, we will use the pivot statement which will help us store the values in temporary variables. Here, we have used 1,2,3, etc and to replace NULL values with 0 we have made the use of COALESCE function.
Code:
SELECT assigned_date,
COALESCE ([ 1, 0) ] AS [ Pending Articles ],
COALESCE ([ 2, 0) ] AS [ Approved Articles ],
COALESCE ([ 3, 0) ] AS [ Submitted Articles ],
[ 1 ] + [ 2 ] + [ 3 ] AS Total FROM (
SELECT assigned_date,
STATUS,
id FROM educba_articles
) AS src
PIVOT
(COUNT (id) FOR STATUS IN ([ 1 ], [ 2 ], [ 3 ])) AS pvt
ORDER BY assigned_date ;Output:
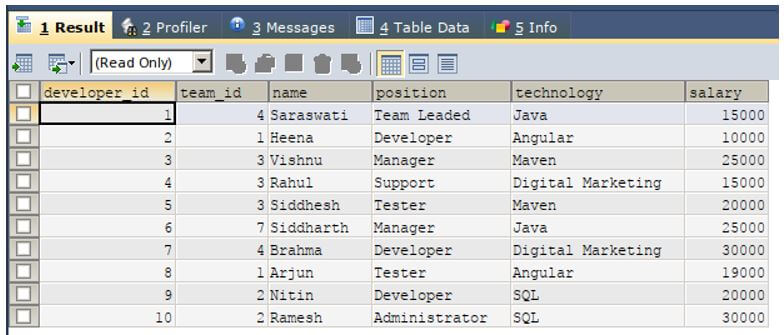
Let us consider one more example, we have a table named developers in the database named educba which stores the positionwise workers and their salaries and has columns maintained in the table which includes the name, position, technology and salary of that article.
The contents of the tables are as shown in the output of the below query statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM `developers`;Output:
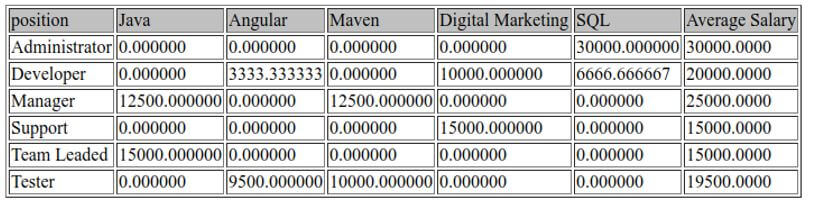
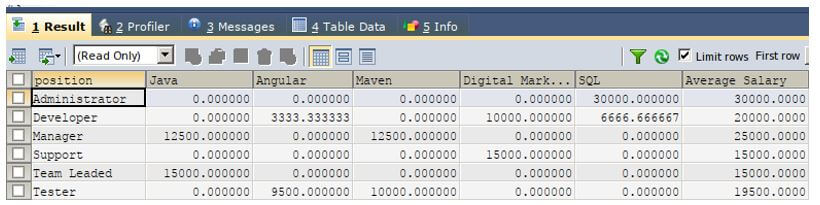
Now, we have to calculate the positionwise average salary of each technology.
Output:
Code:
SELECT
`position`,
AVG(
CASE
WHEN `technology` = "Java"
THEN `salary`
ELSE 0.00
END
) AS "Java",
AVG(
CASE
WHEN `technology` = "Angular"
THEN `salary`
ELSE 0.00
END
) AS "Angular",
AVG(
CASE
WHEN `technology` = "Maven"
THEN `salary`
ELSE 0.00
END
) AS "Maven",
AVG(
CASE
WHEN `technology` = "Digital Marketing"
THEN `salary`
ELSE 0.00
END
) AS "Digital Marketing",
AVG(
CASE
WHEN `technology` = "SQL"
THEN `salary`
ELSE 0.00
END
) AS "SQL",
AVG(salary) AS "Average Salary"
FROM
`developers`
GROUP BY `position` ;Output:
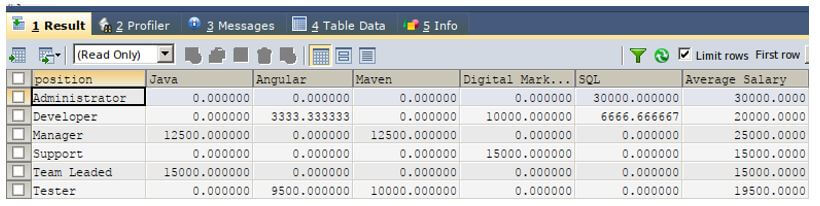
Code:
SELECT technology,
COALESCE ([ 1, 0) ] AS [ Java ],
COALESCE ([ 2, 0) ] AS [ Angular ],
COALESCE ([ 3, 0) ] AS [ Maven ],
COALESCE ([ 4, 0) ] AS [ Digital Marketing ],
COALESCE ([ 5, 0) ] AS [ SQL ],
[ 1 ] + [ 2 ] + [ 3 ] + [ 4 ] + [ 5 ] AS "Average Salary" FROM (
SELECT technology,
salary,
POSITION FROM educba_articles
) AS src
PIVOT
(AVG (POSITION) FOR salary IN ([ 1 ], [ 2 ], [ 3 ], [ 4 ], [ 5 ])) AS pvt
ORDER BY technology ;Output:
Conclusion
We can reverse the display format of column and row values in the table that is transforming the table data by using the pivot statement in SQL. There are mostly two ways of doing so, the standard SQL supports the usage of case statements that can be used to revert the row values to column values and vice versa. Microsoft SQL Server 2005 introduced the support of pivot statement to get the functionality of pivot and implement the same.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL pivot” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.