Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to SQL GROUPING SETS
GROUPING SET in standard query language (SQL) can be considered as a sub-clause of GROUP BY clause. For uninitiated, GROUP BY clause is used to group rows having the same values in a column into summary rows. A grouping set is a set or group of columns by which rows with similar values are grouped together. Functionally, it generates a result set similar to the one generated by a UNION ALL of multiple GROUP BY clauses on a single column. Some other sub-clause of GROUP BY clause such as ROLLUP, CUBE etc also produce result sets equivalent to GROUPING SETS.
Syntax and parameters:
The basic syntax for working with GROUPING SETS() in SQL is as follows :
SELECT
column1,
column2,
aggregate_function(column3)
FROM
table_name
GROUP BY
GROUPING SETS (
(column1, column2),
(column1),
(column2),
()
);The parameters used in the above mentioned syntax are as follows:
- column1, column2: The columns or field names that have to be fetched for the final result set.
- aggregrate_function(column3): The aggregate function and column name on the basis of which group summary will be prepared.
- GROUPING SETS: Set of columns that have to be grouped together.
Examples of SQL GROUPING SETS
In order to illustrate grouping sets in SQL, let us create a dummy to table called “products”. It contains product details such as product_id, price, brand and manufacturing date.
Code:
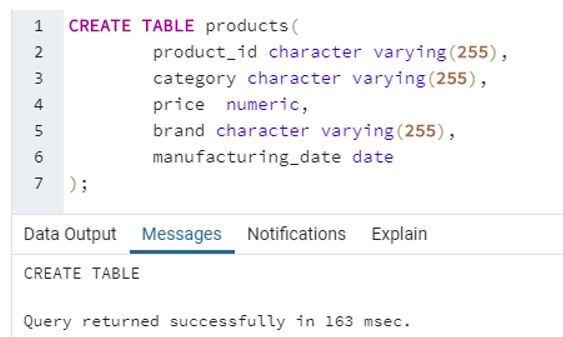
CREATE TABLE products(
product_id character varying(255),
category character varying(255),
price numeric,
brand character varying(255),
manufacturing_date date
);Output:
We have successfully created the table. Next, let us insert some values in the table using the following INSERT query.
Code:
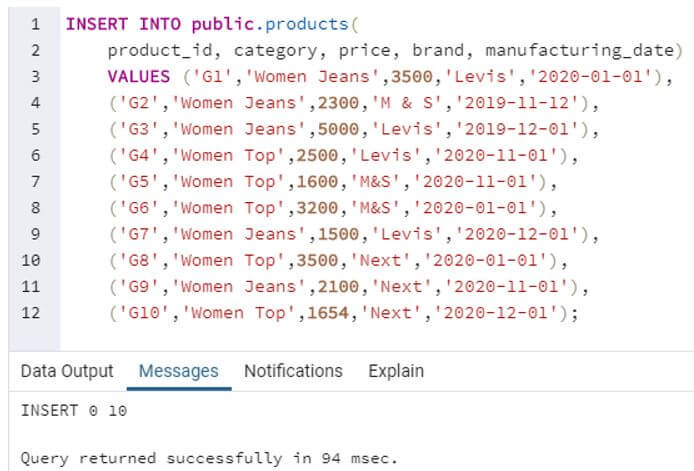
INSERT INTO public.products(
product_id, category, price, brand, manufacturing_date)
VALUES ('G1','Women Jeans',3500,'Levis','2020-01-01'),
('G2','Women Jeans',2300,'M&S','2019-11-12'),
('G3','Women Jeans',5000,'Levis','2019-12-01'),
('G4','Women Top',2500,'Levis','2020-11-01'),
('G5','Women Top',1600,'M&S','2020-11-01'),
('G6','Women Top',3200,'M&S','2020-01-01'),
('G7','Women Jeans',1500,'Levis','2020-12-01'),
('G8','Women Top',3500,'Next','2020-01-01'),
('G9','Women Jeans',2100,'Next','2020-11-01'),
('G10','Women Top',1654,'Next','2020-12-01');Output:
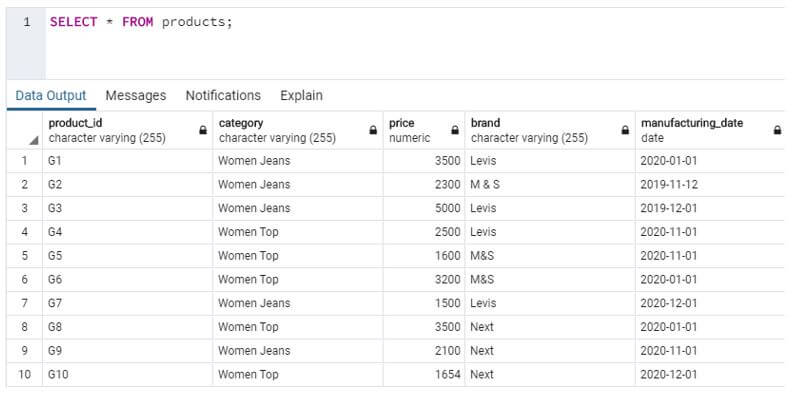
The products table after successful insertion operation looks something like this:
Code:
SELECT * FROM products;Output:
Example #1
Grouping sets in SQL is considered equivalent to UNION ALL on multiple group by clauses. So, our first example is an illustration of the same.
Consider the following SQL queries with GROUP BY clause on category, brand, manufacturing month and finally a summary.
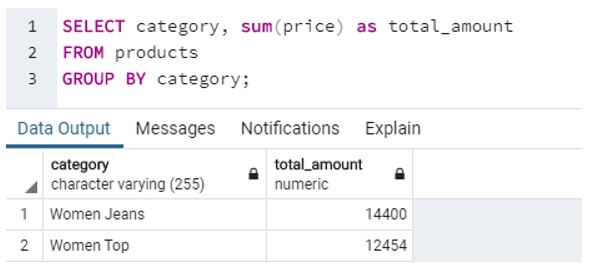
a. SQL query to find total amount for each category.
Code:
SELECT category, sum(price) as total_amount
FROM products
GROUP BY category;Output:
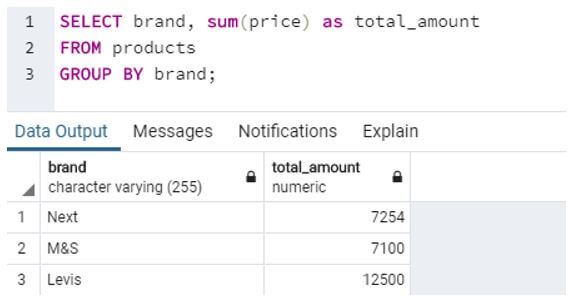
b. SQL query to find total amount for each brand.
Code:
SELECT brand, sum(price) as total_amount
FROM products
GROUP BY brand;Output:
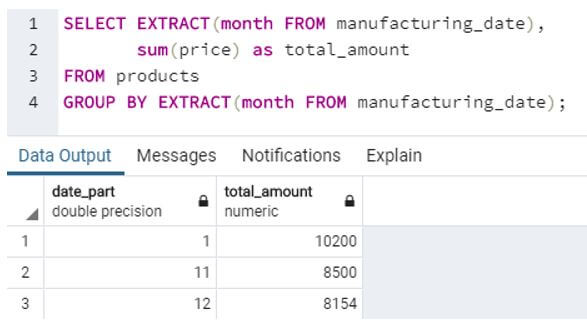
c. SQL query to find total amount for each month of manufacturing.
Code:
SELECT EXTRACT(month FROM manufacturing_date),
sum(price) as total_amount
FROM products
GROUP BY EXTRACT(month FROM manufacturing_date);Output:
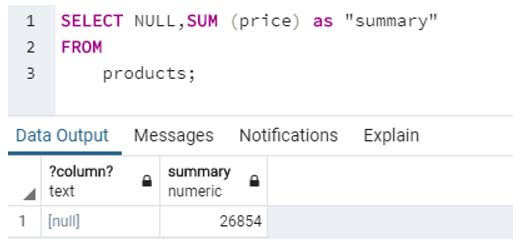
d. SQL query to find total amount for overall.
Code:
SELECT NULL,SUM (price) as "summary"
FROM
products;Output:
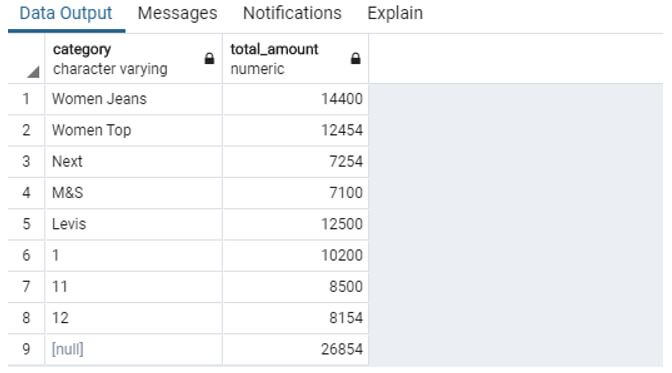
When we combine all of the above GROUP BY queries using UNION ALL as shown below, we get a result set equivalent to the result set obtained by GROUPING SETS.
Code:
SELECT category, sum(price) as total_amount
FROM products
GROUP BY category
UNION ALL
SELECT brand, sum(price) as total_amount
FROM products
GROUP BY brand
UNION ALL
SELECT EXTRACT(month FROM manufacturing_date) :: varchar,
sum(price) as total_amount
FROM products
GROUP BY EXTRACT(month FROM manufacturing_date)
UNION ALL
SELECT NULL,SUM (price) as "summary"
FROM products;Output:
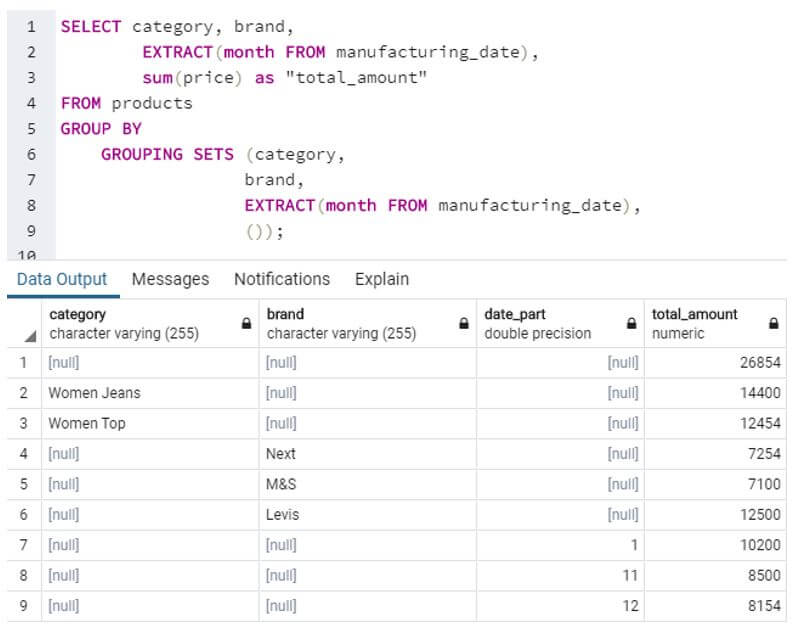
Now observe this next query. Here, we have used grouping sets to group category, brand and month of manufacturing together.
Code:
SELECT category, brand,
EXTRACT(month FROM manufacturing_date),
sum(price) as "total_amount"
FROM products
GROUP BY
GROUPING SETS (category,
brand,
EXTRACT(month FROM manufacturing_date),
());Output:
What do you observe? We observe that the result set obtained from both the queries is the same. The only difference is of NULL values, we can coalesce them using COALESCE function. But most importantly, the second query is more concise and easier to understand.
Example #2
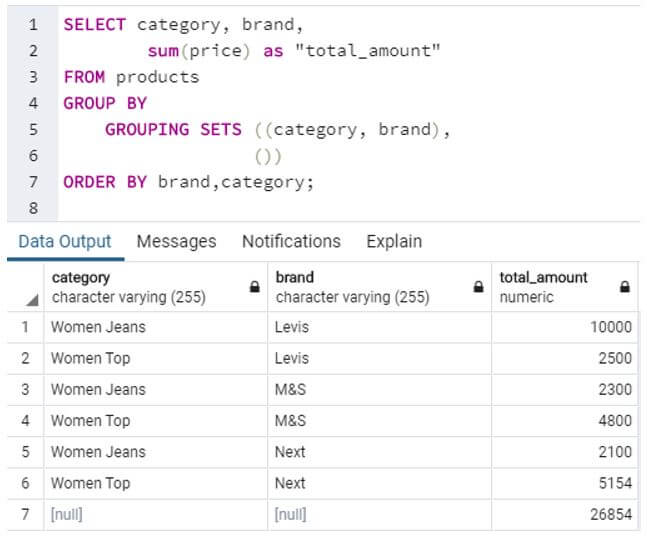
Prepare a summary table for each category brand wise with the total amount under each group.
Code:
SELECT category, brand,
sum(price) as "total_amount"
FROM products
GROUP BY
GROUPING SETS ((category, brand),
())
ORDER BY brand,category;Output:
In this example, we have grouped category and brand together as a single set. Hence, within each category we see further brandwise grouping.
Example #3
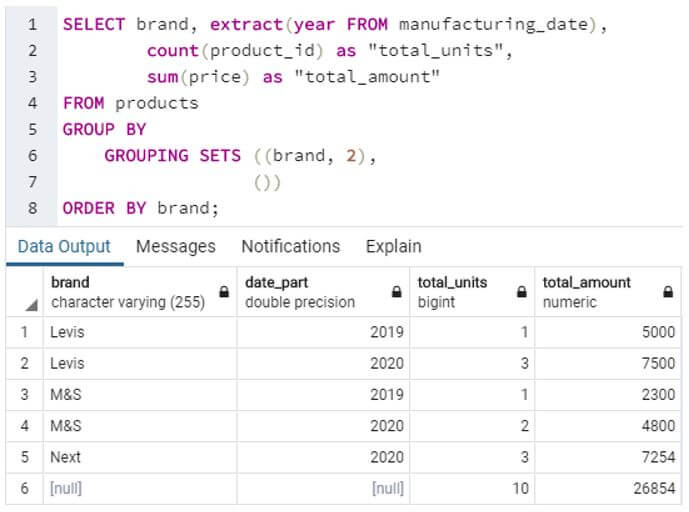
Prepare a summary table with count and total amount of brand wise yearly manufacturing of products.
Code:
SELECT brand, extract(year FROM manufacturing_date),
count(product_id) as "total_units",
sum(price) as "total_amount"
FROM products
GROUP BY
GROUPING SETS ((brand, 2),
())
ORDER BY brand;Output:
Here, we have found the total units and the total amount of garment manufactured for each brand on a yearly basis by grouping brand and year of manufacturing together in a single set.
Conclusion
Grouping sets is like sub-clause under GROUP BY clause that help in preparing summary tables along multiple dimensions. It is equivalent to performing UNION ALL on more than one GROUP BY queries. But it’s more concise and the query is easier to understand.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL GROUPING SETS” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.