Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to SQL Users
In SQL Server a database user can be created either by using Transact-SQL or using SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). Different types of users can be created in SQL but before understanding the types of users let us first understand the user creation flow. Following is the flow for login to the creation of the user and assigning permission.
Typical SQL Users workflow
Below is the workflow of SQL User:
1. Creating Login
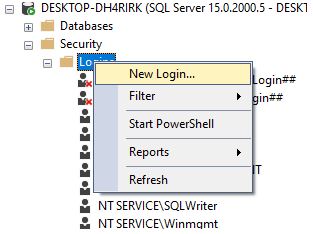
Step 1: First, we need to create a login for a user and to do that navigate to Security -> Login
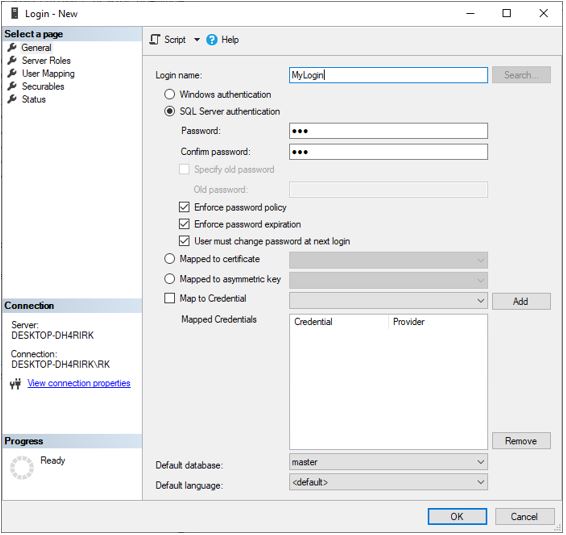
Step 2: Next, we enter the login name and select SQL server authentication with password
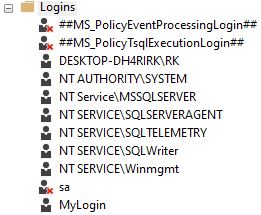
Step 3: This creates the login
The same result can be achieved using the following T-SQL command:
CREATE LOGIN MyLogin WITH PASSWORD = 'abc';2. Creating User
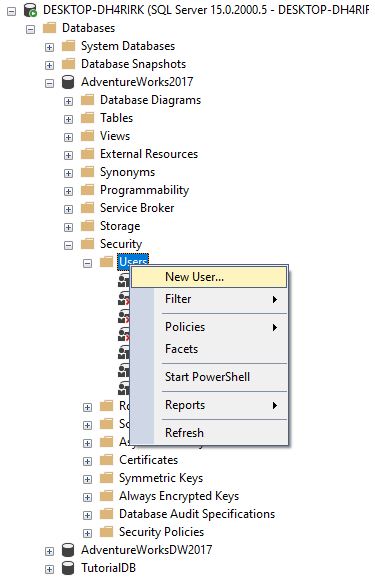
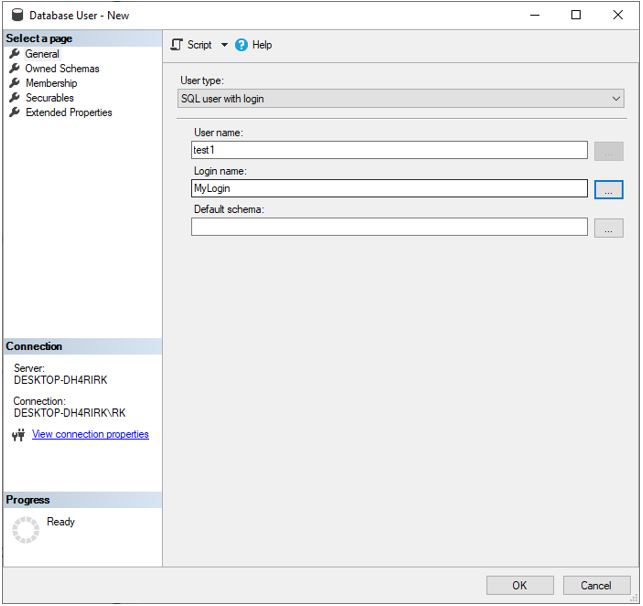
Step 1: To create a user first go the database folder in the object explorer and identify the database for which you have to create the user. In the security folder, there is an option to create a user.
Step 2: Then you will get the following screen in which set the user name and select the login which we have just created as we are creating user of type SQL user with login.
Step 3: The same result can be achieved using the following T-SQL query. To view, the query clicks the script button on create database user window and it will open in a query window.
USE [AdventureWorks2017]
GO
CREATE USER [test1] FOR LOGIN [MyLogin]
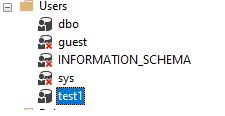
GOWe can see that the user is created and if not visible then refresh the Users folder.
3. Assigning permissions to User
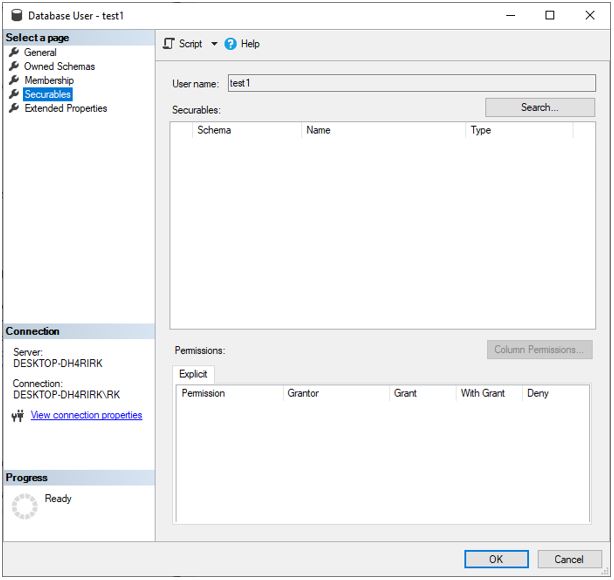
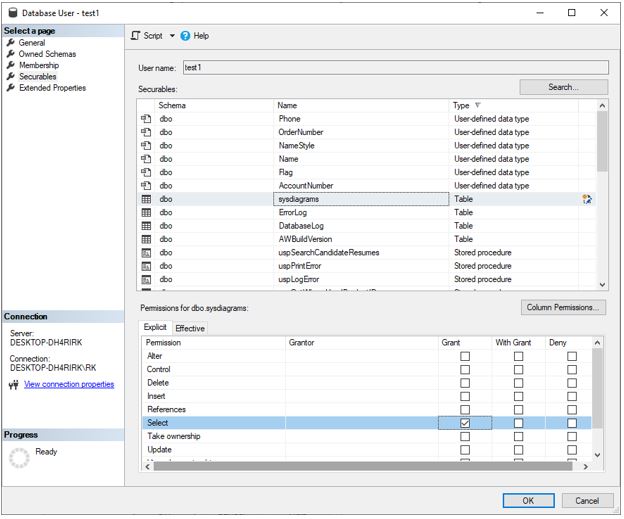
Step 1: Go to the properties of the user test1 using right-click and select the Securables option on the left and click on Search.
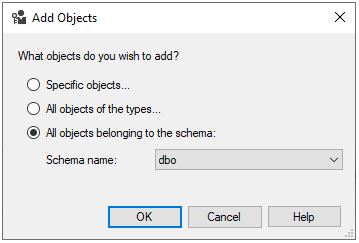
Step 2: Then we select all objects belonging to the schema and the schema which we select is dbo. We have selected dbo(database owner) since it has permissions to perform all activities of the database.
Step 3: Now select a table and in explicit permissions, we give Grant to select.
Same can be achieved using the following T-SQL query
use [AdventureWorks2017]
GO
GRANT SELECTON [dbo].[sysdiagrams] TO [test1]
GOThe permissions will be granted to the user and now we have seen the general workflow of a user. Now we will get into the specifics and look at different types of users.
Types of Users
There are 3 main types of users
- Mapped users are users which are created based on a SQL Server Login
- Unmapped users are users which are created without a SQL Server Login
- Contained users are users that are created without a SQL Server Login, but both the username and password are stored within the database.
Now let’s create the users
SQL User with login
We have seen this type in user creation flow
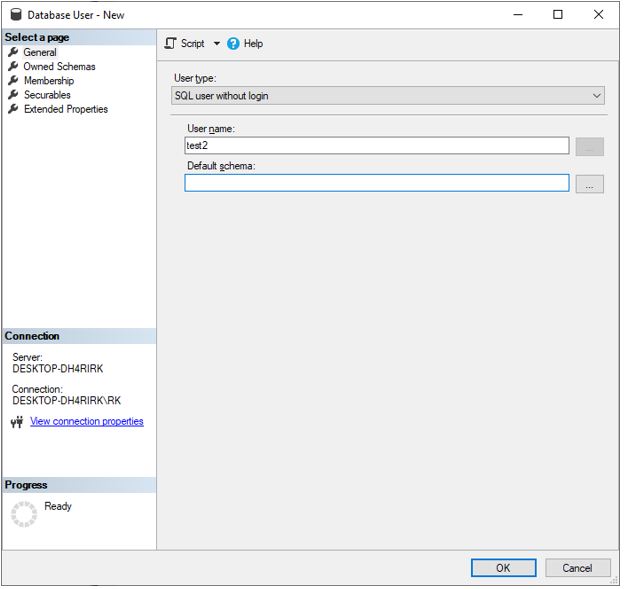
SQL User without login
1. CREATE USER (Transact-SQL)
In this type of user, we do not provide any login information and just give the user name and can select the default schema.
Same can be achieved using the following T-SQL query
USE [AdventureWorks2017]
GO
CREATE USER [test2] WITHOUT LOGIN
GOExplanation: Login based users are created if the person who is making a connection cannot authenticate with windows who are generally persons outside of the organization e.g. Customer who is connecting to your server. For people inside your organization, the windows authentication is a better choice as they will not have to remember an additional password and it also offers a feature of Kerberos.
2. Contained user
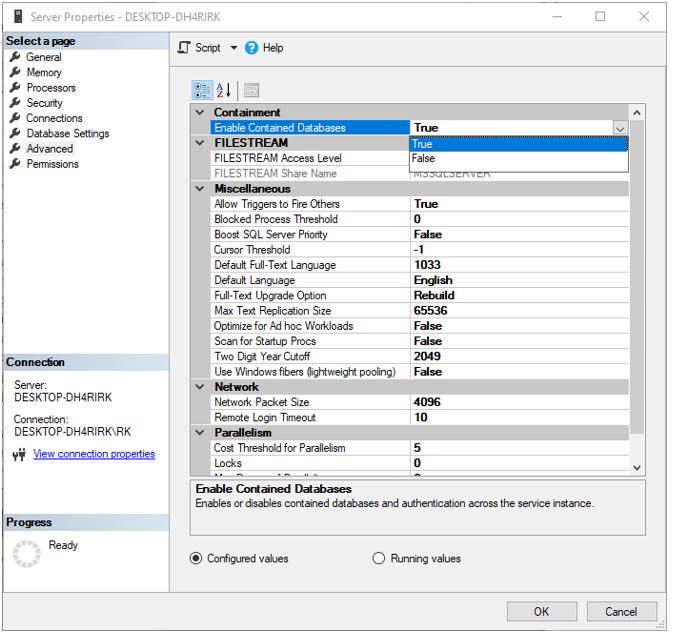
A contained user is not associated with login in the master database. This makes the database portable and this is a good choice if you want to move the database between the instances of SQL Server. To create this type of user the admin must enable the use of the contained database for SQL Server and the database should be first enabled for containment.
To enable containment, go to server properties and set Enable Contained Databases to True.
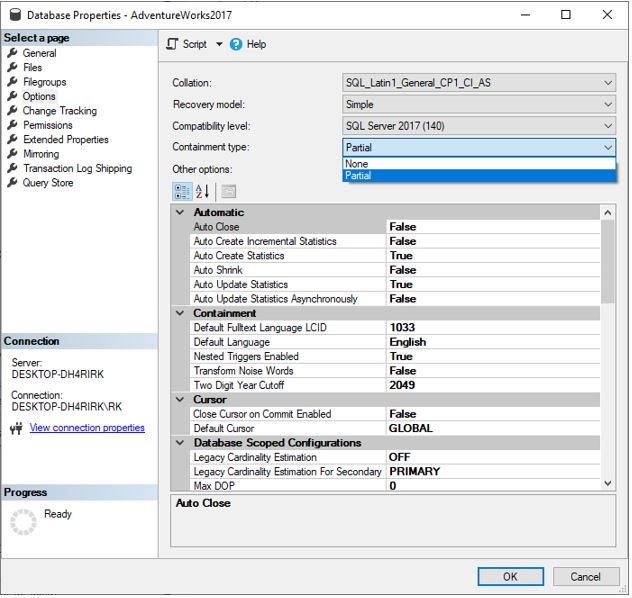
Next, select the properties of your selected database go-to options section and set containment type to partial
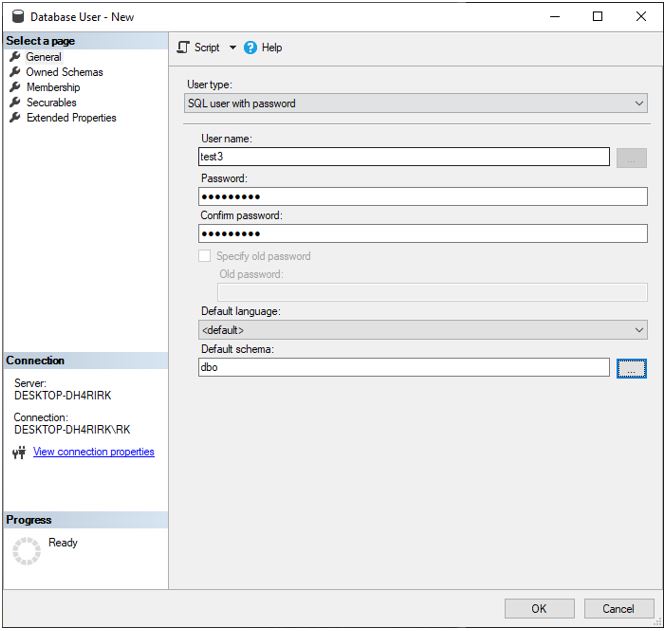
Now let us create a new user using SQL user with password and we have the option to add default language and select default schema.
Same can be achieved using the following T-SQL query
USE [AdventureWorks2017]
GO
CREATE USER [test3] WITH PASSWORD = N'Password1', DEFAULT_SCHEMA = [dbo]
GOGeneral options while adding user
Depending on the user type selected the options may change and some options have a default value so it can be left blank.
Username –You can enter the user name or you can select the Windows user from the type list by clicking the ellipsis (…) and choose from the dialog of Select User
Login name – Enter the login for the user or select from the dialog by clicking the ellipsis (…) and choose from the dialog of Select Login. It is available if Windows useror SQL user with login is selected.
Password and Confirm password –They are used for contained databases where you have to enter a password for the user to authenticate.
Default language – Select the default language for the user.
Default schema – This schema will own objects created by useror select from the dialog by clicking ellipsis (…) and choose from the dialog of Select Schema. For the User type, it is available for Windows user, SQL user with login and SQL user without login
Certificate name – Here you can enter the certificate to be used for the user or select from the dialog by clicking the ellipsis (…) and choose from the dialog of Select Certificate. For the User type, it is available for User mapped to a certificate
Asymmetric key name–We can enter the key to be used for user or select from the dialog by clicking the ellipsis (…) and choose from the dialog of Select Asymmetric key. For the User type, it is available for User mapped to an asymmetric key
Conclusion
So, in this article we have looked at the user creation workflow in SQL server database along with that we have also seen at the types of user which we can create in SQL server management studio as well in T-SQL queries.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Users” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.