Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to SQL DECODE()
DECODE function in Standard Query Language (SQL) is used to add procedural IF – THEN – ELSE like statements to a query. It compares a given expression with each search value one by one and returns a result on the basis of outcomes received from the comparison. A decode function basically performs the task of CASE statements. However, we should keep in mind that DECODE is a built-in function in ORACLE SQL databases and hence it is supported only in ORACLE 9i and above versions of ORACLE/ PL SQL. It is not recognized and supported in other database management servers such as PostgreSQL, SQL Server, MySQL etc. So, now we can use CASE statements to perform IF-THEN-ELSE logic in these databases.
Syntax and Parameters:
The basic syntax for writing DECODE function in SQL is as follows:
DECODE (expression , search_1, result_1[, search_2, result_2], ...,[,search_n,result_n] [, default]);The parameters used in the above mentioned syntax are:
- expression: expression argument is the value which is to be searched and compared with.
- search_1, search_2, …. search_n: These are the values to be searched for and then compared with the expression argument.
- result_1, result_2, … , result_n: These arguments hold the result to be returned when the given comparison returns true. For example, if expression = search_1 then result will be result_1.
- default: default argument holds the default value. It is more or less like the ELSE statement in IF-THEN-ELSE.
We can use the DECODE function as a part of the SELECT statement, ORDER BY etc.
How DECODE() Function works in SQL?
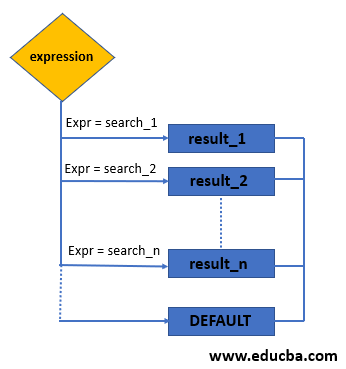
The first step is comparison of expression and search_1, if the expression = search_1 is TRUE then result_1 is returned. If it’s FALSE then DEFAULT value is returned. The DECODE function automatically converts or casts the expression to the data type of the first search argument or search_1. And it finally converts back the data_type of result to the data_type of the expression.
The functionality of DECODE in ORACLE with following flowchart.
Example:
Code:
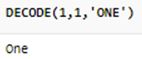
SELECT
DECODE(1, 1, 'One')
FROM dual;Output:
The simple illustration of the above mentioned decode function is as follows:
Code:
IF 1 = 1
THEN result = 'One'
ENDIF;Examples of SQL DECODE()
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Let us first create a ‘college_details’ table which contains college id, college name, location and fees for demonstration purposes.
We can use the following SQL CREATE TABLE statement to perform the task.
Code:
CREATE TABLE college_details(
college_id integer NOT NULL,
college_name character varying(255) NOT NULL,
college_location character varying(255) NOT NULL,
fees numeric NOT NULL
);Output:
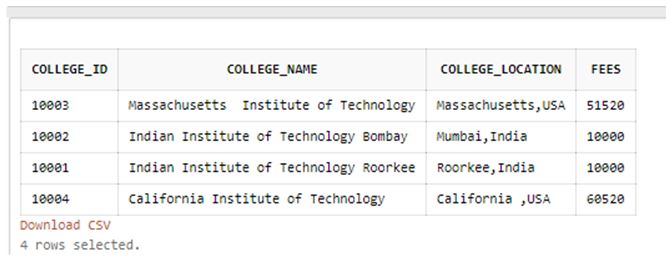
Having created the table, let us now input some random data in it to work with in the subsequent exercises. We can use the following insert statements.
Code:
INSERT INTO college_details VALUES (10001, 'Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee', 'Roorkee,India', 10000);
INSERT INTO college_details VALUES (10002, 'Indian Institute of Technology Bombay', 'Mumbai,India', 10000);
INSERT INTO college_details VALUES (10004, 'California Institute of Technology', 'California ,USA', 60520);
INSERT INTO college_details VALUES (10003, 'Massachusetts Institute of Technology', 'Massachusetts,India', 51520);select * from college_details;The data in the “college_details” table after performing the above mentioned INSERT operations looks something as shown below:
Output:
Example #1
Simple SQL query to illustrate use of DECODE function.
Code:
SELECT college_id,
DECODE (college_id, 10003,'Massachusetts, USA',
10004, 'California, USA',
'India')
FROM college_details;Output:
In this example, we have performed a simple SQL task for categorizing colleges based on their location.
Simple illustration of above mentioned DECODE function is as follows:
Code:
IF college_id = 10003
THEN result = 'Massachusetts'
ELSE IF college_id = 10004
THEN result = 'California'
ELSE
result = 'India'
ENDIF;Example #2
SQL query to illustrate abbreviation of college names based on the available data using DECODE function.
Code:
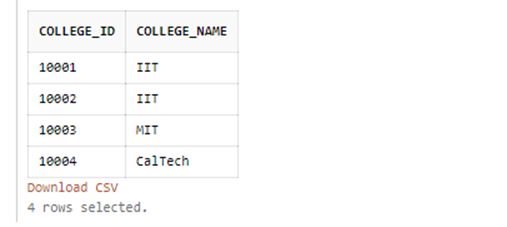
SELECT college_id, DECODE(college_name,'Massachusetts Institute of Technology',
'MIT','California Institute of Technology','CalTech','IIT') as college_name
FROM college_details
ORDER BY college_id;Output:
In the above example, we have performed the following IF-THEN-ELSE logic statements and then ordered the entire result set by college_id.
Code:
IF college_name = 'Massachusetts Institute of Technology'
THEN result = 'MIT'
ELSE IF college_name = 'California Institute of Technology'
THEN result = 'Caltech'
ELSE
result = 'IIT'
ENDIF;Example #3
SQL query to categories college fees into affordable and expensive for an Indian student, considering everything above $ 10000 as expensive.
Code:
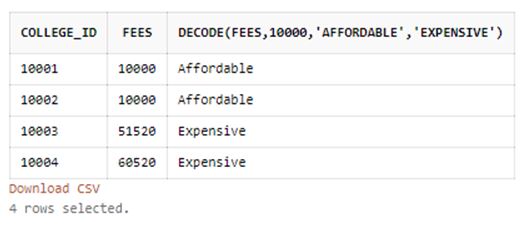
SELECT college_id,fees,
DECODE(fees,10000,'Affordable','Expensive')
FROM college_details
ORDER BY college_id;Output:
In the above example, we have performed the following task using the DECODE function and have then ordered the result set by college_id.
Code:
IF fees = '10000'
THEN result = 'Affordable'
ELSE
result = 'Expensive'
ENDIF;Conclusion
DECODE function is used to perform procedural IF-THEN-ELSE logic in SQL. The function is a close relative of CASE statements. It is a built-in function in ORACLE / PL SQL database management servers.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL DECODE()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.