Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to SQL Enum
Enum or enumerated is a user-defined data type in standard query language (SQL) that contains a static ordered set or lists of values. Enums are
human-readable string values and help in improving data storage efficiency. It can be considered similar to a list of values as a data type. They are equivalent to enum types in C programming language. A very good example of an enumerated data type is continents on earth. This continent data type can only consist of seven names of continents.
In this article, we will be learning about ENUM data type in detail with the help of some practical examples. Let’s begin with syntax and parameters used for creating ENUM types in SQL.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for creating ENUM data type in SQL is as follows :
CREATE TYPE enum_name AS ENUM ('value_1','value_2',..., 'value_n' );The syntax for incorporating ENUM data type in a database table is as follows :
CREATE TABLE table_name (
column_name_1 data type CONSTRAINT,
column_name_2 enum_name CONSTRAINT,
.
.
.
);The parameters used in the above-mentioned syntaxes are as follows :
- enum_name: Name of the enumerated data type.
- (‘value_1′,’value_2’,…, ‘value_n’ ) : Values that are acceptable as a part of this enumerated data type. This set is user-defined, you can mention as many values as you want. For example, Rainbow can only have Violet, Indigo, Blue, Green, Yellow, Orange, and Red as colours.
- Note: Enum values are case-sensitive, by default; ergo ‘RED’ is not similar to ‘red’ or ‘Red’.
Examples of SQL Enum
In order to illustrate working with ENUM data types, let us try a few examples based on it.
Creating Enum Data Type
Example:
Create an enumerated data type called “continents” that contains a list of seven continents on Earth.
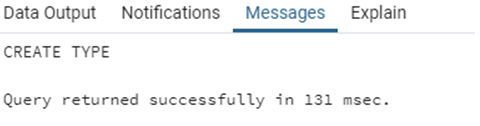
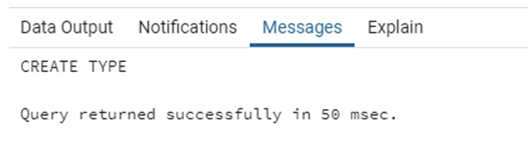
CREATE TYPE continents AS ENUM ('Asia', 'Africa', 'North America', 'South America', 'Antarctica', 'Europe','Australia');We have successfully created our first enum type “continents”. Now let us use it in a database table.
Here, we are creating a database table known as “country_list”. This table has a field “country_region” that is of continents type a.k.a the enum data type we just created. Follow the given sql statement for creating this table.
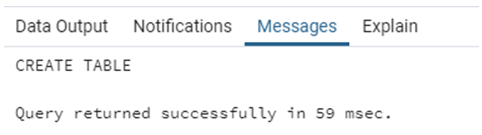
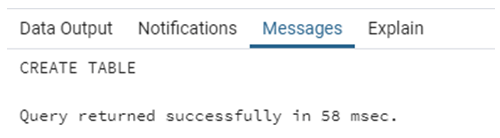
CREATE TABLE country_list (
country_id INT,
country_name VARCHAR(50),
country_region continents
);The CREATE TABLE statement has been successfully executed. The next task is to insert a few records in the “country_list” table to understand how values are inserted in enum type.
Here is an INSERT statement to insert a new row with a column of continents type.
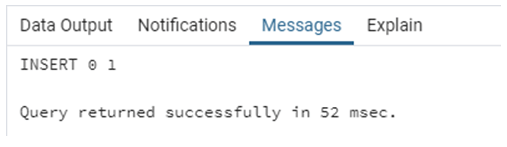
INSERT INTO public.country_list(
country_id, country_name, country_region)
VALUES (1,'India','Asia');The command executed successfully.
Now try this next insert statement which is similar to the previous statement.
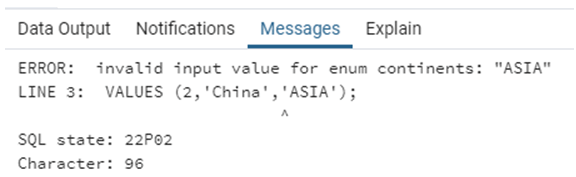
INSERT INTO public.country_list(
country_id, country_name, country_region)
VALUES (2,'China','ASIA');Why did we get an error message? This is because enumerated data types are case-sensitive. ASIA is not similar to Asia or asia. So remember this when creating and working with enum data types.
Ordering in Enum Data Type
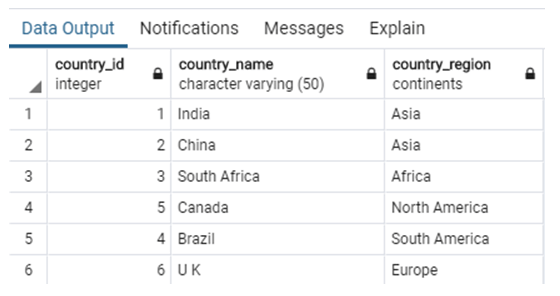
In order to illustrate ordering or sorting in enumerated data types, let us insert a few records in the “country_list” table. We can use the following INSERT statement for this task.
INSERT INTO public.country_list(
country_id, country_name, country_region)
VALUES (2,'China','Asia'),
(3,'South Africa', 'Africa'),
(4,'Brazil', 'South America'),
(5,'Canada', 'North America'),
(6,'U K ', 'Europe');Example:
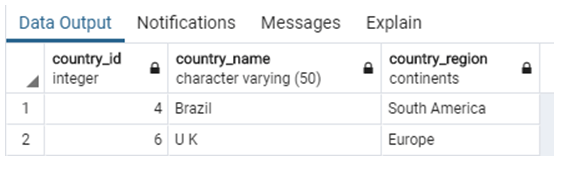
Find the details of countries from country_list with country_region greater than ‘North America’.
SELECT country_id, country_name, country_region
FROM country_list
WHERE country_region > 'North America';As seen in the data output above, the server returned ‘South America’ and ‘Europe’ as greater than ‘North America’. This is not correct lexilogically. Then why did we receive such a result? This is because ‘South America’ and ‘Europe’ are placed after ‘North America’ in the ENUM list. Scroll up and have a look at the “continents” type. So the moral of the story is that ENUM types are ordered sets and they maintain a sorting sequence as specified at the time of creation.
Let’s try a few more examples on ordering.
Example:
Find the details of countries from country_list with country_region lesser than ‘North America’.
SELECT country_id, country_name, country_region
FROM country_list
WHERE country_region < 'North America';If you still have any doubts, just have a look at the result obtained from the order by country_region clause.
SELECT country_id, country_name, country_region
FROM country_list
ORDER BY country_region;However, we can compare the values of an enumerated data type as mentioned below.
Example:
Find the details of countries from country_list with country_region as ‘North America’.
SELECT country_id, country_name, country_region
FROM country_list
WHERE country_region = 'North America';However, we should keep this in mind that enumerated values of one enum type cannot be used to compare values from other enum type.
Whitespaces and Enum Data Types
Enum data types are space sensitive. That is, trailing and leading spaces while specifying values in ENUM types should be avoided. Here is an example to illustrate it in detail.
Creating an enum type.
CREATE TYPE status AS ENUM (' Active','Inactive ');Using status type in a table.
CREATE TABLE profile_status (
profile_id INT,
profile_status status
);Inserting a row with status type without watching for whitespaces.
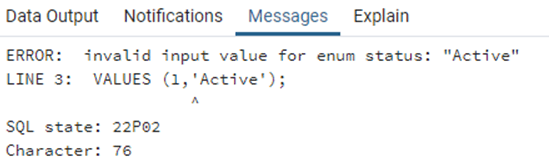
INSERT INTO public.profile_status(
profile_id, profile_status)
VALUES (1,'Active');The server did not recognise ‘Active’ as a value of status type.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Enum” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.