Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to CUBE in SQL
SQL CUBE is a data structure, more or less like a matrix or a two-dimensional array that makes it possible to aggregate values and summary reports on multiple axes and provides a more detailed analysis by performing grouping of data along with more than one column and creating multiple grouping sets while using just a single query.
It helps in performing an analysis of data from multiple perspectives. It comes very handily when we want to prepare detailed summary reports. It enables us to perform multiple groups by operations using one SQL query and at once. It helps in overcoming some limitations of relational databases, where we cannot get the overall view of data at once, but CUBE solves that to some extent.
Syntax and parameters:
Creating a SQL CUBE is as follows :
SELECT aggregate_function {MIN,MAX,SUM,COUNT,AVG}(column_name), column_name1, column_name2, column_name3
FROM table_name
GROUP BY
CUBE(column_name1,column_name2,column_name3);The parameters used in the above syntax are:
1. SELECT: It is used to select the required data from the database.
2. Aggregate_function {MIN,MAX,SUM,COUNT,AVG}: Specify the aggregate function that will be used for summarization of data in the columns.
3. column_name: Specify the column name on which aggregate operation will be performed.
4. column_name1, column_name2, column_name3: Specify the column names along with which the group sets will be made.
5. FROM: It is used to specify the source from which data has to be fetched.
6. GROUP BY: It is used to group rows, having similar values into summary rows.
7. CUBE(column_name1,column_name2,column_name3): It is used to group data along with multiple axes. Specify the same column names which you have mentioned in the SELECT statement.
Of the above-mentioned parameters, all the parameters are mandatory. You may use JOINS, WHERE, ORDER BY AND HAVING clauses based on your requirement
In order to understand the concept better, we will take the help of three tables.
- employees (contains personal details of all the employees)
- department ( contains details like department id, name, and its hod)
- tasks (contains details and status of projects)
The data in the “department” table look something like this:
| departmentid | departmentname | head |
| 4001 | Sales & Marketing | 10028 |
| 4002 | Products | 10023 |
| 4003 | Human Resources | 10022 |
The data in the “employees” table is as follows:
| employeeid | lastname | firstname | departmentid | address | city | salary | create_at |
| 10028 | Becker | Todd | 4001 | 27 street | Manhattan | 15000 | 2007-01-03 |
| 10026 | Sharma | Deepak | 4002 | 10th street | New Delhi | 12876 | 2007-12-03 |
| 10027 | Tobby | Riya | 4002 | 31 street | Manhattan | 13456 | 2006-01-03 |
| 10024 | Krishna | Lina | 4001 | 27 street | Oslo | 12000 | 2006-01-02 |
| 10022 | Mayers | David | 4003 | 27 street | Manhattan | 15000 | 2002-01-31 |
| 10023 | Jackson | David | 4002 | 27 street | Manhattan | 16543 | 2001-12-31 |
The data in the “tasks” table look something like this:
| taskid | departmentid | employeeid | status |
| p23 | 4002 | 10026 | completed |
| p123 | 4002 | 10026 | process |
| hr12 | 4003 | 10022 | completed |
| p231 | 4002 | 10023 | process |
Examples of CUBE in SQL
Given below are the examples of CUBE in SQL:
Example #1
SQL Query to illustrate the basic functionality of CUBE.
Code:
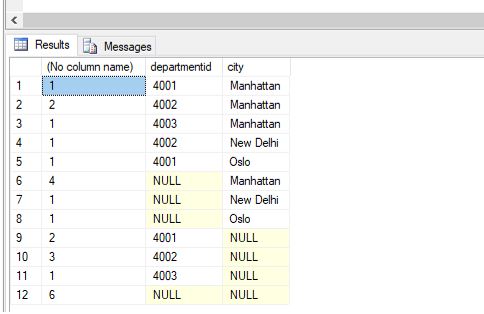
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT employeeid), departmentid, city
FROM employees
GROUP BY
CUBE(departmentid,city);Output:
In the above example, we have tried to find the count of employees along with each department and city.
Example #2
Find the number of distinct employees in each department grouped by their salaries earning a salary between 12000 and 13000.
Code:
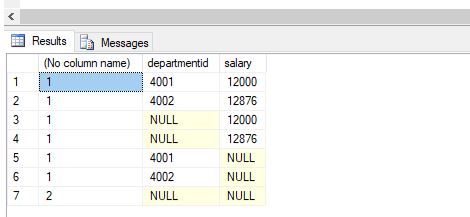
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT employeeid), departmentid, salary
FROM employees
WHERE salary BETWEEN '12000' AND '13000'
GROUP BY
CUBE(departmentid,salary);Output:
The above example illustrates the use of the WHERE clause in the CUBE query.
Example #3
Summarize the salaries of employees along with each department and city.
Code:
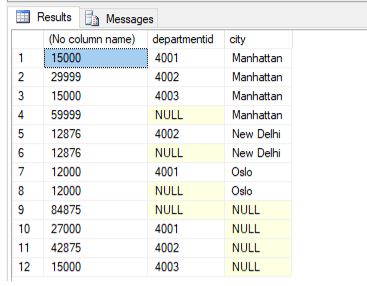
SELECT sum(salary),departmentid, city
FROM employees
GROUP BY
CUBE(departmentid,city);Output:
Example #4
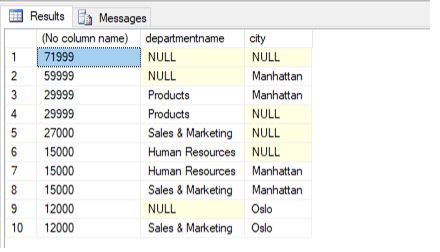
Summarize the salaries of employees along with each department(with department name in the resulting set) and city.
Code:
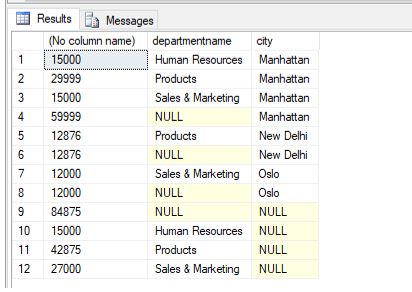
SELECT sum(salary),d.departmentname, city
FROM employees as e INNER JOIN department as d
ON e.departmentid = d.departmentid
GROUP BY
CUBE(d.departmentname,e.city);
<>Output:
The above example is to demonstrate, use of JOINS in SQL cube query.
Example #5
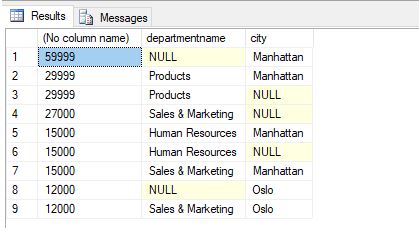
Summarize the salaries of employees from Manhattan and Oslo along with each department(with department name in the resulting set) ordered by salaries and departmentname.
Code:
SELECT sum(e.salary),d.departmentname, city
FROM employees as e INNER JOIN department as d
ON e.departmentid = d.departmentid
WHERE e.city = 'Manhattan' OR e.city = 'Oslo'
GROUP BY
CUBE(d.departmentname,e.city)
ORDER BY sum(e.salary)DESC ,d.departmentname ASC;Output:
In the above example, we illustrated the use of the ORDER BY clause in the SQL CUBE query.
We can remove the first NULL values by using a HAVING clause in the same query.
Code:
SELECT sum(e.salary),d.departmentname, city
FROM employees as e INNER JOIN department as d
ON e.departmentid = d.departmentid
WHERE e.city = 'Manhattan' OR e.city = 'Oslo'
GROUP BY
CUBE(d.departmentname,e.city)
HAVING SUM(e.salary) < '60000'
ORDER BY sum(e.salary)DESC ,d.departmentname ASC;Output:
Example #6
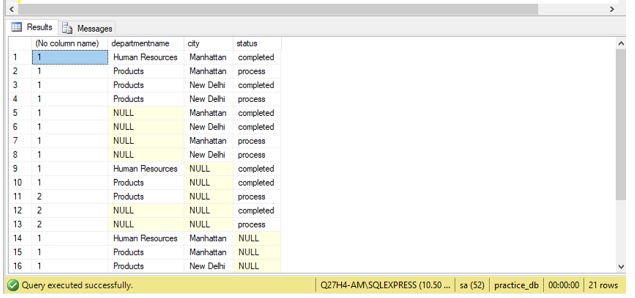
Find the number of employees in each department(with department name in the resulting set), city and the status of the project completed by them.
Code:
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT e.employeeid),d.departmentname,e.city, t.status
FROM employees as e JOIN department as d
ON e.departmentid = d.departmentid
INNER JOIN tasks as t
ON e.employeeid = t.employeeid
GROUP BY
CUBE(d.departmentname,e.city, t.status);Output:
The above example is to illustrate the joining of more than one table in the SQL CUBE query.
Conclusion
SQL CUBE is metadata which is used to group data along more than one column. This is very helpful in summarizing data along with multiple axes. Hence, helps to fasten up analysis and reporting.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “CUBE in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.