Updated March 14, 2023
Introduction to BETWEEN in SQL
BETWEEN is an expression operator generally used in the WHERE clause of a SQL INSERT, SELECT, DELETE and UPDATE query, that allows for specifying a range to test and filters the values or records within the given range while being inclusive and selecting both the begin and end values in the final result.
The SQL BETWEEN operator can be used for defining a specified range for Text, Numerical or data, and timestamp values. It is almost similar to an IN operator when used in a sequential manner. The counterpart of BETWEEN is NOT BETWEEN which does just the opposite. We will be discussing all the cases where BETWEEN can be used in detail.
Syntax and parameters
The basic syntax for writing SQL BETWEEN in WHERE clause is as follows:
SELECT column_name(s)
FROM table_name
WHERE test_expression { BETWEEN | NOT BETWEEN } begin_value AND end_value ;The parameters used in the above syntax are :
SELECT column_name(s): It is used to select the required data from the database. Mention the column names that you want in the result set.
FROM table_name: Mention the table name or source from which the columns will be fetched.
WHERE: It is used to specify the conditions to filter records.
Test_expression: It is the expression for which we want to perform the test or the column name for which we want to specify the BETWEEN condition.
{ BETWEEN | NOT BETWEEN }: It is the expression operators that compare if the values are within the mentioned range or not.
Begin_value: The starting value of the range.
End_value: The last value of the range.
Of the above-mentioned parameters, all the parameters are mandatory. You may use GROUP
BY, ORDER BY and HAVING clauses based on your requirement.
Going ahead we will be discussing the above mentioned BETWEEN operator in great detail.
In order to understand the concept better, we will take the help of two tables, Employees (this contains personal details of all the employees) and departments (it contains details like department id, name, and its hod).
The data in the department’s table look something like this :
| departmentid | departmentname | head |
| 4001 | Sales & Marketing | 10024 |
| 4002 | Products | 10023 |
| 4003 | Human Resources | 10022 |
The data in the employee’s table is as follows:
| employeeid | lastname | firstname | departmentid | address | city | create_dt | Salary |
| 10028 | Becker | Todd | 4001 | 27 street | Oslo | 2007-1-03 | 12000 |
| 10029 | Rebecca | Ginny | 4001 | 27 street | Manhattan | 2007-12-03 | 12000 |
| 10027 | Tobby | Riya | 4002 | 31 street | Manhattan | 2006-1-03
|
15000 |
| 10026 | Sharma | Deepak | 4002 | 10th street | New Delhi | 2006-1-02 | 15000 |
| 10024 | Krishna | Lina | 4001 | 27 street | Oslo | 2002-1-31 | 12000 |
| 10023 | Jackson | David | 4002 | 27 street | Manhattan | 2001-12-31 | 15000 |
| 10022 | Mayers | David | 4003 | 27 street | Manhattan | 2000-12-31
|
10000 |
Examples of BETWEEN in SQL
Here are the following examples mention below
Example #1 – With integer or numerical values
Find the names of the employees who earn a salary in the range of 12000 to 15000.
Code:
SELECT firstname,lastname
FROM employees
WHERE salary BETWEEN '12000' AND '15000';In the above example, we tried to select only those employees whose salary lies in between 12000 and 15000. Since BETWEEN is inclusive in nature it filters the beginning i.e 12000 and ending values i.e 15000 as well.
Output:
Example #2 – With character/text values
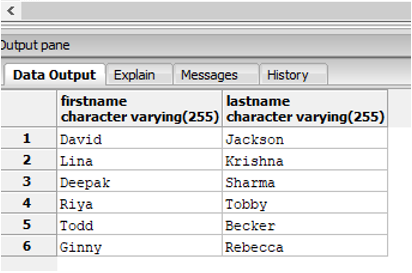
Find the names of the employees, whose name starts with letters between ‘D’ and ‘G’.
Code:
SELECT firstname,lastname
FROM employees
WHERE firstname BETWEEN 'D' AND 'G';Output:
Example #3 – With DATE values
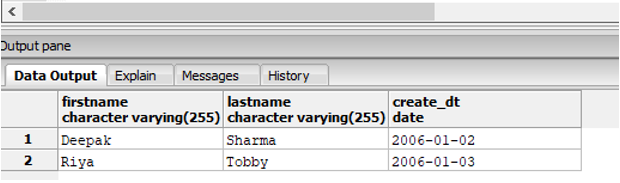
Find the names of the employees, who joined the company between 2003 and 2006.
Code:
SELECT firstname,lastname, create_dt :: Date
FROM employees
WHERE create_dt :: Date BETWEEN '2003-01-01' AND '2006-12-31';Output:
Example #4 – With IN operator
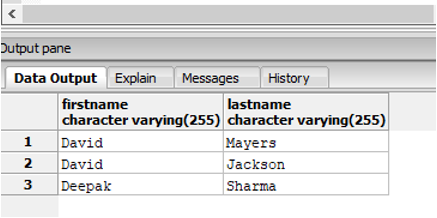
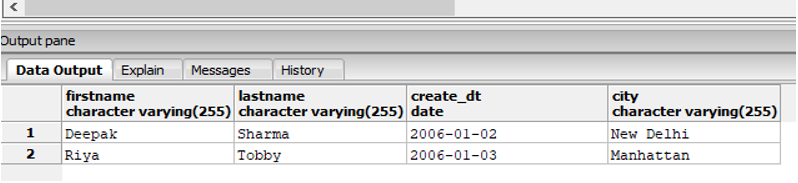
Find the names of the employees, who joined the company between 2003 and 2006 and are from Manhattan or New Delhi.
IN expression operator is very frequently used along with the BETWEEN operator in the WHERE clause. It is used to specify an additional condition in the query. IN filters only those rows/records which are present in the mentioned set.
Code:
SELECT firstname,lastname, create_dt :: Date, city
FROM employees
WHERE create_dt :: Date BETWEEN '2003-01-01' AND '2006-12-31'
AND city IN ('Manhattan', 'New Delhi');Output:
Example #5
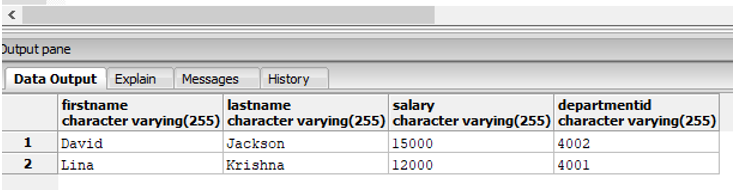
Find the names of the employees, who earn a salary between 12000 and 15000 and are also head of their department.
Code:
SELECT firstname,lastname, salary, departmentid
FROM employees
WHERE salary BETWEEN '12000' AND '15000'
AND employeeid IN (SELECT head::integer FROM department);Output:
As the name suggests, NOT Between can be thought of as an expression operator that filters the values which do not belong to the specified range.
Example #6 – Using NOT BETWEEN expression operator
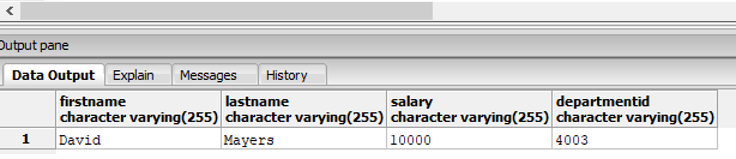
Find the details of the employees who do not earn a salary in the range of 12000 to 15000.
Code:
SELECT firstname,lastname, salary,departmentid
FROM employees
WHERE salary NOT BETWEEN '12000' AND '15000';Output:
Using BETWEEN in the table join queries
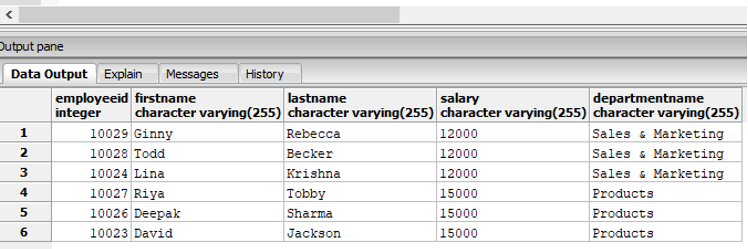
Find the details of the employees along with the department name, who earn a salary in the range of 12000 to 15000.
Code:
SELECT e.employeeid, e.firstname, e.lastname, e.salary, d.departmentname
FROM employees as e INNER JOIN department as d
ON e.departmentid::integer = d.departmentid
WHERE e.salary BETWEEN '12000' AND '15000';Output:
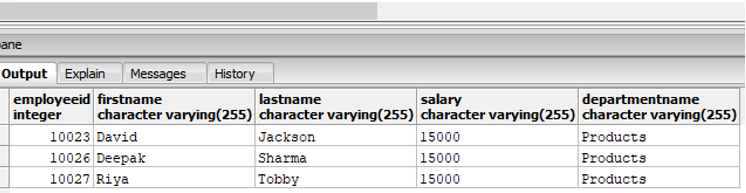
Example #7
Find the details of the employees along with the department name, who earn a salary in the range of 12000 to 15000 AND they work for the products department.
Code:
SELECT e.employeeid, e.firstname,e.lastname,e.salary, d.departmentname
FROM employees as e INNER JOIN department as d
ON e.departmentid::integer = d.departmentid
WHERE e.salary BETWEEN '12000' AND '15000' AND
d.departmentname ='Products' ;Output:
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned that BETWEEN is an expression operator that is used to filter only those values which are in the specified range. It is inclusive in nature that means it selects both the beginning as well as ending values. It is mostly used in the WHERE clause part of the SQL query.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “BETWEEN in SQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.