Updated March 6, 2023
Introduction to Spanning Tree Algorithm
A spanning tree is defined as a tree which is a subset of the graph that have the same vertices as graph and edges same as a graph, but one less edge than the given graph makes the graph a spanning tree where all the vertices are covered with one less than edges of the given graph which makes it cycle free graph. In general, we can define a spanning tree as a tree that does not have any cycles, and the given graph can never be a disconnected graph as every connected and undirected graph can have at least one spanning tree that holds an equal number of vertices as a graph and edges one less than the given graph.
How Spanning tree algorithm works?
In any programming language, the spanning tree is defined as a graph that is not connected and undirected graph with an equal number of vertices as the given graph and one fewer edge of the edges of the given graph and making the spanning-tree a sub-graph of the given graph but note that if any of the vertexes is missed of the given graph, then it cannot be made as spanning tree. So if we consider graph as G with an undirected and connected graph with vertices V and edges E with G = (V, E) that includes vertex V and edges E, then the spanning tree would have the same number of vertices as the graph G, and the edges in the spanning tree would have equal of edges as a graph with minus 1, and therefore we can indicate it as G’(V’, E’).
Example
Now let us see few examples of spanning-tree; suppose if we have a graph with n nodes or vertices and the number of spanning trees created are n(n-2). Therefore, if we say n=3 as n is several vertices in the given complete graph, the maximum number of spanning trees that can be created is 3(3-2) = 3 from a graph with 3 vertices.
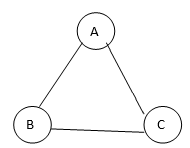
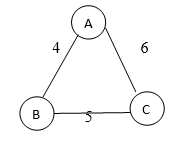
So the graph given may look like
So spanning trees created from the above-given graph is as shown below:
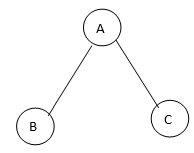
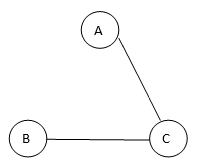
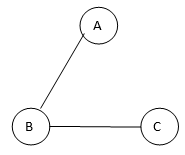
In this example, we saw the given graph contains 3 vertices, and therefore, even spanning trees which are spanning trees created from the above-given graph are as shown below:
In this example, we saw the given graph contains 3 vertices, and therefore even spanning trees will have 3 vertices, but the edges in the spanning tree will always be one less than the given graph, and therefore the edges for the spanning tree will be 3-1 = 2 edges in any spanning tree that is formed by the above-given graph. Hence we can also calculate how many spanning trees can be formed using the number of vertices in the given complete graph; as shown in the above section, we can for 3 different spanning trees, and they all have 3 vertices, but the edges in the spanning tree will always be one less than the given graph, and therefore the edges for spanning tree will be 3-1 = 2 edges in any spanning tree that is formed by the above-given graph. Hence we can also calculate how many spanning trees can be formed using the number of vertices in the given complete graph; as shown in the above section, we can for 3 different spanning trees, and they are:
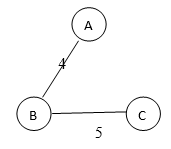
Spanning tree 1
Spanning tree 2
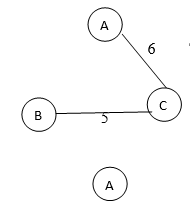
Spanning tree 3
In spanning tree, which was discussed above, was with no weights given for edges, but if any graph given with weight for edges can also be used for finding the spanning trees. There is a concept called the minimum spanning tree in which the graph with weighted edges is used for finding spanning trees with edges having the minimum sum of the edges that would be considered as a minimum spanning tree. There are different algorithms used for finding minimum spanning trees, such as Kruskal’s algorithm and Prim’s algorithm.
Example
For the minimum spanning tree, we will take a graph having weights for each edge.
The total weight of the complete graph is 15.
The total Weight of spanning tree1 is 9.
The total Weight of spanning-tree 2 is 11.
The total weight of spanning tree 3 is 10.
In the above example we saw spanning tree 1 has total weight = 4 + 5 = 9, spanning tree 2 has total weight as 6 + 5 = 11, and spanning tree 3 has total weight as 4 + 6 = 10. Therefore from the above example, we can say spanning tree 1 is a minimum spanning tree of the given graph as its total weight is 9, which has minimum weight among the 3 spanning trees.
Advantages and Disadvantages of spanning-tree
Advantages:
- Spanning trees are used to avoid or prevent broadcast storms in spanning tree protocol when used in networks
- This is also used in providing redundancy for preventing undesirable loops in the spanning tree or network.
- Another advantage is that it provides backup when using spanning tree protocol for the networks, which is activated as this protocol provides various paths where it can choose any open path and closes the other whenever the opened path is not functioning properly.
- A minimum spanning tree is used to find easy paths in maps and is also used for designing networks such as water supply networks or any electrical grid networks.
Disadvantages:
- There are automatic recalculations in spanning trees whenever a new spanning tree is formed, or any new network spanning tree is formed, but the drawback of this is it may cause a network outage sometimes when it modifies automatically.
- There is a protocol called spanning tree protocol; when using the spanning-tree concept in any network, this protocol may block the service if any newer protocols prevent loops while keeping the links, and such newer protocols are TRILL or NPB.
Conclusion
In this article, we can conclude that the spanning tree in any programming language is a graph with unconnected edges and equal vertices as the same as the given graph; the spanning tree is formed with one less edge than the given graph or any tree. There are different algorithms used to find the minimum spanning trees, such as Kruskal’s and Prim’s algorithm where it also helps to find running time with an efficient way of using spanning trees in any networking such as spanning tree protocols.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Spanning Tree Algorithm. Here we discuss the Introduction, How Spanning tree algorithm works? Advantages and Disadvantages of spanning-tree, examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –