Updated June 29, 2023
Solvency Ratio Formula (Table of Contents)
- Solvency Ratio Formula
- Examples of Solvency Ratio Formula (With Excel Template)
- Solvency Ratio Formula Calculator
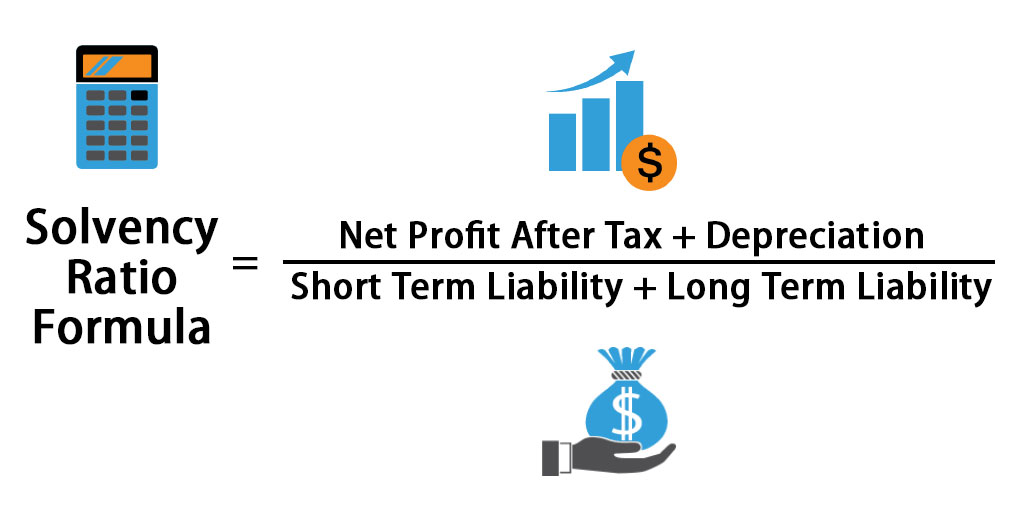
Solvency Ratio Formula
Here’s the Solvency Ratio formula –
Examples of Solvency Ratio Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Solvency Ratio formula in a better manner.
Example #1
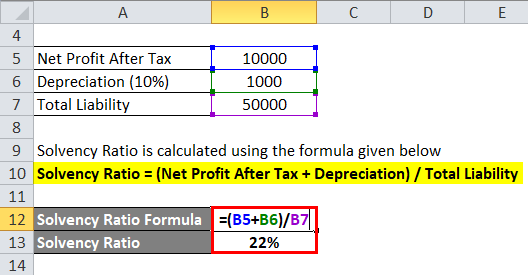
An ltd made a profit for this financial year-end after tax is 10000. The company has an asset of Rs 10000. The depreciation rate applicable per Company law is 10% (Straight-line method). Long-term and short-term liability is 50000. From the above information, calculate the solvency ratio.
Solution:
The formula to calculate Solvency Ratio is as below:
Solvency Ratio = (Net Profit After Tax + Depreciation) / Total Liability
- Solvency Ratio = (10000 + 1000) / 50000
- Solvency Ratio = 22%
Thus, the above ratio indicates that the company has short-term and long-term liability over a period of time. The solvency ratio differs from industry to industry, so a solvency ratio greater than 20 considers the company financially healthy. A higher solvency ratio is good for the company and vice versa.
Example #2
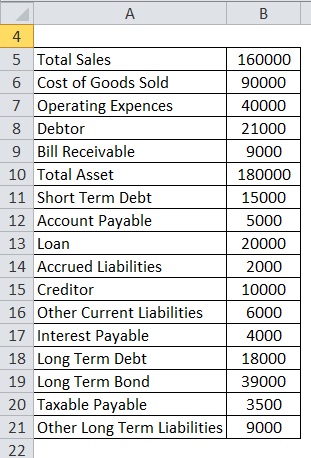
Dmart has the following information available for the financial year-end. So, calculate the solvency ratio from the below information. The depreciation rate is 10 %. Use the straight-line method for calculating depreciation. And the tax rate is 30%.
Solution:
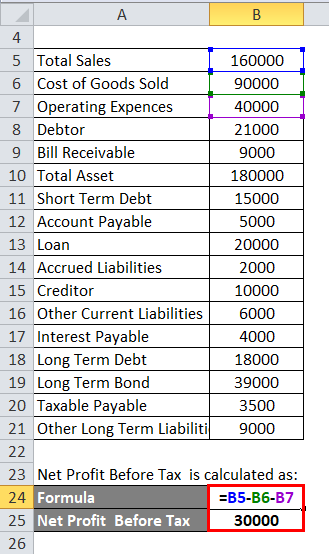
The calculation for Net Profit Before Tax is as below:
- Net Profit Before Tax = 1,60,000 – 90,000 – 40,000
- Net Profit Before Tax = 30,000
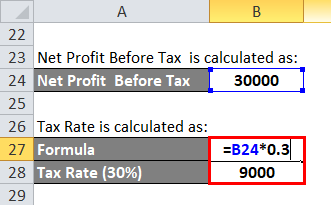
The calculation for Tax Rate is as below:
- Tax Rate = 30,000 * 0.3
- Tax Rate = 9,000
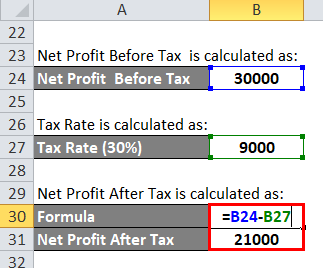
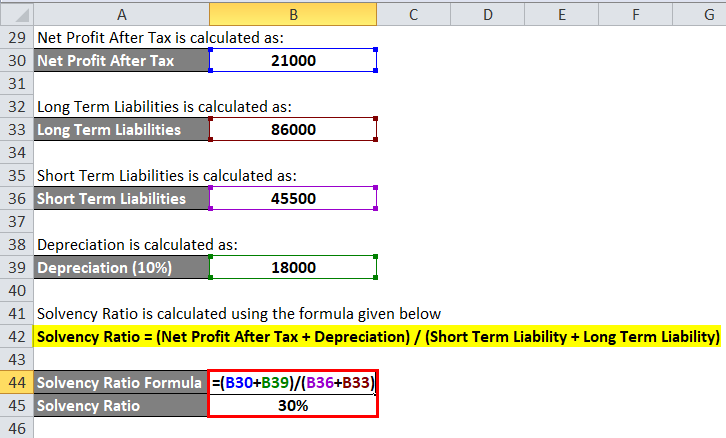
The calculation for Net Profit After Tax is as below:
- Net Profit After Tax = 30,000 – 9,000
- Net Profit After Tax = 21,000
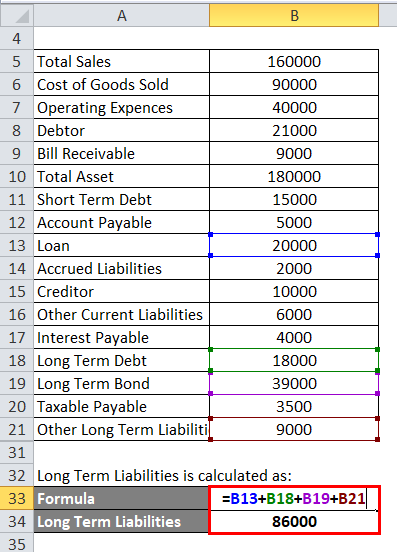
The calculation for Long Term Liabilities is as below:
- Long Term Liabilities = 20,000 + 18,000 + 39,000 + 9,000
- Long Term Liabilities = 86,000
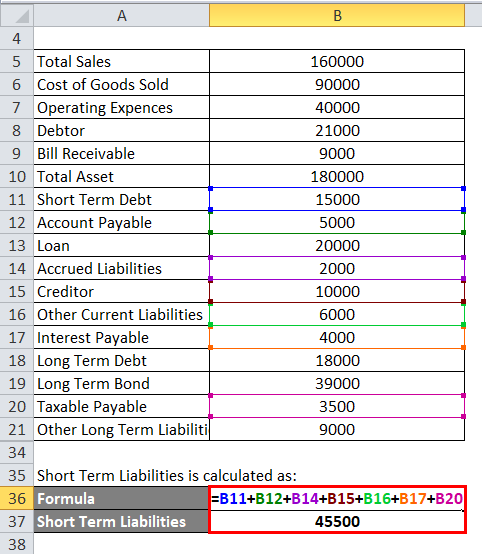
Short Term Liabilities is calculated as:
- Short Term Liabilities = 15,000 + 5,000 + 2,000 + 10,000 + 6,000 + 4,000 + 3,500
- Short term liabilities = 45,500
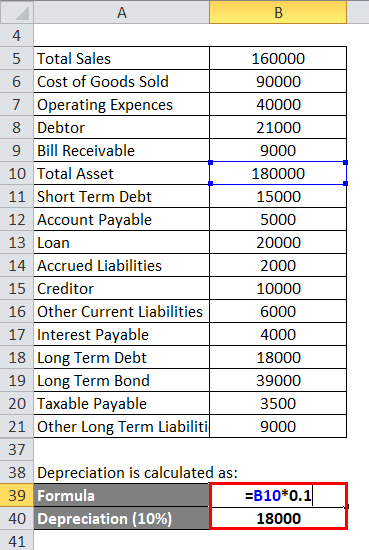
Depreciation is calculated as:
- Depreciation = 1,80,000 * 0.1
- Depreciation = 18,000
Solvency Ratio = (Net Profit After Tax + Depreciation) / (Short Term Liability + Long Term Liability)
- Solvency Ratio = (21,000 + 18,000) / (45,500 + 86,000)
- Solvency Ratio = 30%
Example #3
Tata Sponge has the following information, the tax rate is 35%, and the depreciation rate is 10%. Calculate the solvency ratio for the below information.
Solution:
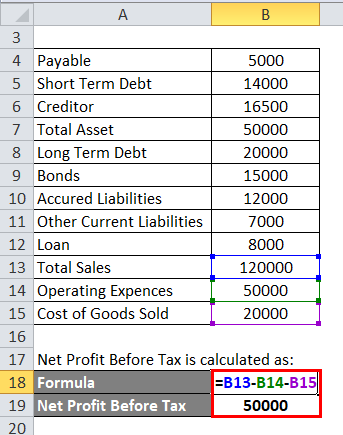
Net Profit Before Tax is calculated as:
- Net Profit Before Tax = 1,20,000 – 50,000 – 20,000
- Net Profit Before Tax = 50,000
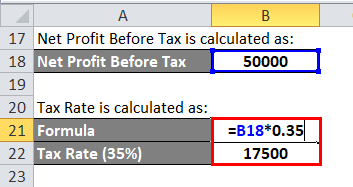
Tax Rate is calculated as:
- Tax Rate = 50,000 *0.35
- Tax Rate = 17,500
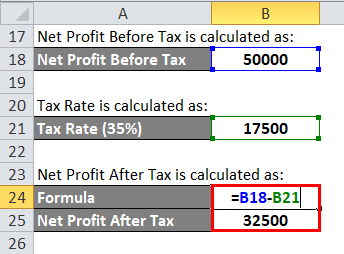
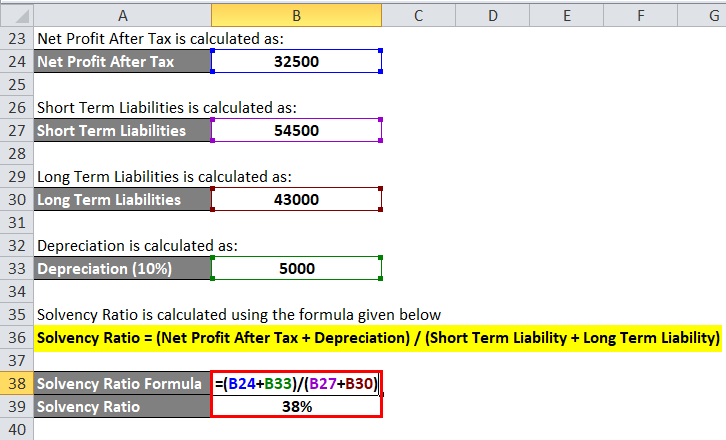
Net Profit After Tax is calculated as:
- Net Profit After Tax = 50,000 – 17,500
- Net Profit After Tax = 32,500
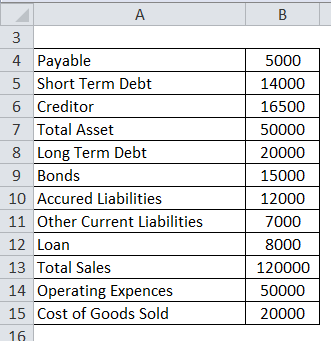
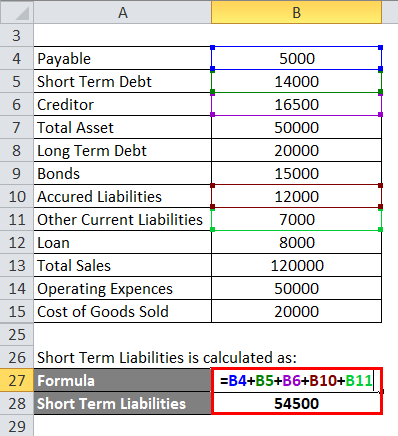
Short Term Liabilities is calculated as:
- Short Term Liabilities = 5,000 + 14,000 +16,500 +12,000 + 7,000
- Short Term Liabilities = 54,500
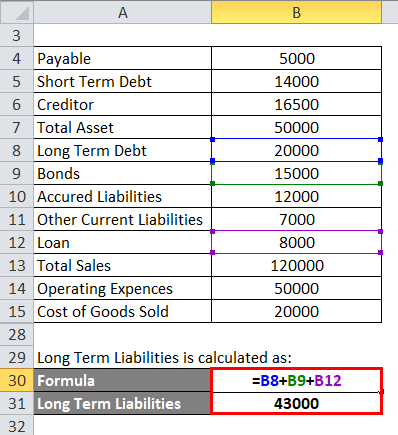
Long Term Liabilities is calculated as:
- Long Term Liabilities = 20,000 + 15,000 + 8,000
- Long Term Liabilities = 43,000
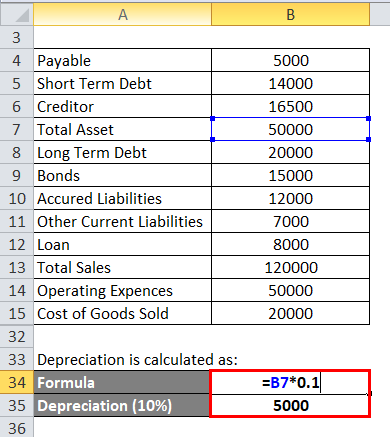
Depreciation is calculated as:
- Depreciation = 50,000 *0.1
- Depreciation = 5000
Solvency Ratio = (Net Profit After Tax + Depreciation) / (Short Term Liability + Long Term Liability)
- Solvency Ratio = (32,500 + 5,000) / (54,500 + 43,000)
- Solvency Ratio= 38%
Explanation of Solvency Ratio Formula
The solvency ratio is one of the quantitative measures used in finance for judging the company’s financial health over a long period of time. The creditor uses the solvency ratio to know the ability of a company to pay its short and long-term liability. In finance, the solvency ratio plays a vital role in judging the company’s ability to make payments of their long-term and short-term over time.
The solvency ratio indicates whether a company’s cash flow is sufficient to pay its liabilities and obligation. With a lower solvency ratio, there are more chances that the company will default in paying its debt and vice versa. It is always favorable if a company has a higher solvency ratio.
In the solvency ratio, many terms and amounts took into consideration for calculation. The solvency ratio includes net profit after tax, depreciation from the profit and loss statement, and long-term and short-term liability from the balance sheet. For the purpose of calculating depreciation, we have to take into consideration the total asset from the balance sheet.
The solvency ratio includes three steps for calculation. The first step is to calculate the company’s net profit after excluding all expenses and taxes. The second step is to calculate depreciation on the asset, and the last step is to calculate short-term and long-term liability. The solvency ratio is very important from the point of view of the creditor and the debenture holder who wants to invest in the company by giving credit or investing in the debenture. Hence, the solvency ratio formula is very important to know the company’s creditworthiness in the long run and helps to know the company’s financial stability.
Relevance and Uses of Solvency Ratio Formula
Solvency ratios have relevance in finance. The solvency ratio has much more important because a company’s financial health is the major concern for each and every business and company itself.
- The solvency ratio has relevance in the field of commerce and finance.
- To know the financial stability of a company
- For ensuring the amount which the creditor invests in the form of credit sale to a company
- For ensuring the debenture holder gave credit to the company in exchange for interest.
- Cash flows are sufficient to pay its obligation in the long run
- To know the creditworthiness of the company
- To know the liquidity of the company in the long run.
Calculator
You can use the following Solvency Ratio Calculator.
| Net Profit After Tax | |
| Depreciation | |
| Short Term Liability | |
| Long Term Liability | |
| Solvency Ratio Formula = | |
| Solvency Ratio Formula = |
| |||||||||
|
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Solvency Ratio formula. Here we discuss How to Calculate the Solvency Ratio along with practical examples. We also provide a Solvency Ratio Calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –