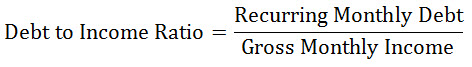Updated November 23, 2023
Debt to Income Ratio Formula (Table of Contents)
- Debt to Income Ratio Formula
- Debt to Income Ratio Calculator
- Debt to Income Ratio Formula in Excel(With Excel Template)
Debt to Income Ratio Formula
The debt to income ratio is the measure of estimating an individual’s capacity to repay the debt by comparing his recurring monthly debt to gross monthly income.
Examples of Debt to Income Ratio Formula
Example #1
Therefore,
- Overall Recurring Monthly Debt for Jim = $4500
- Gross Monthly Income = $10000
Using the Debt to Income Ratio Formula, We get –
- Debt to Income Ratio = Overall Recurring Monthly Debt for Jim/Gross Monthly Income
- Debt to Income Ratio = $4500/$10000
- Debt to Income Ratio = 0.45 or 45%
Example #2
Generally, Debt to Income Ratios are used by lenders to determine whether the borrower will be able to repay the loan. It is assumed that the highest debt-to-income ratio is 43%, beyond which the borrower has a diminishing ability to return the loan.
Suppose John has a gross monthly income of $20000 while Alan has a gross monthly income of $15000. John has a recurring monthly debt of $ 10,000, while Alan has a recurring monthly debt of $ 5,000.
Therefore,
The debt to Income Ratio of John is Calculated as:
- Debt to Income Ratio of John = Recurring Monthly Debt/Gross Monthly Income
- Debt to Income Ratio of John = $10000/$20000
- Debt to Income Ratio of John = 0.5 or 50%
Debt to debt-to-income ratio of Alan is Calculated as follows:
- Debt to Income Ratio of Alan = Recurring Monthly Debt/Gross Monthly Income
- Debt to Income Ratio of Alan = $5000/$15000
- Debt to Income Ratio of Alan = 0.33 or 33%
Hence, lenders will be more inclined to lend money to Alan as his debt-to-income ratio is lower.
Example #3
There are two types of Debt to Income ratios: the Front-end debt to income ratio and the Back-end debt to income ratio. The front-end debt to income ratio generally indicates the percentage of income that goes towards housing costs, whether rent or payment towards a mortgage, which includes both principal and interest. The back-end debt to income ratio encompasses all other recurring debt payments such as car loans, credit card payments, education loans, etc.
Lenders use a debt to income ratio of 28/36 to determine whether the borrower should be lent money. 28/36 norm indicates that 28% of the gross income can be expensed for housing costs, while 36% can be used to expense all other recurring debt payments.
For example,
- If the gross monthly income = $10000.
- The amount allowed for housing expenses = 0.28*10000
- The amount allowed for housing expenses = $2800
- The amount allowed for housing expenses and recurring debt = 0.36*10000
- The amount allowed for housing expenses and recurring debt = $3600
Therefore, the amount allowed for housing expenses is $2800, and the amount allowed for housing expenses and recurring debt is $3600
Explanation of Debt to Income Ratio Formula
Lenders use the debt to income ratio to determine whether a further loan could be issued to the borrower and whether the borrower can return the loan payments. It is generally preferred that the borrower should have a low Debt to Income Ratio. A ratio of 28% is usually preferable, while 43% is the highest that the Debt to Income ratio could be. A debt ratio to income higher than 43% signals that the borrower might not be able to return the loan taken.
As can be understood from the formula, there are two ways of lowering one’s debt to income ratio. One can reduce their recurring monthly debt or increase their gross monthly income. Lowering recurring debt payments can be achieved by prepaying some of the loans.
Significance and Use of Debt to Income Ratio Formula
As stated above, lenders use debt to income ratio to determine whether borrowers should be issued new loans or not. There are two types of Debt to Income ratios: the Front-end debt to income ratio and the Back-end debt to income ratio. The front-end debt to income ratio generally indicates the percentage of income that goes towards housing costs, whether rent or payment towards a mortgage, which includes both principal and interest. The back-end debt to income ratio encompasses all other recurring debt payments such as car loans, credit card payments, education loans, etc.
Lenders usually use a figure such as 28/36 to determine the amount of the expense that a borrower can afford for it to be eligible to give loans.
Numerator 28 indicates the Front-end debt to income ratio should be 28% of the overall gross monthly income. In contrast, denominator 36 indicates that the back-end debt to income ratio should be 36% of the overall gross monthly income.
Debt to Income Ratio Formula Calculator
You can use the following Debt to Income Ratio Formula Calculator
| Recurring Monthly Debt | |
| Gross Monthly Income | |
| Debt to Income Ratio Formula | |
| Debt to Income Ratio Formula | = |
|
|
Debt to Income Ratio Formula in Excel (With Excel Template)
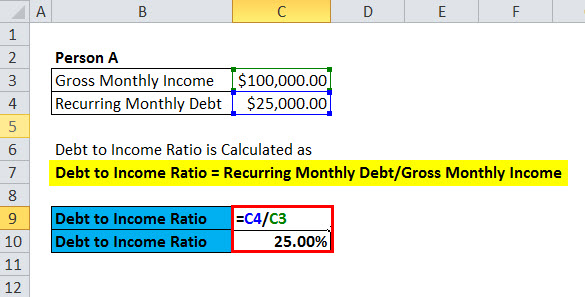
Here, we will do an Excel example of the Debt to Income Ratio Formula. It is very easy and simple. You need to provide the two inputs, i.e., Recurring Monthly Debt and Gross Monthly Income
You can easily calculate the Debt to Income Ratio Formula in the template provided.
Conclusion
Debt income ratio is one of the essential criteria, along with the credit score, that creditors use to determine whether further debt can be given to the borrowers. The historical limit of 28/36 has been extended since. Currently, housing prices are higher all over the world. Even if borrowers have DTI ratios as high as 50%, they are given loans at a higher interest rate than others.
Recommended Articles
This has guided the Debt to Income Ratio Formula; here, we discuss its uses and practical examples. We also provide a Debt to Income Ratio calculator and a downloadable Excel template.