What is a Sealed Class in C#?
A Sealed Class is a class that does not allow inheritance, which means the Sealed Class will restrict users from inheriting a class. A Sealed Class is defined by using a sealed keyword; that keyword notifies the compiler that the defined class is sealed so that it cannot be extended, and there is no chance of inheriting a specific class. A Sealed Class restricts a class derived from a Sealed Class. The main purpose of the sealed class is to stop inheriting the specific class from other classes. In C#, for our code security, we go for a sealed class to secure overriding particular methods or properties depending on our conditions. A Sealed Class is a class where we cannot derive or create a new class. In other words, other classes can’t inherit the Sealed Class, and by using a sealed modifier, we can also define a class that is declared called Sealed Class.

Table of Content
- What is a Sealed Class in C#?
- How to Seal a Class in C#
- Uses of Sealed in C#
- How does Sealed Class Work in C#?
- Sealed Methods in C#
- Advantages in Sealed Class
- Alternatives to Sealed Classes in C#
How to Seal a Class in C#
In C#, you seal a class by using the sealed modifier in the class declaration. Here’s the syntax:
Syntax
sealed class MyClass
{
//data members
//methods
//class memeber and Implementation
}Parameter:
- Using the sealed keyword in the class declaration prevents other classes from inheriting from it.
- Sealing a class prevents subclasses from extending or overriding it.
- This ensures that the class’s implementation remains unchanged, enhancing security and control over its behavior.
- Sealed classes provide a level of certainty in the design, ensuring that no unintended modifications occur through inheritance.
Code:
using System;
// Sealed class
sealed class SealedClass
{
public void Display()
{
Console.WriteLine("This is a sealed class.");
}
}
// Attempting to inherit from the sealed class will result in a compile-time error
// class DerivedClass : SealedClass {} // Uncommenting this line will result in a compilation error
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// Creating an instance of the sealed class
SealedClass sealedObj = new SealedClass();
sealedObj.Display(); // Output: This is a sealed class.
}
}Output
![]()
Explanation:
- We define a SealedClass with the sealed keyword.
- An attempt to derive a class from SealedClass (DerivedClass) results in a compilation error, demonstrating that sealed classes cannot be inherited.
- We create an instance of SealedClass in the Main method and call its Display method, verifying that instances of sealed classes can still be instantiated and used as usual.
Uses of Sealed in C#
Below are some of the uses of Sealed in C#:
- We cannot extend or drive any other class from the sealed class.
- We can also use it for methods so that no other class can modify or implement it. People primarily use this for security reasons.
- It is mainly used when we have static members. For example, bat and ball classes of the system.cricket namespace. The ball represents the ball which is of standard colors. This ball class has static members only. Like a ball.white represents the ball of white color. Similarly, the bat class represents the standard bats only. When designing a class and aiming to restrict its extension by developers, the “sealed” keyword can be used.
- The sealed method is always an override method of the child class.
- We can not again override the sealed method.
- The sealed method is only available with the method overriding.
- The sealed keyword is not available with the method of hiding.
- Sealed is used together with the override method.
- We can not make a normal method as sealed.
How does Sealed Class Work in C#?
In general, while creating a class with the help of inheritance, we inherit all the methods and properties in any of the classes. By using a sealed class, we can restrict access to the classes and their members with the help of a sealed keyword and avoid inheriting the defined classes from other classes. In C#, a sealed class is a class that another class cannot inherit but can be instantiated. Sealed Class is often used for security purposes to prevent the derived class from unwanted users. A Sealed Class is, for the most part, designed to boundary line the extensibility of the classes.
There are several points while working with Sealed Class, they are:
- A sealed class is entirely different from an abstract class.
- Abstract methods cannot be used in a sealed class.
- In the inheritance hierarchy, it must be the bottom-most class.
- Sealed class is purposely used to avoid inheritance.
- The sealed keyword is used with methods, classes, properties, and instances.
Let’s see the Working Process of the Sealed Class:
Code:
using System;
public class DemoClass
{
public static void Main (string[] args)
{
SealedDemo _sealedObject=new SealedDemo();
int result=_sealedObject.Addition(5,5);
Console.WriteLine("Total Value="+result.ToString());
}
} //sealedClass starts here
sealed class SealedDemo
{
public int Addition(int x, int y)
{
return x+y;
}
}Output:
![]()
When you define a class as sealed, you prevent inheritance. This means other classes cannot use the sealed class as a base class. Developers primarily use sealed classes to restrict the inheritance aspect of object-oriented programming (OOP).
Sealed Methods in C#
Sealed methods are parent-class methods designed to prevent overriding by child classes. In contrast, declaring a method as virtual within a class allows child classes to override its implementation.
Example #1
Code:
using System;
public class Sample_Employee
{
protected int Emp_id, Emp_age;
protected string Emp_name, Emp_address;
public virtual void GetEmployeeDetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE DETAILS");
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE ID");
Emp_id = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE NAME");
Emp_name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE ADDRESS");
Emp_address = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE AGE");
Emp_age = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
}
public virtual void DisplayEmployeeDetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("\nEMPLOEE DETAILS:");
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE ID : " + Emp_id);
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE NAME : " + Emp_name);
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE ADDRESS :" + Emp_address);
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE AGE : " + Emp_age);
}
}
public sealed class Emp_Manager : Sample_Employee
{
double Bonus, CA;
public override void GetEmployeeDetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("ENTER MANAGER DETAILS:");
Console.WriteLine("ENTER THE ID");
Emp_id = int.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("ENTER THE NAME");
Emp_name = Console.ReadLine();
Console.WriteLine("ENTER THE BONUS");
Bonus = double.Parse(Console.ReadLine());
Console.WriteLine("ENTER THE CA");
CA = Convert.ToDouble(Console.ReadLine());
}
public override void DisplayEmployeeDetails()
{
Console.WriteLine("MANAGER DETAILS");
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE ID: " + Emp_id);
Console.WriteLine("EMPLOYEE NAME: " + Emp_name);
Console.WriteLine("MANAGER BONUS: " + Bonus);
Console.WriteLine("MANAGER CA : " + CA);
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Emp_Manager m1 = new Emp_Manager ();
m1.GetEmployeeDetails();
m1.DisplayEmployeeDetails();
Console.ReadKey();
}
}Output:
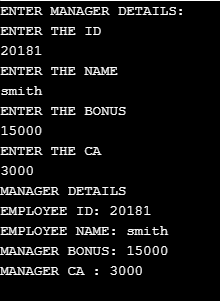
We can use a sealed modifier on a property or method that overrides the virtual method in the base class, which enables us to allow classes to derive from the class and secure developers using classes from overriding particular virtual properties or methods. There are a few points which we must define sealed class are:
- We never want to override all properties or methods of a class in sub-classes
- There is no need to expand our class functionalities.
Example #2
The main purpose of using a sealed class is to secure the inheritance of a class; we do not require any classes to enlarge the functionality of a class. Let’s see the sample program for the sealed class:
Code:
using System;
using System.Text;
namespace test_SealedClass
{
public class SampleProgram1
{
public sealed class TestBaseClass
{
public static void TestDisplay()
{
Console.WriteLine("Here the SealedClass cannot be inherited");
}
}
public class TestDerived : TestBaseClass
{
// here Derived class cannot be inherited because it's a sealed class
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
TestBaseClass _object = new TestBaseClass();
_object.TestDisplay();
Console.ReadLine();
}
}
}When you attempt to derive a class from a sealed class compiler throws a fault error. “TestDerived: cannot derive from sealed type TestBaseClass”.
Advantages in Sealed Class
- Security and Control: Sealing a class prevents unintended modifications to its behavior through inheritance, providing a level of certainty in the design. This ensures that the class’s functionality remains intact and that no unforeseen changes occur due to subclassing.
- Enhanced Performance: The compiler can optimize the usage of sealed classes more effectively because they cannot be inherited. This optimization can improve performance, especially in scenarios involving virtual method calls, as there’s no need for dynamic dispatch.
- Simplified Design: Sealing a class directly tells developers that they should not extend it. This simplifies the class’s design and reduces the cognitive load for other developers interacting with the codebase, as they can trust that the class’s behavior won’t be altered by inheritance.
- Preventing Fragile Base Class Problem: Sealing a class helps mitigate the fragile base class problem, where changes to a base class unintentionally affect derived classes. Sealing the class prevents derived classes from relying on potentially fragile aspects of the base class’s implementation, thus promoting code stability and maintainability.
- Enforcing Design Contracts: Sealed classes enforce design contracts by limiting the scope of class extension. This encourages developers to adhere to the intended design patterns and prevents deviations that may lead to code complexity or architectural inconsistencies.
- Compiler Optimizations: Sealed classes enable the compiler to make certain optimizations, such as inlining method calls or eliminating runtime checks related to inheritance, which can result in more efficient code execution.
Alternatives to Sealed Classes in C#
1. Comparison over Inheritance
Composition emphasizes building classes by combining smaller components rather than inheriting behavior. It promotes flexibility and code reuse by reducing coupling and allowing for easier modifications and extensions without impacting the entire class hierarchy.
- Pros:
- Greater flexibility to switch out the “contained” class with a different implementation.
- Useful when you need a subset of functionality from a potential base class.
- Cons:
- Exposes the contained object’s public interface (you may have to create wrapper methods to control access to its functionality).
2. Interfaces and Abstract Classes
Interfaces define contracts for classes to implement, specifying methods and properties. Abstract classes provide partial implementations that subclasses can extend. Both support polymorphism and code reuse, offering flexibility in designing class hierarchies.
- Pros:
- Ensures consistent behavior across derived classes.
- Excellent for defining reusable contracts.
- Abstract classes can provide some base implementation to reduce code duplication.
- Cons:
- Using multiple levels of inheritance can increase complexity.
Example:
We want to process different payment types (credit card, PayPal, etc.) but want to restrict uncontrolled extension in some cases.
Code:
using System;
// 1. Interface-based approach
interface IPaymentProcessor
{
void ProcessPayment(double amount);
}
class CreditCardPaymentProcessor : IPaymentProcessor
{
public void ProcessPayment(double amount)
{
Console.WriteLine("Processing credit card payment of $" + amount);
}
}
class PayPalPaymentProcessor : IPaymentProcessor
{
public void ProcessPayment(double amount)
{
Console.WriteLine("Processing PayPal payment of $" + amount);
}
}
// 2. Composition example
class SecurePaymentProcessor
{
private IPaymentProcessor _processor;
public SecurePaymentProcessor(IPaymentProcessor processor)
{
_processor = processor;
}
public void ProcessSecurely(double amount)
{
// Add security logic here
Console.WriteLine("Applying extra security...");
_processor.ProcessPayment(amount);
}
}
// Usage
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IPaymentProcessor creditCardProcessor = new CreditCardPaymentProcessor();
SecurePaymentProcessor secureProcessor = new SecurePaymentProcessor(creditCardProcessor);
secureProcessor.ProcessSecurely(100.00);
}
}Output
![]()
Conclusion
A sealed class in C# blocks inheritance, preventing subclasses from extending or overriding it. This enhances security and control over the class’s behavior and design. Sealed classes offer advantages such as maintaining code integrity, enhancing performance, and simplifying design. Alternatives like composition over inheritance and the use of interfaces and abstract classes provide flexibility and code reuse, addressing scenarios where sealed classes might limit extensibility. While sealed classes ensure certainty in design, alternative approaches offer more flexibility and maintainability, allowing developers to choose the best fit for their project requirements and design goals.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Sealed Class in C#” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


