Updated June 17, 2023
Introduction to SDLC Methodologies
SDLC Methodologies is a standard procedure or a method followed by the software industry to describe how to define, build, implement, and develop an application, and it follows the software development life cycle(SDLC) process. It is also known as a blueprint for designing software. Depending on the project, we choose an appropriate methodology to develop it, and it upgrades the quality of the software and the Software development process. Software methodology is a part of software engineering to develop a software application. It provides guidelines for developing an application.
Popular SDLC Methodologies
There are several types of SDLC methodologies or models, but here we discuss some popular SDLC Methodologies, such as:
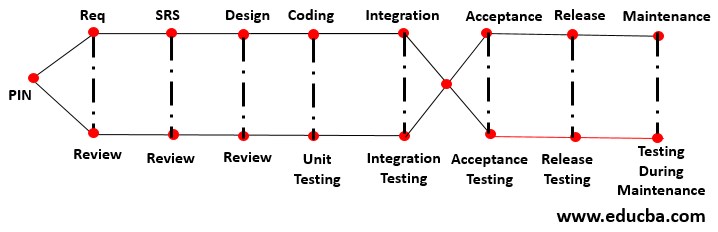
1. Fish Model
It is a time-consuming and expensive SDLC model. Here both verification and validation are done parallel by the different teams.
It looks like fish, so the model name shows the Fish model. In this model, first, we go for Project Initiation Node (PIN), i.e., a service level agreement would be signed for starting the project. Then the requirements are gathered from the client and analyzed to prepare SRS (Software Requirement Specifications).In every step, we review the process, i.e., verification. After that, we go for coding, module integration, acceptance, release, and development maintenance. For this process, we go for each level of testing, i.e., validation.
Advantages:
- It provides a high-quality software product.
- It is mainly used for secured projects.
Disadvantages:
- It is a time-consuming process to develop the product.
- It is expensive to process.
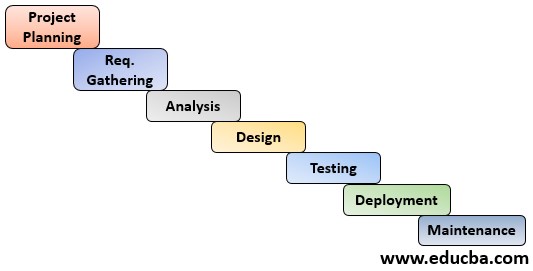
2. Waterfall Model
It is a rigid model where requirements are fixed. So it is called the Sequential model. Here, until one phase is completed, we can’t go for the next phase.
In this model, after coding, the planning, preparation, and execution of the test are possible. So that is rigid and has a bottleneck activity of testing. (Less time for testing).
Advantages:
- It is a straight model and simple.
- It is easy to implement.
Disadvantages:
- 100% requirements are needed at the beginning of the project and no change later.
- Testing could become a bottleneck activity.
- Late Validation.
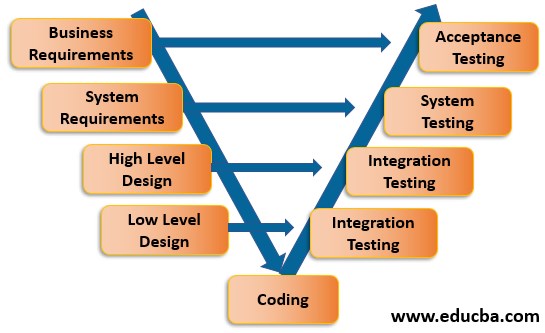
3. V Model
It is also called the Overlapping model. In this model, in every phase, we have test preparation & planning done simultaneously; after coding, we go for execution.
Advantages:
- It produces a high-quality product.
- The testing process started early.
Disadvantages:
- 100% requirements are needed at the beginning of the project and no change later.
- It is a time-consuming and expensive process.
- Late Validation.
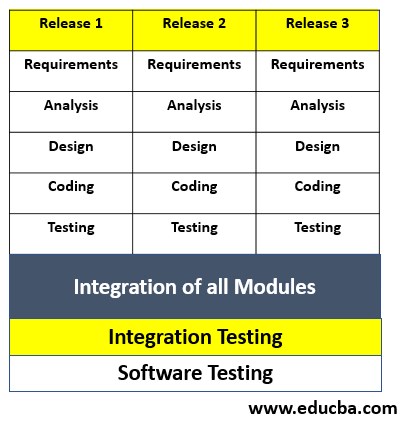
4. RAD model
It stands for Rapid Application Development. Unlike the waterfall and V-model, completing the entire project in this particular model requires multiple cycles of SDLC instead of just one. The team divides the project into a specific number of releases, with each release undergoing one cycle of SDLC. So it is also called the Iterative model. In every release, the number of requirements should be the same. After completing all the releases, we integrate them and proceed with integration testing. We complete one module or release and then present it to the client, but we keep it aside without releasing it. It overcomes all the problems of the waterfall & V-model.
Advantages:
- We don’t need 100% requirements at the beginning of the project.
- Testing is not a bottleneck activity.
- No late Validation by the client.
Disadvantages:
- It is a complex model.
- Late return on investment, i.e., the client can’t use the software even after complete earlier.
5. Incremental Model
It is also known as the Spiral model. In this methodology, we break down the project into different releases. At the end of each release, we present it to the client for approval and release the basic version of the software product. The testing process of this model becomes increasingly complex and time-consuming as the release version increases. So it is incremental in nature.
| Requirements | Requirements | Requirements | Requirements |
| Analysis | Analysis | Analysis | Analysis |
| Design | Design | Design | Design |
| Coding | Coding | Coding | Coding |
| Testing | Testing | Testing | Testing |
| Release Version 1.1 | |||
| Release Version 1.2 | |||
| Release Version 1.3 | |||
| Release Version
1.4 |
Advantages:
- Early Return of Investment (ROI).
- The client can start to use the basic version of the software.
Disadvantages:
- It is a complex model.
- Time-consuming Testing process.
- Risk of regression is more (side effect)
6. Agile Model
Software organizations mainly prefer this model to develop the application. It is the combination of the Iterative and Incremental models. Every release breaks into small parts called sprints, each having one cycle of SDLC. The number of requirements should vary in every sprint; at the last sprint, we integrate the entire sprint and go for integration testing. Each sprint has a time limit (2 – 4 weeks) to complete. It is also known as an adaptive model.
Advantages:
- It can deliver frequently and satisfy the client or customer.
- Continuous attention to sustainable development.
- The client can change or add the requirements at any stage of development.
- It deals with self-organizing teams working together.
- It helps customer collaboration and response to change.
Disadvantages:
- It is an expensive model.
- For a small project, it is not useful.
Conclusion
In this article, we discuss some popular SDLC methodologies briefly. Similarly, other SDLC methodologies like the Lean, DevOps, and Big Bang models exist. Selecting an appropriate SDLC methodology for developing a software application is essential. The most popular SDLC methodology is the Agile model.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SDLC Methodologies. Here we discuss the Introduction to SDLC Methodologies like Fish Model, RAD Model, Waterfall Model, etc., along with Advantages and Disadvantages. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –