Updated July 28, 2023
Introduction to Rust Iterator
Whenever we want to iterate over a collection of values like vectors, maps, arrays, etc., we use iterators in Rust. The iterator implements the iterator trait defined in the standard library of Rust. The values in the iterator object are called items, and the items in the iterator can be traversed using the next() method. This method returns a None value when the iterator reaches the end of the collection. Once the iterator trait is implemented, the collection can be traversed using for loop with in keyword as well.
The syntax to declare an iterator in Rust is as follows:
let mut iterator_name = collection_name.iter();Where mut is the keyword to represent a mutable variable,
- iterator_name is the name of the iterator.
- collection_name is the name of the collection of arrays, maps, or vectors.
Working of Iterator in Rust
Working of iterator in Rust is as follows:
- A sequence of values can be produced using objects called iterators so that they can be looped over or iterated.
- The iterator can iterate over a collection of values such as maps, arrays, vectors, etc.
- The iterator implements the iterator trait defined in the standard library of Rust.
- The values in the iterator object are called items.
- To go through the items in the iterator, just utilize the next() method.
- The next() method returns a None value when the iterator reaches the end of the collection.
- Once you implement the iterator trait, you can traverse the collection easily by using a for loop and the “in” keyword.
Examples
Let us discuss examples of Rust Iterator.
Example #1
Rust program to demonstrate iterator in which we declare an array and use the iterator to read the values from the array and make use of the next() method to traverse through the next elements in the array and display the output on the screen:
Code:
fn main()
{
//declaring an array of strings and storing it in a variable called arrayname
let arrayname = ["Welcome","to","EDUCBA"];
//defining an iterator trait and storing it in a mutable variable called iteratorname
let mut iteratorname = arrayname.iter();
//printing all the elements of the array using iterator object
println!("The items in the collection are:\n");
println!("{:?}",iteratorname);
println!("\n");
//displaying individual items in the collection by traversing through the collection until the end of the collection is reached
println!("The individual items in the collection are:\n");
println!("{:?}",iteratorname.next());
println!("{:?}",iteratorname.next());
println!("{:?}",iteratorname.next());
println!("{:?}",iteratorname.next());
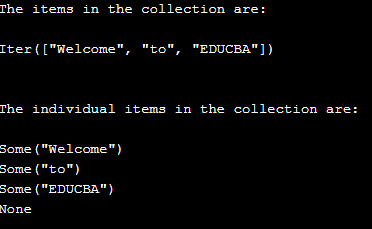
}The output of the above program is as shown in the snapshot below:
In the above program, we are declaring an array of strings and storing it in a variable called array name. Then we define an iterator trait and store it in a mutable variable called iterator name. Then we print all the array elements using the iterator object as the output on the screen. To display each item individually, go through the collection item by item until you reach the end. The snapshot provided above displays the output.
Example #2
Rust program to demonstrate iterator in which we declare an array and use the iterator to read the values from the array and make use of for loop along with in keyword to read each item in the array and display the output on the screen:
Code:
fn main()
{
//declaring an array of strings and storing it in a variable called arrayname
let arrayname = ["Welcome","to","EDUCBA"];
//defining an iterator trait and storing it in a mutable variable called iteratorname
let iteratorname = arrayname.iter();
//printing all the elements of the array using iterator object
println!("The items in the collection are:\n");
println!("{:?}",iteratorname);
println!("\n");
//displaying individual items in the collection by traversing through the collection using for loop
println!("The individual items in the collection are:\n");
for eachitem in iteratorname
{
print!("{}\t",eachitem);
}
}The output of the above program is as shown in the snapshot below:
In the above program, we are declaring an array of strings and storing it in a variable called array name. Then we define an iterator trait and store it in a mutable variable called iterator name. We print all the array elements using the iterator object as the output on the screen. Then displaying individual items in the collection by traversing through the collection using for loop and a keyword. The snapshot provided above shows the output.
Example #3
Rust program to demonstrate iterator in which we declare an array and use the iterator to read the values from the array and make use of for loop along within keyword to read each item in the array and display the output on the screen:
Code:
fn main()
{
//declaring an array of strings and storing it in a variable called arrayname
let arrayname = ["Learning","is","fun"];
//defining an iterator trait and storing it in a mutable variable called iteratorname
let iteratorname = arrayname.iter();
//printing all the elements of the array using iterator object
println!("The items in the collection are:\n");
println!("{:?}",iteratorname);
println!("\n");
//displaying individual items in the collection by traversing through the collection using for loop
println!("The individual items in the collection are:\n");
for eachitem in iteratorname
{
print!("{}\t",eachitem);
}
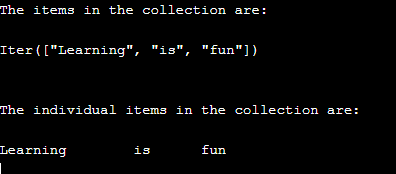
}The output of the above program is as shown in the snapshot below:
In the above program, we are declaring an array of strings and storing it in a variable called arrayname. Then we define an iterator trait and store it in a mutable variable called iteratorname. Then we print all the array elements using the iterator object as the output on the screen. Next, by iterating through the collection using a for loop and the in keyword, each individual item in the collection will be displayed. The output is shown in the snapshot above.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned the concept of an iterator in Rust-through definition, syntax, and working of an iterator in Rust with corresponding programming examples and their outputs to demonstrate them.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Rust Iterator” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.