Updated June 1, 2023
Introduction to Rust hashset
A collection with a unique value inside it while not allowing duplicate values inside the group is called a HashSet on Rust. It differs from the HashMap in that it does not hold any key-value pairs inside the collection, and the elements inside it must be accessed directly. HashSet’s structure is defined inside std::collections of the Rust, which is to be imported in the program at the beginning to be able to make use of HashSet structure, and we make use of the static method new() to create a HashSet.
The syntax to create HashSet in Rust is as follows:
let mut HashSet_name= HashSet::new();
where mut is a keyword to define mutable variable,
HashSet_name is the variable representing the name of the HashSet and
new() is the static method used to create a HashSetWorking of HashSet in Rust
- HashSet is a collection that holds unique values while not allowing duplicate values in Rust.
- To access the values inside the HashSet, you need to access them directly. It’s important to note that HashSet does not hold any key-value pairs.
- In Rust, the structure of HashSet is defined inside std::collections. To use the HashSet structure in a program, you need to import it at the beginning.
- We use the static method new() to create a HashSet.
- You can implement the HashSet using several functions available in the Rust library.
- The functions available in the Rust library are insert() function, len() function, get() function, iter() function, contains() function, and remove() function.
- The insert() function inserts the data into the HashSet.
- We use the len() function to obtain the length of the HashSet or the number of elements present in the HashSet.
- The get() function returns a reference to the value if there is a matching value to this value in the HashSet.
- We can use the iter() function to access all the elements of the HashSet in a random order of our choice.
- The contains() function returns a value if the value is present in the HashSet.
- We use the remove() function to remove an element from the HashSet.
Examples of Rust hashset
Here are the following example mention below:
Example #1
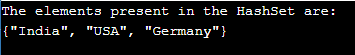
Rust program to generate to create a HashSet and insert the elements into the HashSet and display the elements present in the HashSet as the output of the program:
//importing std::collections to be able to make use of HashSet in the program
use std::collections::HashSet;
fn main()
{
//defining a mutable variable called country to store the created HashSet
let mut country = HashSet::new();
//using insert() function to insert the elements in the HashSet
country.insert("India");
country.insert("USA");
country.insert("Germany");
//displaying the elements of the HashSet as the output on the screen
println!("The elements present in the HashSet are:");
println!("{:?}", country);
}The output of the above program is as shown in the snapshot below:
In the above program, we are importing the collections std::collections to be able to make use of HashSet in the program. Then we create a new HashSet and defining a mutable variable called the country to store the created HashSet. Then we use the insert() function to insert the elements in the HashSet. Finally, we display the elements of the HashSet as the output on the screen.
Example #2
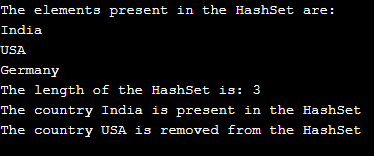
Rust program to create a HashSet and demonstrate insert() function, len() function, get() function, remove() function and contains the () function to insert the data into HashSet, determine the length of the HashSet, to determine if an element is present in the HashSet or not and then remove an element and confirm if it is removed or not and then display the result as the output on the screen:
//importing std::collections to be able to make use of HashSet in the program
use std::collections::HashSet;
fn main()
{
//defining a mutable variable called country to store the created HashSet
let mut country = HashSet::new();
//using insert() function to insert the elements in the HashSet
country.insert("India");
country.insert("USA");
country.insert("Germany");
//displaying the elements of the HashSet using iter() function as the output on the screen
println!("The elements present in the HashSet are:");
for coun in country.iter(){
println!("{}", coun);
}
//displaying the length of the HashSet
println!("The length of the HashSet is: {}", country.len());
//using get function to determine if a given element is present in the HashSet or not
match country.get(& "India") {
Some(value) => {
println!("The country {} is present in the HashSet", value);
}
None => {
println!("The country is not present in the HashSet");
}
}
//using remove() function to remove an element from the HashSet and checking if the element is removed or not using contains() function
country.remove( & "USA");
if country.contains( & "USA") {
println!("The country USA is not removed from the HashSet");
}
else {
println!("The country USA is removed from the HashSet");
}
}The output of the above program is as shown in the snapshot below:
In the above program, we are importing the collections std::collections to be able to make use of HashSet in the program. Then we create a new HashSet and defining a mutable variable called the country to store the created HashSet. Then we use the insert() function to insert the elements in the HashSet. Next, we utilize the iter() function to display the HashSet elements as output on the screen. Then we use the len() function to display the length of the HashSet as the output on the screen. Then we use the get() function to determine if an element is present in the HashSet. We use the remove() function to eliminate an element from the HashSet, and then we use the contains() function to confirm whether the remove() function has successfully removed the element.
Conclusion
In this article, we have learned the concept of HashSet in Rust through the definition, syntax, and working of HashSet in Rust with corresponding programming examples and their outputs to demonstrate them.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Rust hashset” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.