Updated June 16, 2023
Introduction to Reshape in Matlab
Reshape function gives a new shape to the array with a specified number of rows and columns. The reshaped array should be compatible with the original array. It is used in Python and Matlab to execute various operations in the array. After reshaping the array, it adjusts the memory allocation accordingly. Reshaping can be in the form of increasing or decreasing the dimension of the array. People use these functions in many fields, including data science and image modification.
Working of Reshape Function in Matlab
Many operations can be performed using one-dimensional or two-dimensional arrays. The reshape function in Matlab modifies the original or existing array into a different array with varying dimensions or sequences.
There are various syntax which is used in Matlab like:
R=reshape (X, size)
This function reshapes the original matrix X into R, using the size defined in the ‘size’ vector.’ The vector should contain at least 2 elements in it.
For example, if it reshapes (X, [1,3]): it will reshape X into a 1 by 3 matrix.
R=reshape (X, size 1, size 2…. size n)
You can reshape A into a specified size using this function, where size1 and size2 indicate each dimension. We can specify the dimension as [], which will calculate the dimension automatically so that the number of elements present in the reshaped array matches the total count of elements in the input array. The input array, i.e.,’ ‘X’, can be a vector, matrix, or multidimensional array. It supports data types such as single, double, int16, int8, int32, int64, unit8, uint16, unit32, unit64, char, string, logical, date time, and duration. It also supports complex numbers.
The size of the resultant array should be specified with a vector of integers, and the size should be in such a way that the number of elements should be the same as the original array. We should provide at least 2 dimension sizes; if there is at most one dimension, they can be specified as []. The output or results should be a vector, matrix, multidimensional array, or cell array. The data types and the number of elements in the reshaped array should always be the same as that of the original array. The data types supported by the reshaped array are single, double, int16, int8, int32, int64, unit8, uint16, unit32, unit64, char, string, logical, date time, and duration. We can also reshape the symbolic array present in Matlab.
There are different syntaxes for these:
R=reshape (X, y1, y2)
The purpose of this process is to generate a matrix, denoted as y1 by y2, which has the same number of elements as the array X. We take the resulting matrix elements by extracting them column-wise from the given array ‘X.’
R=reshape (X, y1, y2…yn)
This is used to return y1 by …yn matrix, which has an equal number of elements as that of X. The elements that are present in the resultant matrix are taken column-wise from the given array ‘X.’ In the above syntax, the input array is X which can be a symbolic vector, symbolic matrix, or symbolic multidimensional array. y1 and y2 represent the dimension of the reshaped matrix, separated by commas, and the number of elements should be the same as that of the original array.
For example, reshaping (X,2,3) gives the reshaped array as two by 3 matrix. If there is more dimension, then they are represented in the same way.
For example: reshaping (X,2,3,3) results in a 2 by 3 by 3 matrix.
Examples of Reshape in Matlab
Given below are the examples of Reshape in Matlab:
Example #1
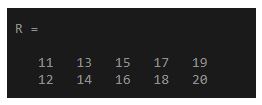
To reshape an 11:20 vector into a 2 by 5 matrix
X = 11:20;
R = reshape(X,[2,5])
Output:
Example #2
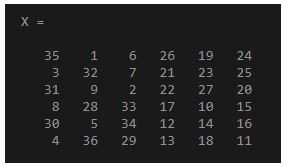
To reshape the matrix with the specified number of columns in the input arguments.
X = magic(6)
Output:
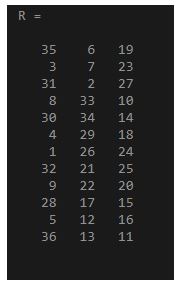
After reshaping the above matrix by specifying the number of columns as 3 and we have given [] instead of a total number of rows so that it calculates the number of rows automatically. Please find the below matrix after applying the required function:
R = reshape(X,[],3)
Output:
The reshaped matrix is a 12 by 3 matrix with 12 rows and 3 columns with the same number of elements as the original array X, i.e., 36.
Example #3
To reshape a matrix into a 3 by 4 matrix.
X = [1 2 4 7 6 1; 2 9 4 1 7 3];
R = reshape(X,3,4)
After reshaping the above matrix into a 3 by 4 matrix, we get the desired matrix with the same number of elements as the original array.
Output:
Example #4
To use reshape function with a multidimensional array and convert them into a 4 by 3 matrix. The input array is a multidimensional array of dimensions 2 by 3 by 2.
X = zeros(2,3,2);
R = reshape(X,4,3)
Output:
Conclusion
Various sectors, such as artificial intelligence, data science, image compression, image extension, etc., utilize the reshape function. It is essential to understand the working of reshape function, whether in Matlab, R, or Python, to perform the operations with the desired array size per the business requirements. You can use them to change the dimension of the array, whether it is one-dimensional or multidimensional, as long as the output and input arrays have the same number of elements.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Reshape in Matlab. Here we discuss the basic concept and working of the reshape function in Matlab with various examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –