Updated May 31, 2023
Introduction of Natural Log in Matlab
In this article, we will discuss Natural Log in Matlab. The logarithm is defined as the inverse of an exponential function. Logarithms are used in most mathematics, Physics or any domain-related to Calculus field. For example, 2 raised to power 3 will give 8 as the output, this can be represented by the exponential equation as 2^3 = 8. Now, if there is a question stating 2 raised to x power is 8 and our goal is to find x then we use logarithmic equation which is given by log2(8) =3, which is referred as log base 2 of 8 is 3.Here base is given as 2 and the exponent we got is 3.
Working of Natural Log in Matlab with Examples
Natural logarithms form an important topic in Mathematics and Matlab. The base of the logarithmic equation can be changed depending on the case. If a logarithmic equation is written without base, then it is considered to have based as 10 and is known as a common logarithm. While if the base of the logarithmic equation is represented using e (also known as Euler’s number), then it is known as a natural logarithm. The value of e is given by 2.71828 and it is also denoted by a log. So, we should be careful while using a base in any logarithmic equation.
In Matlab, natural logarithm is given by log(y) which represents the natural logarithm of y. The natural logarithm is also defined for all the complex numbers where y is not equal to 0. There are several rules which should be followed while working with natural logarithmic equations:
X= log(y)
- If y is of the data type numeric then it is represented as log(e^y) =y+ai2π, where a is an integer and imaginary part of the result ranges from – π to π.
- If y is not a positive integer, then it is represented as log(y) = i π + log (- y).
- If y is given in the form of an integer, then it is given by equation log(1/y) =-log(y).
If the input argument type is of floating-point, then the output is also floating-point. If the result contains an imaginary part, then it ranges from – π to π. The input argument of a logarithmic equation can be represented in the form of a vector, scalar, matrix or multi-dimensional array. It can handle single and double data types with complex number support. The output can also be in the form of vector, matrix, scalar or multi-dimensional array. If there are positive values for y in the range of 0 to infinity, then the output i.e. X is in the range of –Inf to Inf. If the input argument is in complex and negative form, then the output is also complex. The data type used in the input argument should always be the same as the output argument. Arithmetic operations like log(ab) = log(a)+log(b) is not valid for complex numbers in Matlab.
Example #1
To find the natural logarithm of 1.
log (1)
Output:
Example #2
To find the natural logarithm of -1.
log (-1)
Output:
We can also find the natural logarithm of the arrays. Here the input argument is of type array, then the output is also of type array. The size of input and output arguments should be the same and the input array should contain only positive elements. In Matlab, we use real log () function to find the natural logarithm of each element present in an array. Please find the below example depicting how natural logarithm is used in arrays:
X= reallog(y)
Here y is the input argument which is an array and X gives the natural logarithm of each element present in y.
Example #3
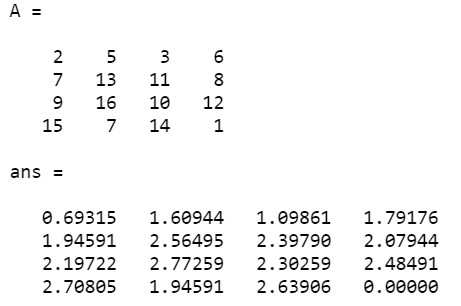
To find the natural logarithm of the below array given by A:
A = [2 5 3 6; 7 13 11 8; 9 16 10 12; 15 7 14 1]
reallog(A)
Output:
Example #4
Find the natural logarithm of the following expression:
log (7.8 + 5.6*i)
Output:
There are different functions that handle natural logarithms like diff, limit, float, etc. Log and log should be used carefully because both give different results. Log means it treats the base as 10 and log considers the base as e to give the results.
There are four different properties or rules in the natural log like:
- Multiplication or Product Property: This rule states that if the natural log of the product of m and n is equal to the sum of the natural logarithm of m and the natural logarithm of n.
log(m)(n) =log(m)+log(n) - Quotient Property: This rule states that is the natural log of m and n divided is equal to the difference of natural logarithm of m and n.
log(m/n) =log(m)-log(n) - Reciprocal Property: The reciprocal of the natural logarithm of m is negative of m.
log(1/m) =-log(m) - Power Property: Please find the below syntax for this rule:
log(m^n) =n*log(m)
Applications of Natural Log
Let us discuss the application of natural log.
- Natural Logarithm is used in the field of mathematics which deals with calculus problems.
- Natural Logarithm is also used in the field of physics for the problems related to integration and differential equations.
- Natural Logarithm is used to solve the problems dealing with decay.
- Logarithms also play an important role in the field of data analytics and data science. For example, in linear regression, there is an assumption which states that the independent and dependent variables should have a linear relationship but somehow if the variables are not linear, we can use many transformation methods like logarithmic transformation to satisfy the assumption and then apply the regression equation between the independent and dependent variables to satisfy the condition of linearity.
- Logarithmic coefficients are also used in logistic regression to define the relationship between the dependent and independent variables and are also used for predicting the output.
Conclusion
Natural logarithms are mainly used to solve any exponential or decay problems. They are mainly used in mathematics and physics domain. Sometimes, it is used in the financial domain to solve the problems related to compound interest. Logarithms are also used in Data science to transform any variable if it doesn’t meet any requirements. So, it is essential to learn the properties of the logarithm to use it properly.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Natural Log in Matlab. Here we discuss the introduction and applications along with working of Natural Log in Matlab with Examples. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –