Updated June 30, 2023
Introduction to Rational Unified Process
The Rational Unified Process (RUP) is a software development process. Rational Software Corporation develops it; it has been part of IBM since 2003. We carefully monitor our development process to ensure that we produce a top-notch software product. It is nothing but a model for the software development process. This development process involves multiple stages like business modeling or planning, analysis, and design, implementation or coding, testing, and deployment, etc.
Workflows of Rational Unified Process
This process passes through six main workflows and three supporting workflows:
Main Workflows:
- Business Modelling(Planning)
- Requirement Gathering
- Analysis & Design
- Coding
- Testing
- Deployment
Supporting Workflows:
- Project Management
- Configuration &Change Management
- Environment Management
The Rational Unified Process outlines the details of the development process, including who will do what, when, and how.
These four building blocks are:
- (Roles) the ‘Who’: It shows the responsibilities for developing the software product. It may be an individual or a group of individuals working on it together as a team.
- (Work Products) the ‘What’: It indicates what will be produced. That shows the behavior and type of software product.
- (Workflows) the ‘When’: It represents the flowchart of activities to produce a software product.
- (Tasks) the ‘How’: It describes how the development will take place, i.e., a unit of work assigned to a Role to perform and that provides a meaningful result.
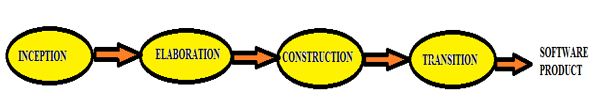
Phases Involved in the Rational Unified Process
It consists of four phases to complete the RUP process, each with a specific purpose.
- Inception Phase
- Elaboration Phase
- Construction Phase
- Transition Phase
1. Inception Phase
It is the initial phase of the developing process. During this phase, the project’s basic ideas and structure will be determined to prepare a business suite, i.e., the team will decide the purpose of the project, success criteria, estimated cost, risk assessment, scheduled time, and resources required to complete it, etc. It is just like an evaluation of the project. The project may be canceled or considered if it fails to pass the criteria below.
The conclusions of the inception phase are:
- It provides a general vision project initiative document with multiple parameters.
- We get the project scope with the initial project model.
- An initial business suite with financial analysis.
- A project plan with different phases with a business model.
- Requirement understanding.
- Actual expenditures versus planned expenditures.
- Actual expenditures versus planned expenditures.
2. Elaboration Phase
This is the second phase of the development process. During this phase, analyze the project’s requirements and necessary architecture, i.e., review the problems, develop the project plan and architect, and eliminate the high-risk elements from the project. It is the most critical phase among the four phases. The actual development and coding will take place in the following phase.
The conclusions of the Elaboration phase are:
- It provides a full model of the project with functional and non-functional requirements.
- A full Software Architecture Description is provided.
- It provides the stability of the project, like the vision of the product & architecture of the product stable or not?
- Similarly, the project plan will approve or not?
- Is the actual resource cost versus planned resource cost acceptable or not?
3. Construction Phase
This is the third phase of the development process. During this phase, the project is developed and completed. Here all the features are developed and integrated into the product, i.e., the software is designed, written, and tested successfully. So the development product will be deployable. It measures the completeness of the product.
The conclusions of the Construction phase are:
- The software product is integrated into different modules.
- It provides a user manual.
- Is the product release stable or not?
- Does it meet client requirements or not?
- Is the actual resource cost versus planned resource cost acceptable or not?
4. Transition Phase
This is the last phase of the development process. The software is released and delivered to the public or customers during this phase. The product will be updated or changed based on the end-users feedback. It is the process of deployment.
The conclusions of the Transition phase are:
- It is one type of “beta testing” to validate the product as per user expectations.
- It provides the end-user to satisfy or not.
- All types of training manuals for the user.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Rational Unified Process
The following are some advantages and disadvantages:
Advantages
- It allows us to deal with changing requirements within the project’s development life cycle as per the client or customer needs, i.e., it welcomes change.
- It supports incremental build of the software product.
- The software product provides proper documentation.
- It helps to use the resources efficiently.
- It helps to identify issues early in the process life cycle.
- Process control and risk management are improved.
- It enhances team productivity.
- It helps reduces unexpected development costs.
Disadvantages
- It is a complex model to implement as it has multiple workflow stages.
- It is challenging for organizations to implement which has small team sizes or projects.
- Individuals or teams should prioritize achieving highly tangible results.
- It emphasizes the integration of modules throughout the software development process, creating trouble during the testing phase.
Conclusion
This article discusses the Rational Unified Process (RUP), an Iterative software development process. It manages requirements, component-based architecture, software models, risk control, welcome to changes, and software quality.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Rational Unified Process. Here we discuss the introduction and phases involved in the Rational Unified Process. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –