Updated March 20, 2023
Difference Between Raid 10 vs Raid 5
In this article, we will see an outline of Raid 10 vs Raid 5. RAID stands for Redundant Array of Independent Disks. It stores the same data in different places on various disks to protect from drive failure. The term RAID was coined by David Patterson, Garth A. Gibson and Randy Katz in 1987. There are standard RAID levels in computer storage. Various Raid levels protect data and are an upgrade from the previous one. Fault tolerance is done in Raid level 5, and data is distributed in multiple disks, whereas Raid 10 combines disk mirroring and disk striping for safe and secure data. Raid 5 takes some time to build the configuration.
Head to Head Comparison between Raid 10 vs Raid 5 (Infographics)
Below are the top 17 comparisons between Raid 10 vs Raid 5:
Key Differences Between Raid 10 vs Raid 5
Let us discuss some key differences between Raid 10 vs Raid 5 in the following points:
- Raid 10 combines features of Raid 0 and Raid 1 while Raid 5 distributes data in multiple disks equally.
- Information about data and disks are stored in Raid 5 so that even if the hard disk fails, the data can be recovered. If two disks of Raid 10 fails, the data cannot be recovered.
- The fault tolerance of Raid 10 is very good, while Raid 5 allows fault tolerance of only 1 disk.
- Raid 10 works similar to Raid 0 in terms of writing speed which is slow when compared with Raid 5.
- Raid 10 uses logical mirrors and block-level striping, while Parity disk is used well in Raid 5.
- Data loss cannot be managed and unacceptable in Raid 10 if the information is written on only 1 disk. Raid 5 has good failure resistance and better security.
- The performance is great in Raid 10, but in Raid 5, performance is slow due to disks’ redundancy.
- Raid 10 needs 4 disks to write the data, and Raid 5 needs 3 disks to write the data.
- The read performance of Raid 10 is 2 times better when compared with Raid 5.
- The storage efficiency of Raid 10 is less when compared with Raid 5. Raid 5 has two-third of storage efficiency, while Raid 10 has only half of the storage efficiency.
- RAid 5 is designed as a storage server where storage efficiency is high. Raid 10 is used for production and hosting servers.
- Performance and data security are high in Raid 10 when we compare it with Raid 5. Secure data makes users check Raid 10 often.
- When more databases are there, it is better to use Raid 10. In Raid 5, parity creates data blocks for missing data blocks and databases are not used often.
- Raid 1 is the choice for the high-end level of applications, whereas Raid 5 is considered for a medium level of applications.
- Raid 5 takes a long time to rebuild the application. And while rebuilding, we cannot use the application as well. This problem is solved by Raid 10 as it takes less time to rebuild, and during the rebuild, we can use the application.
- If an Uncorrectable Read Error (URE) occurs in the data while rebuild in Raid 5, the data is lost and cannot be recovered. This problem does not happen in Raid 10.
Comparison Table of Raid 10 vs Raid 5
The table below summarizes the comparisons between Raid 10 vs Raid 5:
| Raid 10 | Raid 5 |
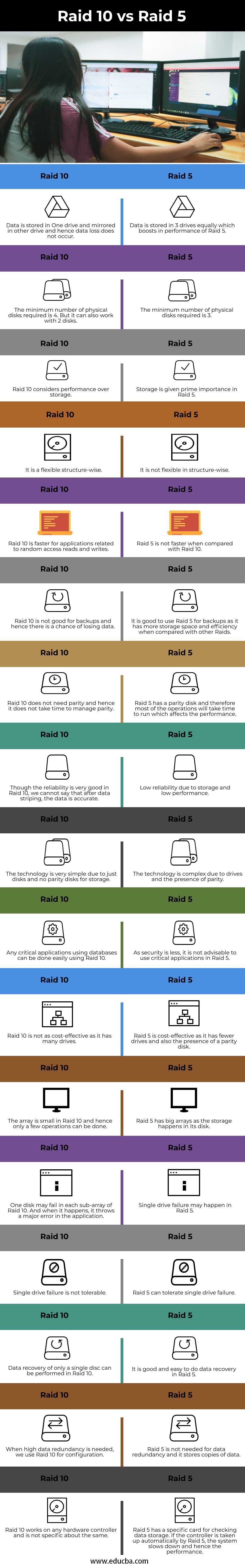
| Data is stored in One drive and mirrored in other drives, and hence data loss does not occur. | Data is stored in 3 drives equally, which boosts in performance of Raid 5. |
| The minimum number of physical disks required is 4. But it can also work with 2 disks. | The minimum number of physical disks required is 3. |
| Raid 10 considers performance over storage. | Storage is given prime importance in Raid 5. |
| It is flexible structure-wise. | It is not flexible in structure-wise. |
| Raid 10 is faster for applications related to random access reads and writes. | Raid 5 is not faster when compared with Raid 10. |
| Raid 10 is not good for backups, and hence there is a chance of losing data. | It is good to use Raid 5 for backups as it has more storage space and efficiency when compared with other Raids. |
| Raid 10 does not need parity, and hence it does not take time to manage parity. | Raid 5 has a parity disk, and therefore most of the operations will take time to run, which affects the performance. |
| Though the reliability is very good in Raid 10, we cannot say that the data is accurate after data striping. | Low reliability due to storage and low performance. |
| The technology is very simple due to just disks and no parity disks for storage. | The technology is complex due to drives and the presence of parity. |
| Any critical applications using databases can be done easily using Raid 10. | As security is less, it is not advisable to use critical applications in Raid 5. |
| Raid 10 is not as cost-effective as it has many drives. | Raid 5 is cost-effective as it has fewer drives and also the presence of a parity disk. |
| The array is small in Raid 10, and hence only a few operations can be done. | Raid 5 has big arrays as the storage happens in its disk. |
| One disk may fail in each sub-array of Raid 10. And when it happens, it throws a major error in the application. | Single drive failure may happen in Raid 5. |
| Single drive failure is not tolerable. | Raid 5 can tolerate single drive failure. |
| Data recovery of only a single disc can be performed in Raid 10. | It is good and easy to do data recovery in Raid 5. |
| When high data redundancy is needed, we use Raid 10 for configuration. | Raid 5 is not needed for data redundancy, and it stores copies of data. |
| Raid 10 works on any hardware controller and is not specific about the same. | Raid 5 has a specific card for checking data storage. If the controller is taken up automatically by Raid 5, the system slows down and hence the performance. |
Conclusion
Most Raid levels provide protection and recovery of data but do not protect data from losing from the user. There are also software errors and malware attacks from which Raid cannot protect the data. Raid is not a replacement for a backup plan. We can say that Raid is a building block to protect heavy data loss.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Raid 10 vs Raid 5. Here we also discuss the Raid 10 vs Raid 5 key differences with infographics and comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –