Difference Between Cassandra vs MySQL
Cassandra vs MySQL in this Data is everything, and with a boom in the amount of data today, choosing the right database management system is all the more important for all businesses. In a world that Oracle and SQL Server dominated, there are endless solutions to choose from now. One of the main reasons is the innovation possible due to open source solutions. In this article, I will be talking about two open-source databases. One is Cassandra which has gained much momentum over the past few years. And the other MySQL, which is the most common and popular database.
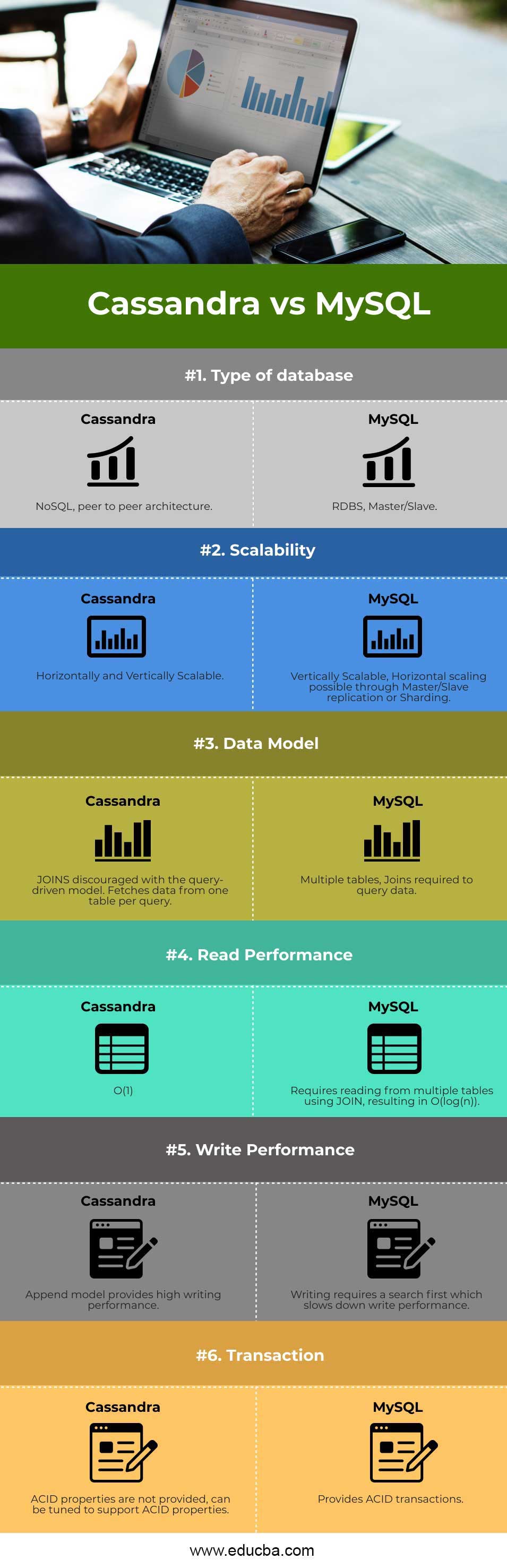
Head-to-Head Comparison Between Cassandra vs MySQL(Infographics)
Below are the Top 6 differences between Cassandra and MySQL:
Key Differences Between Cassandra vs MySQL
This article will look at the key differences between these two databases, which will help you determine which database to use.
Type of database
Cassandra is a NoSQL database. The Apache Software Foundation developed it. It was released in 2008. NoSQL(Not only SQL) databases were developed in response to the shortcomings of relational database management systems and to meet the demands of modern software development. NoSQL databases support a wide range of data, including key-value, document, and graph formats. It can store both unstructured and semi-structured data. It follows a peer-to-peer architecture.
MySQL is an open-source Relational Database Management System developed by Oracle and released in 1995. Compared to Cassandra, it is quite an old database. SQL databases support related data stored among different tables. MySQL stores structured data(high degree of organization). Essentially the relational model consists of tables (relations) that can be interlinked by keys common to multiple tables. It follows a Master/Slave architecture.
1. Scalability
MySQL provides support for vertical scaling. Horizontal scaling is possible with the help of some other approaches like Master/Slave replication and sharding.
Cassandra was developed with support for both horizontal and vertical scaling. Horizontal scaling is possible due to the cluster node model. Data is partitioned among different nodes in a cluster.
2. Data Model
The main difference that can be seen between MySQL and Cassandra is how the data is modeled.
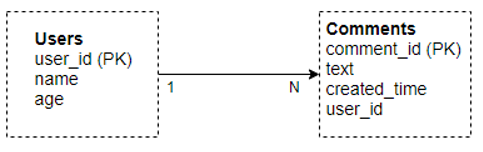
Let us take an example to show how there is a significant difference between data modeling in these two databases. Consider a portal where a user can comment on a post made by another user; If we wanted to store this information, it would be stored in different ways in these two databases.
In MySQL, we would have to make two tables with one to many relationships between them, like below. MySQL doesn’t allow unstructured data, e.g., a List or a Map, so we require one-to-many relationships among these tables.
To fetch data, you would typically use JOINS on these tables.
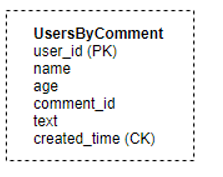
In Cassandra, this information can be stored in one table; we can store the comments for each user in the form of a List which would be stored as one row. Here user_id is the Partition key (using which data would be partitioned among the different nodes), and created_time is the cluster key using which the data would be sorted in a particular node.
3. Read Performance
Now that we have looked at how we can model data in both databases. Let us analyze how our read performance changes from one database to another.
In MySQL, the query to get the comments made by a user with id say ‘3’ will look something like this,
SELECT * from Users u, Comments c WHERE u.user_id=c.user_id and user_id=3;
First, finding a user would be of O(log(U)). This is because when you use indexing in MySQL, it stores the data in the form of a binary tree, so any time you search for comments made by a user, you are only going to traverse through half of the tree. As there is a one to many relationships between the two, this would now take C*O(log(C)) as we will have to find each comment_id for a particular user_id.
In Cassandra, surprisingly, this decreases to just O(1).
Our query will look something like this,
SELECT * from Users WHERE user_id=3;
As we discussed, we would only have to store one row in Cassandra for a user_id. It would just require one lookup. In the worst case, it can go up to O(log(U)).
4. Write Performance
In MySQL, every INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE operation necessitates the execution of a search if you want to update a record with a primary key already in the table.
- It will first search for the row
- Then update it
Cassandra, on the other hand, uses an append-only model. Insert and update have no fundamental difference. If we insert a row with the same primary key as an existing one, the row will be replaced. If you update a row and the primary key does not exist, Cassandra will create that row.
5. Transactions
As with any other RDBMS database, MySQL provides ACID transactions
- Atomicity
- Consistency
- Isolation
- Durability
Whereas Cassandra has limitations when it comes to providing ACID transactions. To provide high read performance, you would see data duplication. One way to achieve consistency would be to tune Cassandra not to allow data duplication, but then it kills Cassandra’s trump- Availability. So for systems highly based on ACID transactions like banking systems choosing any NoSQL database is a NO.
Let us summarize the key differences we looked at between Cassandra and MySQL. In case you did not read through the article and want to get the gist of it.
Cassandra and MySQL Comparison Table
Let’s discuss the top comparison between Cassandra and MySQL:
| Basis of Comparison | Cassandra | MySQL |
| Type of database | NoSQL, peer-to-peer architecture. | RDBS, Master/Slave. |
| Scalability | Horizontally and Vertically Scalable. | Vertically Scalable, Horizontal scaling is possible through Master/Slave replication or sharding. |
| Data Model | JOINS discouraged with the query-driven model—Fetches data from one table per query. | Multiple tables, Joins required to query data.
|
| Read Performance | O(1) | Requires reading from multiple tables using JOIN, resulting in O(log(n)). |
| Write Performance | The append model provides high writing performance. | Writing requires a search first, which slows down writing performance. |
| Transaction | ACID properties are not provided but can be tuned to support ACID properties. | Provides ACID transactions.
|
Conclusion
This article taught us some key differences between Cassandra and MySQL. In Data Science, most businesses utilize Cassandra for write-heavy workloads, while MySQL is the preferred choice for all other types of workloads. Hopefully, this will give you the knowledge to choose the proper database according to your needs.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cassandra vs MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.