Updated April 7, 2023
Introduction to PyTorch Squeeze
Squeeze is a function that is provided by the Pytorch, in deep learning we need to manipulate the tensor. That means we need to drop all existing dimensions of input those having size 1 at that time we can use the squeeze function. Basically, the squeeze() function consists of two different parameters such as input and another one is that dimension, so by using these two-parameters we can manipulate the dimension of tensors as per our requirement. Sometimes if we have batch size then it also removes the batch dimension which can show the unexpected result, in this case, squeeze only return the dimensions.
PyTorch Squeeze Overviews
- Basically, PyTorch provides the reshape functionality to the user, in deep learning it is an important part. The Squeeze in PyTorch is utilized for controlling a tensor by dropping every one of its elements of sources of info having size 1. Now in the underneath code scrap, we are utilizing the crushing capacity of PyTorch. As it very well may be seen, the tensor whose sources of info are having the component of size 1 is dropped. PyTorch unsqueeze work is utilized to create another tensor as yield by adding another element of size one at the ideal position.
- For example, here we take a tensor of 2x2x2 and use PyTorch level capacity to get a tensor of a solitary measurement having size 8. In another word we can say that it returns a tensor with every one of the elements of the contribution of size 1 removed, If the tensor has a group measurement of size 1, then, at that point, squeeze (input) will likewise eliminate the cluster measurement, which can prompt unforeseen errors, dim (int, optional) – whenever given, the info will be crushed distinctly in this dimension. The returned tensor offers the limit with the data tensor, so changing the dimension of one tensor is an application for another tensor.
- When faint is given, a press activity is done uniquely in the given measurement. Whenever the input is of shape: (X × 1 × Y) (X \times 1 \ time Y) (X×1×Y), squeeze (input, 0) leaves the tensor unaltered, however, squeeze (input, 1) will press the tensor to the shape (X × Y) (X \times Y) (X×Y).
PyTorch Squeeze Function Code
Given below is the squeeze function code:
torch.squeeze() eliminates each of the 1-dimensional parts from a tensor, view and permute are slightly unique. View changes the request for the tensors while permute just changes the axis, we will carry out the absolute most usually utilized tensor activities and after having utilized PyTorch for a long time now, we view it as the best profound learning system out there.
Code:
import torch
A= torch.zeros(1,3,1,2,1)
print(A)
print('Tensor Dimension:', A.size())Explanation:
- In the above code, we created a tensor by using Pytorch zero function with having size 1 as shown.
- The final output of the above code we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Output:
Now we need to use the squeeze() function as follows.
Code:
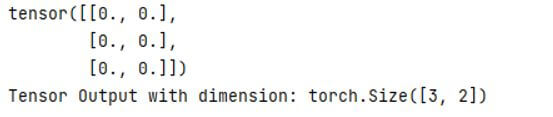
B = torch.squeeze(A)
print(B)
print('Tensor Output with dimension:', y.size())Explanation:
- In the above code, we use the squeeze() function to remove all tensor dimensions of those sizes having 1.
- The final output of the above code we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Output:
PyTorch Parameters Squeeze
Given below are the different parameters we need to use in squeeze() function as follows:
Syntax:
torch.squeeze(specified input, specified dimension = None(optional), output=None )Explanation:
Basically, there are two parameters we need to consider in the squeeze function as shown in the above syntax.
- Specified input: Specified input means the actual tensor value that we provide as tensor input as per our requirement.
- Specified dimension: Specified dimension is user-provided dimension and squeeze() function is restricted, basically it is an optional part of squeeze syntax.
- Output: This is the last parameter in the squeeze() function and it is an optional part of the squeeze function. Normally it acts as the output of the tensor.
Examples of PyTorch Squeeze
Different examples are mentioned below:
Example #1
First, we need to create the tensor by using the following code as follows.
Code:
import torch
A= torch.zeros(1,4,1,2,1,5)
print(A)
print("Tensor input Dimension is : ", A.size())Explanation:
- In the above example, we first created a tensor by using the zero function as shown and after that, we try to print the size of the tensor and tensor.
- In the final output of the above program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Output:
Now that we have tensor we can apply the squeeze function as follows.
Code:
import torch
A= torch.zeros(1,4,1,2,1,5)
print(A)
print("Tensor input Dimension is : ", A.size())
Z = torch.squeeze(A)
print(Z)
print('Tensor Output with Dimension is :', Z.size())Explanation:
- In the above code, we added the squeeze() function as shown it removes all dimensions of those input sizes having 1. In this example, we use an already created tensor for implementation.
- In the final output of the above program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Output:
Now let’s see another example of squeeze() function as follows.
Example #2
Code:
import torch
A = torch.zeros(5,1,3,1,2)
print("Input Dimension is:", A.size())
B = torch.squeeze(A)
print("Squeeze of Tensor is:", B.size())
B = torch.squeeze(A,0)
print("Squeeze of Tensor is:", B.size())
B = torch.squeeze(A,1)
print("Squeeze of Tensor is:", B.size())Explanation:
- In the above example first, we need to import the torch package, after that, we created a tensor by using the PyTorch zeros function as shown. Here we first print the actual dimension of the tensor and after that, we apply the squeeze function with different values as shown, that is tensor size with 0 and tensor size with 1 as shown.
- The squeeze removes dimension as per specified requirement. The final output of the above program we illustrated by using the following screenshot as follows.
Output:
Conclusion
From the above article, we have taken in the essential idea of the Pytorch squeeze and we also saw the representation and example of the Pytorch squeeze. From this article, we saw how and when we use the Pytorch squeeze.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PyTorch Squeeze” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.