Updated June 12, 2023
Definition of Python 3 zip
Python 3 zip function takes containers and produces a single iterator object with all of the container’s mapped values. It’s used to map many containers with similar indexes accessed through a single object. The zip function joins iterable contents into a single object. A zip object is returned by zip. This is a tuple iterator that stores all of the values we have supplied as arguments as pairs.
Overview
- In iterable objects, the zip function returns a tuple iterator. Zip provides an empty iterator when no parameters are given.
- 3 zip produces tuples of an iterator with only one element per tuple if only a single iterable is given. The iterator comes to a halt when the shortest iterable has been exhausted.
- Zip provides tuples from iterables that are given, each tuple containing elements from all of the iterables.
How to Use Python 3 zip?
- Zip (*iterables) is the definition of a zip function. Iterables are sent in as arguments, and an iterator is returned.
- This iterator creates a succession of tuples from each iterable’s element. Any type of iterable can be passed to zip, including files.
1) The zip function combines elements from multiple data sources into a single one. The zip method takes an iterable as an input, such as a dictionary. The function will return a list of tuples containing elements. To unzip the list, use the * operator in conjunction with zip.
2) If the lengths of the supplied iterators differ, the new iterator’s length is determined by the iterator of the fewest items.
3) The zip() function returns a zip object, which is a tuple iterator in which the item will pass together, then the second item in each passed iterator is paired together, and so on.
Follow the below example,
Code:
py_zip1 = ("ABC", "PQR", "XYZ")
py_zip2 = ("BCD", "QRS", "ZXY")
py_zip3 = zip (py_zip1, py_zip2)
print (tuple (py_zip3))Output:
Python 3 zip Function
- The zip method takes sequences to and creates a tuple from the items in the sequences. It comes to a halt after the shortest sequence has been exhausted.
- When working with a big amount of data, zip in Python 2 delivers an actual list, which is inefficient. As a result, zip function will return iterable in Python 3, which provides the output on demand.
- The zip function in the following example will return the iterable tuples from the specified list are as follows.
Code:
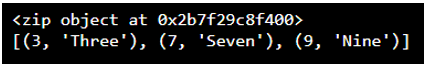
py_num = [3, 7, 9]
py_str = ['Three', 'Seven', 'Nine']
py_res = zip (py_num, py_str)
print (py_res)
print (list(py_res))Output:
Object of zip converted to a tuple list. Both list parameters will contain corresponding members in each tuple. The below example shows how zip object is converted into zip are as follows.
Code:
py_num = ['Three', 'Seven', 'Nine']
num = ['One', 'Three', 'Five']
py_zip = zip (py_num, num)
py_list = list(py_zip)
print (py_list)Output:
Unzip objects into independent tuples is not supported by Python. The zip function is used to unzip files when it is combined with the * operator. The below example shows how to unpack the object by using the zip function are as follows.
Code:
py_num = [3, 2, 7, 9, 4, 1, 6]
py_numworld = ['Three', 'two', 'seven', 'nine’, ‘four', 'one', 'six']
py_zip = zip(digits, words)
p,q = zip (*py_zip)
print (p)
print (q)Output:
The iterator function will collect characters until the shortest string has no more characters. Use the zip longest function defined in the itertools module if we wish to include mismatched zipped characters from the strings object.
Python 3 zip Parameters
Below is the parameter available as follows. We are using only one parameter. We are using multiple iterator values in a single line. We are joining the iterator object together.
Syntax:
Zip (iterator1, iterator2, ……)Iterator –
- Python is full of iterators. They’re beautifully implemented within loops, comprehensions, generators, and other components, but they’re concealed from view.
- Iterables are the most common built-in containers, such as list, tuple, string, and so on. Two specific methods, __iter__() and __next__(), are referred to as the iterator protocol.
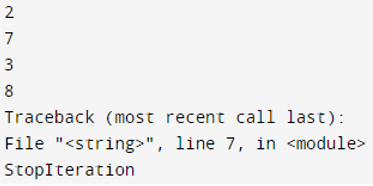
The below example shows how to use an iterator.
Code:
py_list = [2, 7, 3, 8]
py_iter = iter(py_list)
print (next(py_iter))
print (next(py_iter))
print (py_iter.__next__())
print (py_iter.__next__())
next (py_iter)Output:
Examples
Below is the example as follows.
1. Python 3 zip with two list
Code:
stud_name = [ "ABC", "PQR", "XYZ", ]
stud_rno = [ 14, 11, 13 ]
py_zip = zip(stud_name, stud_rno)
print(set(py_zip))Output:
2. Python 3 zip with enumerate
Code:
stud_name = [ "ABC", "PQR", "XYZ", ]
stud_rno = [ 14, 11, 13 ]
for p, (stud_name, stud_rno) in enumerate(zip(stud_name, stud_rno)):
print(p, stud_name, stud_rno)Output:
3. Python 3 zip dictionary
Code:
stud_name = [ "ABC", "PQR", "XYZ", ]
stud_rno = [ 14, 11, 13 ]
py_dict = {stud_name: stud_rno for stud_name,
stud_rno in zip(stud_name, stud_rno)}
print (py_dict)Output:
4. Python 3 zip practical applications
Code:
stud_name = [ "ABC", "PQR", "XYZ", ]
stud_rno = [ 14, 11, 13 ]
for sname, srno in zip(stud_name, stud_rno):
print("stud_name : %s Score : %d" % (sname, srno))Output:
Conclusion
Python includes a variety of built-in routines for looping through data. Zip is one of these routines. Zip (*iterables) is the definition of a zip function. Iterables are sent in as arguments, and an iterator is returned. This iterator creates a succession of tuples from each iterable’s element.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Python 3 zip. Here we discuss the definition, overview, How to use python 3 zip?, and Examples with code implementation. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –