Difference between Private key and Public key
We must first know what a key is before we get to know the difference between public and private key. A cryptographical key is a component that converts plain text into a code type (ciphertext) or the other way around with a cryptographic algorithm. It is this private key that enables secure communication. The cryptographic key is the core component of any cryptographic operation. Some systems involve encryption and decryption pairs of activities. A key aspect of this type of operation involves providing variable data as input to a cryptographic algorithm. The protection of the scheme in a properly specified cryptographic framework depends on the protection of the key.
What is the private Key?
In symmetric key cryptography, the sender and recipient of authenticated confidential information share the private key, which they use for both encrypting and decrypting data. Its encryption is quicker than the method of public-key encryption.
A private key, generated and retained in secret by an individual or organization, serves for decryption and digital signature generation in asymmetric encryption systems. Confidentiality of the private key is essential, and only the owner should be aware of it.
What is Public Key?
Using the public key to encrypt and decrypt the data with a private key. The sender and receiver exchange the encrypted confidential information using the private key. Asymmetric cryptography is often referred to as public key cryptography.
A public key is derived from a private key and is meant to be shared with others. It is publicly distributed and can be freely shared with anyone. The public key is used for encryption and verification of digital signatures. While it is computationally easy to generate a public key from a private key, it is virtually impossible to derive the private key from a given public key.
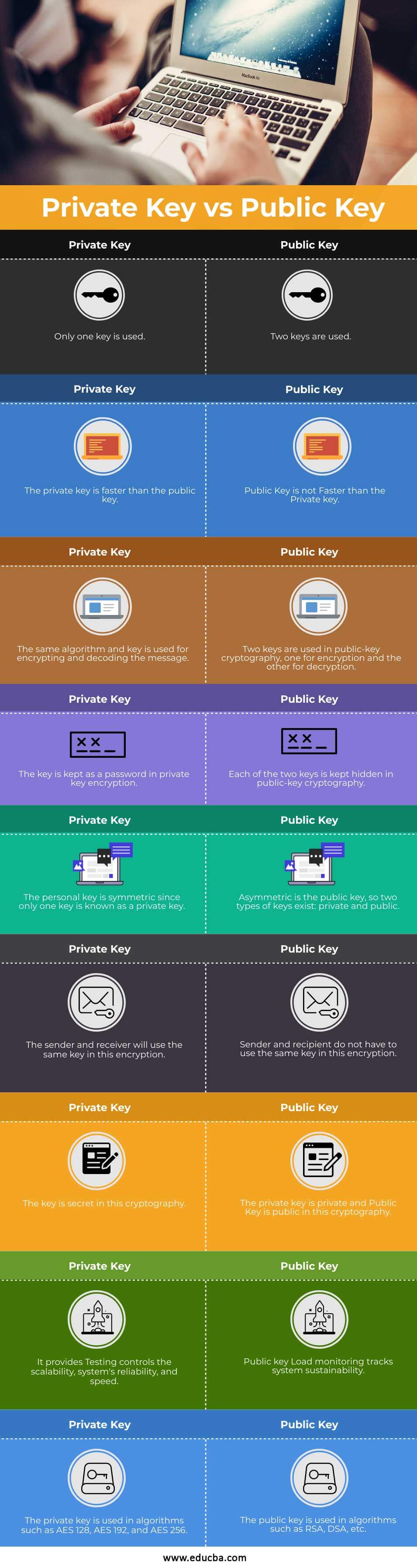
Private Key and Public Key – Infographics
Below is the Infographics of Private Key and Public Key
Key Differences Between
Here are the key differences between private keys and public keys:
- To use public-key cryptography, one key encrypts a simple text message and transforms it to ciphertext, while the recipient employs the decryption key to read the original message. In short, the biggest difference between a private to a public key is that one encrypts and the other decrypts.
- Asymmetric encryption uses a lock with an encryption algorithm to convert a message into an unreadable format and a separate lock with a decryption algorithm to convert the received message back to its original form.
- The public key is distributed widely, while the private key is kept secret.
- Scalability, the system’s reliability, and speed are the main features of a private key, whereas Public key Load monitoring tracks system sustainability.
- Compared to public keys, private keys are usually longer in size.
- You can change or revoke private keys by generating a new one. Once generated, public keys cannot undergo changes or revocations.
- Private keys should never be shared or distributed. Public keys, on the other hand, can be freely shared or distributed.
- AES 128, AES 192, and AES 256 use private keys in their algorithms, while RSA, DSA, and others use public keys.
Comparison Table
Here’s a comparison table highlighted between private keys and public keys:
| Section | Private Key | Public Key |
| Usage | Used by the owner to digitally sign transactions or messages. | Used by anyone to encrypt messages for the owner or verify their digital signatures. |
| Faster | It is faster than the public key. | It is not Faster than the Private key. |
| Encryption | Symmetric key cryptography uses the same algorithm and key for both encrypting and decrypting the message. | Public-key cryptography uses two keys, one for encryption and the other for decryption. |
| Key | Private key encryption stores the key as a password. | Public-key cryptography hides both of the keys. |
| Personal | The personal key is symmetric since only one key is known as a private key. | Asymmetric is the public key, so two types of keys exist: private vs public. |
| Encryption | The sender and receiver will use the same key in this encryption. | The sender and recipient do not have to use the same key in this encryption. |
| Cryptography | The key is secret in this cryptography. | The private key is private, and the Public Key is public in this cryptography. |
| System | It provides Testing controls for scalability, system reliability, and speed. | Public key Load monitoring tracks system sustainability. |
| Algorithms | Algorithms like AES 128, AES 192, and AES 256 use the private key. | Algorithms like RSA, DSA, and others use the public key. |
| Purpose | Used for creating digital signatures and decrypting encrypted data. | Used for encrypting data and verifying digital signatures. |
| Secrecy | You must keep them secret and never share them with anyone. | Can be freely shared with others. |
| Generation | Created by a user during the generation of a cryptographic key pair. | Derived from the private key during the generation of a cryptographic key pair. |
| Size | Typically longer than public keys. | Typically shorter than private keys. |
| Ownership | Unique to an individual or entity. | Unique to an individual or entity but can be associated with multiple private keys. |
| Identification | Not used for directly identifying an individual or entity. | Can be used for identifying an individual or entity. |
| Distribution | Never shared or distributed. | You can freely share or distribute them. |
| Revocation | You can change or revoke them by generating a new private key. | Cannot change or revoke. |
Conclusion
Digital keys are a vital component, enabling ownership features in many cryptographically secure systems. Storing digital keys separately from the token networks is crucial. Instead, digital token wallets store and generate keys independently of the network. These keys form pairs, with one being a public key and the other being a private key, as discussed above. You can think of it like an individual’s bank account, where the private key serves as the bank’s hidden PIN. So in this article, we have seen what the public and private keys are and the differences between them.
FAQs
Q1. What Are Digital Signatures, and How Do They Relate to Keys?
Answers: In asymmetric cryptography, digital signatures verify the authenticity and integrity of a message or document. The sender creates them using their private key, and they can be verified using the sender’s public key.
Q2. What Happens If I Lose My Private Key?
Answers: Losing your private key can be catastrophic. It can result in data loss, inability to access encrypted information, and a need to re-establish secure communication channels with new keys.
Q3. How Often Should I Rotate My Keys?
Answers: Key rotation frequency depends on your security policy, but it’s generally a good practice to rotate keys periodically to minimize the impact of key compromise. The specific timeframe varies depending on the level of security required.
Q4. Can I Share My Private Key with Others?
Answers: No, you should never share your private key with anyone. It should be kept confidential and known only to you.
Q5. How are Public Keys Shared Securely?
Answers: You can freely share public keys because they serve the purpose of encryption, not decryption. People often include them in digital certificates, share them on websites, or exchange them during secure communication protocols.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Private Key and Public Key. Here we discuss the Key differences with infographics and a comparison table. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –