Price Elasticity Formula (Table of Contents)
- Price Elasticity Formula
- Examples of Price Elasticity Formula (With Excel Template)
- Price Elasticity Formula Calculator
Price Elasticity Formula
Price elasticity of demand can be regarded as a reflection of the customer or the consumer behavior because of a change in the price; on the other hand, the price elasticity of supply will measure the producer’s behavior.
Both metrics feed into the other. Each of them is important while analyzing marketplace economics. Still, at the end of the day, most entities or companies will look to the price elasticity of demand while establishing their sales strategy. Price elasticity is an important element to building the most profitable online businesses.
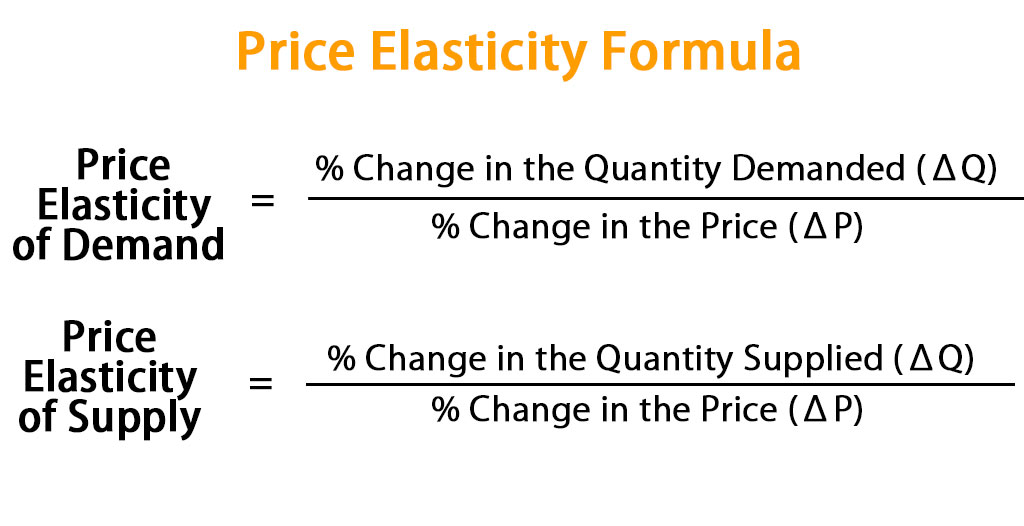
So, to calculate the price elasticity of demand, the following formula can be used.
Examples of Price Elasticity Formula (With Excel Template)
Let’s take an example to understand the calculation of the Price Elasticity formula in a better manner.
Price Elasticity Formula – Example #1
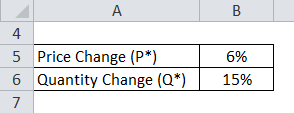
Let’s take a simple example to understand the same. Suppose the price of oranges will fall by 6%, say from $3.49 a bushel to $3.29 a bushel. Responding to that, grocery shoppers will increase their oranges purchases by 15%. So what is its price elasticity?
Solution:
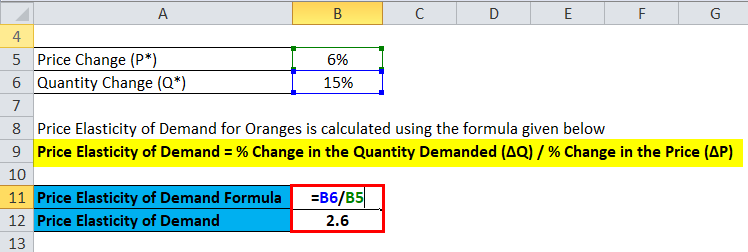
The formula to calculate the Price Elasticity of Demand for Oranges is as below:
Price Elasticity of Demand = % Change in the Quantity Demanded (ΔQ) / % Change in the Price (ΔP)
- Price Elasticity of Demand = 15% / 6%
- Price Elasticity of Demand = 2.6
And hence the elasticity will be 2.6 times, indicating that the oranges are quite elastic in relation to their demand.
Price Elasticity Formula – Example #2
Uber is one of the online platforms or an application to book rides of the consumer’s choice and can ride anywhere from his initial place within the city. Uber has the concept of demand and price, where its price keeps changing based on demand. Specifically, it has one contentious surge pricing feature that will use big troves of data on demand (i.e., by riders) and supply (i.e., of drivers) and regulate the prices in real-time and maintain the equilibrium from each and every moment. But, on the other hand, it also has the concept of surging the prices, ultimately dampening the demand.
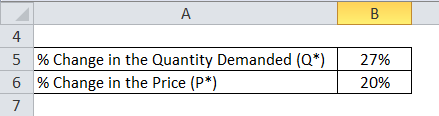
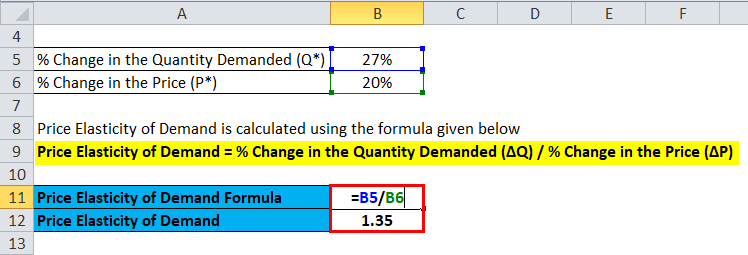
According to data available, when one would go from a nil surge to a 1.2x surge, one would notice a consistently precise drop-in demand of about 27%. So, what is the price elasticity of Uber surge pricing?
Solution:
As one can see, there is a drastic decline in demand when the price surges. So let’s calculate its price elasticity:
Price Elasticity of Demand = % Change in the Quantity Demanded (ΔQ) / % Change in the Price (ΔP)
Price Elasticity of Demand = 27% / 20%
Price Elasticity of Demand = 1.35
Therefore, from the above figure, we can conclude that Uber’s consumers are relatively priced elastic.
Price Elasticity Formula – Example #3
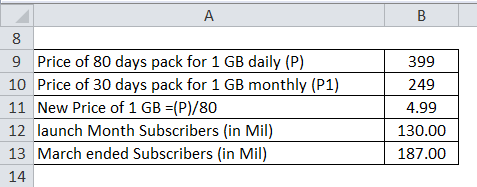
Take another example of the mobile industry in India, says JIO, which launched its network at very cheap data rates; where it provided a plan of 399 where consumers will get 1 GB of data daily until 80 days period and along with free calling and roaming whereas the market was offering 1 GB of data at a price of 249 for 1 GB which only lasted a month. Reliance Jio launched its mobile services commercially in early September 5, 2016. The service provider crossed the 130 million mark in 1 year of its operations. Further, at the end of March 2018, Jio (RIL) reported a subscriber base of 187 million which means the company or the firm added close to 9 million users in the months of April, May, and June.
Solution:
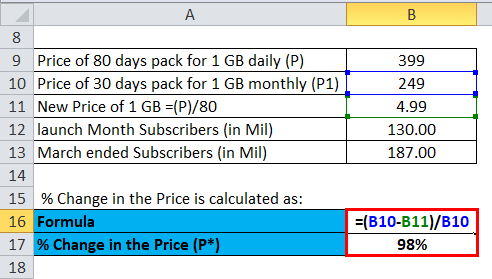
% Change in the Price (ΔP) is calculated as:
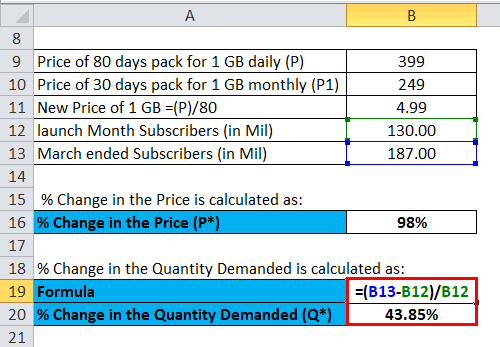
% Change in the Quantity Demanded (ΔQ) is calculated as:
Price Elasticity of Demand = % Change in the Quantity Demanded (ΔQ) / % Change in the Price (ΔP)
Price Elasticity of Demand = 43.85% / 98%
Price Elasticity of Demand = 0.45
Explanation of the Price Elasticity Formula
The law of demand states that as the price of the commodity or the product increases, the demand for that product or the commodity will eventually decrease, all conditions being equal. Consequently, as the price of a product or commodity decreases, the demand for that product or commodity increases as well. Therefore, the law of demand defines an inverse relationship between the quantity factors of a product and the price, which is what the elasticity of the formula tries to say. The first part brings the change in quantity, and the second is the price change.
On the other hand, the law of supply states that an increase in the price of the product will cause an increase in the quantity supplied, all factors being constant. The supplied quantity will move in a similar direction to the price. Production units or the company will invest more in production and supply more products for sale at an increased price to generate a higher product. Therefore, the law of supply will define a direct relationship between the quantity and the price. That was the second formula that tried to say changes in quantity supplied by changes in price.
Relevance and Uses
The product or the commodity would be considered highly elastic if it has a score higher than 1, meaning that the change greatly influences the demand in price.
A score between 0 to 1 can be considered inelastic since the variation or the price change has only a small impact on the product’s demand. A product or commodity with an elasticity of 0 would be considered perfectly inelastic, as the price change will not impact demand. Many bare necessities or household items have very low-price elasticity of demand, as people need them regardless of price. E.g., Gasoline. Luxury items, such as airline tickets and big-screen televisions, generally will have higher price elasticity because they are not essential in routine life.
Price Elasticity Formula Calculator
You can use the following Price Elasticity Calculator.
| % Change in Quantity Demanded | |
| % Change in Price | |
| Price Elasticity of Demand | |
| Price Elasticity of Demand = |
|
|
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to the Price Elasticity formula. Here we discuss How to Calculate Price Elasticity along with practical examples. We also provide a Price Elasticity Calculator with a downloadable Excel template. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –