Updated June 20, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Get-Content
Get-Content in PowerShell is used to read the content from the file (text files) or the program from the specified location. This cmdlet reads the content of the file one at a time and returns it as a collection of objects. From PowerShell 3.0 onwards, you can get the specified number of lines from the beginning or the end of the item.
Syntax:
Get-Content
[-ReadCount <Int64>]
[-TotalCount <Int64>]
[-Tail <Int32>]
[-Path] <String[]>
[-LiteralPath] <String[]>
[-Filter <String>]
[-Include <String[]>]
[-Exclude <String[]>]
[-Force]
[-Credential <PSCredential>]
[-Delimiter <String>]
[-Wait]
[-Raw]
[-Encoding <Encoding>]
[-AsByteStream]
[-Stream <String>]
[<CommonParameters>]
Parameters:
- Path: Path of the file to be read. You can provide one or more paths of the files but not the directories. Wildcard characters are permitted.
- Read Count: Specifies the number of lines of the content sent through the pipeline at a time. The Default value is 1 means it sends one line at a time. If you set the value to 0, it sends the whole content simultaneously. This parameter doesn’t change the content it displays but affects the time it displays. The more the read count value is, the more time it will take to reach the first line, but overall operation time decreases.
- TotalCount: Specifies the total number of lines to display from the beginning. If you set the value to 10, it will display only 10 lines. The default value is -1, which means all the lines will be displayed. Its aliases are Head and First.
- Tail: Specifies the total number of lines to display from the end of the file. Its alias is Last.
- Include: Include parameter is a path qualifier that includes all the items from that path. Wildcard character (*) is permitted. When you use the –Include parameter, you must provide the item’s content. For example, D:\temp\* where (*) specifies the contents of the directory.
- Exclude: Exclude parameter is a path qualifier that excludes all the items specified from that path. Wildcard character (*) is permitted. When using the –Exclude parameter, you must provide the item’s content. For example, D:\Temp\* where (*) specifies the contents of the directory.
- Filter: The filter parameter is more efficient than include or exclude. It is also a path qualifier; you can use the wildcard character (*) for this parameter.
- Force: The function retrieves the contents from the file, and security permissions are the only settings that can restrict it. Force parameter overrides the file’s read-only attribute or creates a directory to complete a file path.
- Credential: When the file is located on a different domain or in Workgroup, you can use the credentials of the file of that location to retrieve its contents.
- Delimiter: While retrieving the contents from the file, it uses a delimiter character to split the files into string objects. The default delimiter is (\n), the end of the line character.
- Wait: When the wait parameter is specified, the Powershell console keeps the file open and waits until manually interrupted by entering CTRL + C or deleting the file. In the second case, there will be a non-terminating error. The wait cannot be combined with Raw Parameter.
- Raw: Returns the multiple lines as a single string but preserves the new lines in the output.
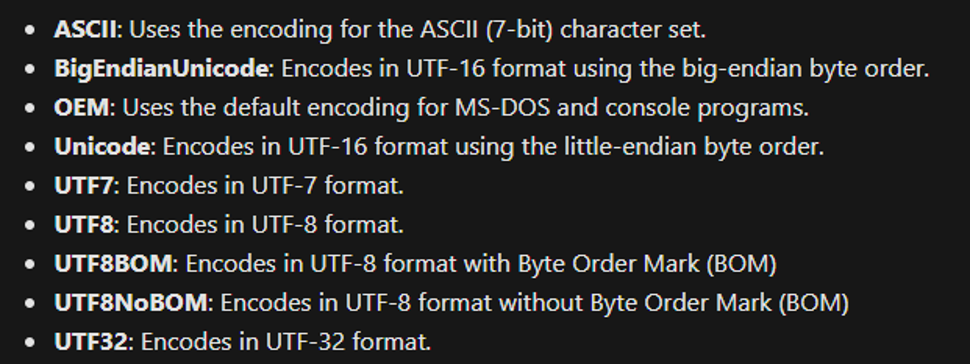
- Encoding: Specifies the type of encoding for the target file. Accepted encoding values.
- AsByteStream: This parameter was introduced in PowerShell 6.0 and specified if the contents should be read as a byte of the stream.
- Stream: We need to establish the stream using this parameter. Once you create a different stream, you can retrieve file changes according to the stream.
- LiteralPath: This parameter specifies the path of one or more locations. Unlike the -path parameter, you cannot specify wildcard characters here because this parameter can’t interpret characters as wildcards. If your path includes any escape characters, mark them under a single quote, and PowerShell will consider it a single path.
- CommonParameters: Below common parameters are used, also called advance function parameters.
Verbose, Debug, ErrorAction, ErrorVariable, WarningAction, WarningAction, WarningVariable, OutBuffer, PipelineVariable, and OutVariable.
Examples of PowerShell Get-Content
The examples of the PowerShell Get-Content are given below:
Example #1
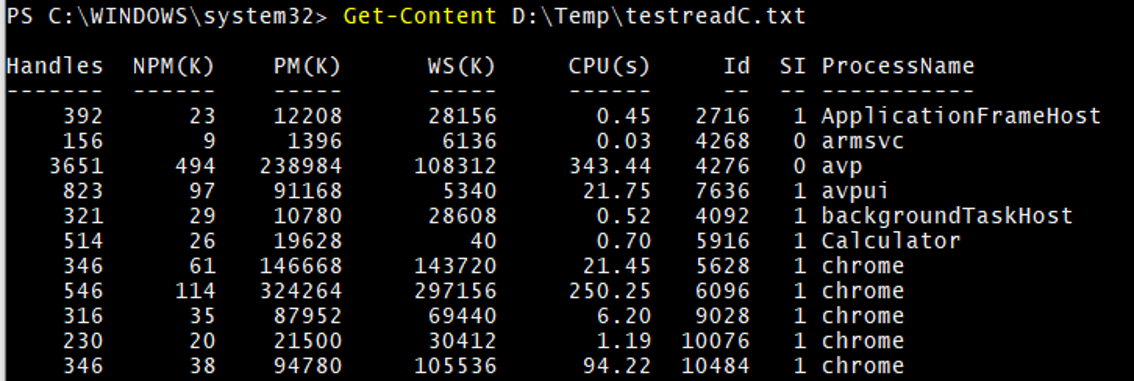
Read the file through Get-Content.
In the testreadC.txt file, we have stored processes.
Get-Content -Path D:\Temp\testreadC.txt
Output:
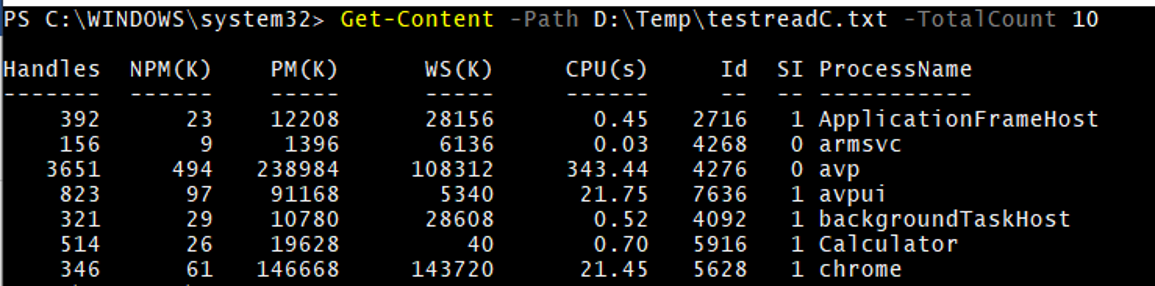
Example #2
GC with TotalCount
Get-Content -Path D:\Temp\testreadC.txt -TotalCount 10
A total of 10 lines will be displayed from the beginning.
Output:
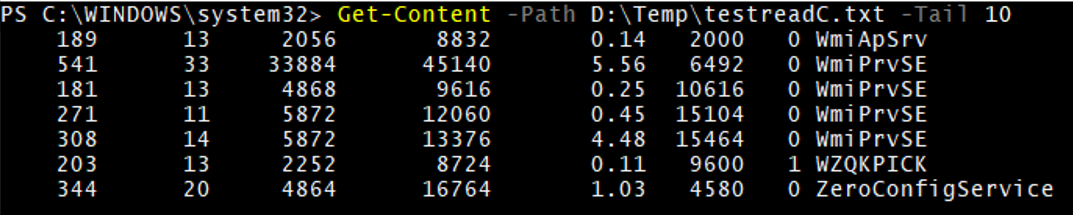
Example #3
GC with Tail
Get-Content -Path D:\Temp\testreadC.txt -Tail 10
A total of 10 lines will be displayed from the bottom.
Output:
Example #4
GC with ReadCount
Get-Content -Path D:\Temp\testreadC.txt -ReadCount 10 | Set-Content D:\Temp\ReadC.txt
The above example will send 10 lines at a time to a new file ReadC.txt.
Example #5
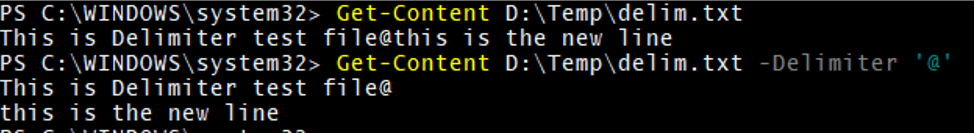
GC with Delimiter
Get-Content D:\Temp\delim.txt -Delimiter '@'
The above command will split the file content with the ‘@’ character and start a new line afterward.
For example,
Example #6
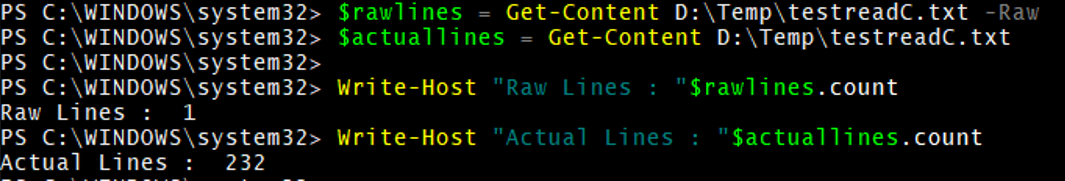
GC with Raw
Get-Content D:\Temp\testreadC.txt -Raw
The above command will store the entire file content into a single string instead of an array. We can check the line count as below.
Output:
Example # 7
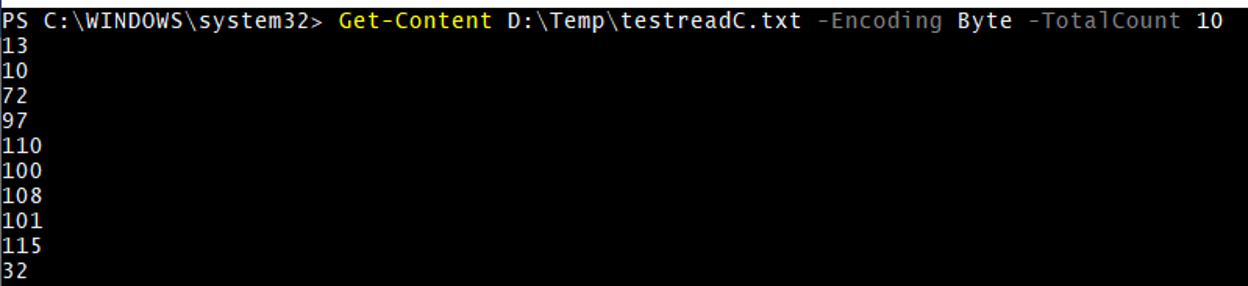
GC with Encoding
Get-Content D:\Temp\testreadC.txt -Encoding Byte -TotalCount 10
Selecting the encoding as “Byte” ensures the data will be in byte format. You can select another formatting as mentioned above in the parameter explanation.
Output:
Example #8
GC with Stream
Get-Content D:\Temp\stream1.txt -Stream $stream1
The above command will keep the existing content in stream1. Recognizing new content added with the new stream in the same file is easy.
Set-Content D:\Temp\stream1.txt -Value "This is the new line" -
Stream $stream2
Get-Content D:\Temp\stream1.txt -Stream $stream2
Output:
Example #9
GC with Filter / Include / Exclude parameter.
Get-Content D:\Temp\* -Filter Testread*
The above command will read all the files that start with “TestRead” in the file name.
Get-Content D:\Temp\* -Include *read*
The command mentioned above will read all files containing “Read” in the file name.
Get-Content D:\Temp\* -Exclude Test*
The above command will exclude all the files starting with “Test” in the file name and read content from other files on the same path.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Get-Content. Here we discuss the introduction, Parameters for the given Syntax, and Examples of PowerShell Get-Content. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more–