Updated May 19, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL TRUNCATE TABLE
PostgreSQL truncate table is used to remove all data from the table, basically, we have used a delete statement to delete data from the table, but for a large table, we have used the truncate command to delete whole data from a table. Truncate command is delete the whole record from the table also, it is faster than the delete command, the delete command deletes single as well as whole data from the table, but truncate is remove all records from the table. Truncate is not used to remove a single record from the table.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of the truncate table statement:
Truncate single table:
Truncate table table_name (Table name which we have used with truncate command);Reset sequences connected to the table column and truncate a single table:
Truncate table table_name (Table name which we have used with truncate command) Restart identity;Truncate multiple tables in angle command:
Truncate table table_name1, table_name2, table_name3, …, table_nameN (Table name which we have used with truncate command);Remove all data from a table using foreign key references:
Truncate table table_name (Table name which we have used with truncate command) CASCADE;Truncate the table by using all parameter:
Truncate table table_name (Table name which we have used to remove all records) [Restart identity or continue identity] [Cascade or Restrict]Parameter
Below is the parameter description syntax of the truncate table statement:
Truncate: This statement in PostgreSQL is used to remove all records from the table.
Table name: The table name is the specified name of the table from which we have removed all rows using the truncate command. We can use a single table as well as multiple tables to remove data from the table.
Restart identity: When using the truncate table command, we can include the restart identity parameter to reset the sequence values associated with the table columns. By utilizing this parameter, we can automatically reset the sequences of columns in the table used in the truncate command.
Continue identity: The continue identity parameter is specified in the truncate command to indicate that it does not alter the sequence value owned by the table column. It is the default value of the table.
Cascade: To truncate all tables with foreign key references on another table, we specify the action of truncating. Additionally, we drop all group tables that were added due to cascade.
Restrict: We utilize the “restrict” option when we want to prevent the deletion of tables that have foreign key references.
How does TRUNCATE TABLE work in PostgreSQL?
Below is the working of the truncate table statement in PostgreSQL.
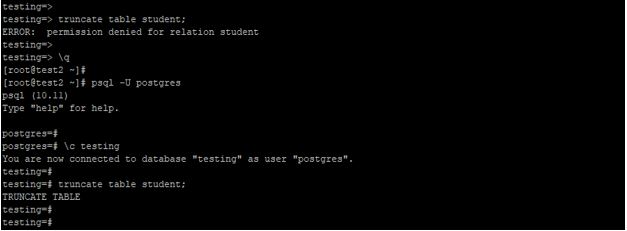
To truncate the table, we need to have privileges of the truncate table of the user. If we do not have the truncate table’s privileges, then we can’t truncate the table. If we do not have the truncate table’s permission, it will issue an error of “ERROR: permission denied for relation relation_name”.
The below example shows that we need the privilege of a truncate table to truncate the table in PostgreSQL.
Code:
truncate table student;
psql -U postgres
\c testing
truncate table student;Output:
Explanation: In the above example, tran_test users have no permission to truncate the table, so it will issue an error and doesn’t truncate the table. But user Postgres have sufficient privilege of the truncate table, using Postgres user, we have truncated the table name as a student. Truncate statement in PostgreSQL will acquire access exclusive lock on the table on which we perform truncate operations. Basically, we have not used a truncate table statement on the table which contained the foreign key references from the other tables because it will truncate all tables which have foreign key references. Truncate table statement is not used with on delete triggers in PostgreSQL, but we have used truncate triggers. The truncate table statement is not safe with the MVCC architecture. When a table is truncated, it deletes all records within it, causing concurrent transactions to perceive it as empty.
The truncate table statement is transaction safe in PostgreSQL. Truncate table rollback the statement if we have not used the commit statement after the truncate table command. Truncate table statement is performed the same operations as delete statements without a where clause. If we have used the where clause delete statement will delete the specified row. Truncate table is faster to delete all records from the table. We can truncate single as well as multiple tables in a single command. Basically, a truncate table does not scan the record to truncate the table, it will delete all rows from a table without scanning. Truncate table statement is to reclaim the storage from the table, we do not need to perform a vacuum on the truncated table.
Examples to Implement PostgreSQL TRUNCATE TABLE
Below is the example mentioned:
1. Truncate single table
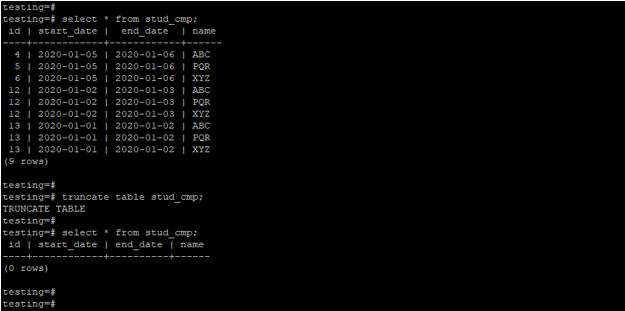
The below example shows a truncate single table in PostgreSQL. We have a truncated stud_cmp table.
Code:
select * from stud_cmp;
truncate table stud_cmp;
select * from stud_cmp;Output:
2. Truncate multiple tables
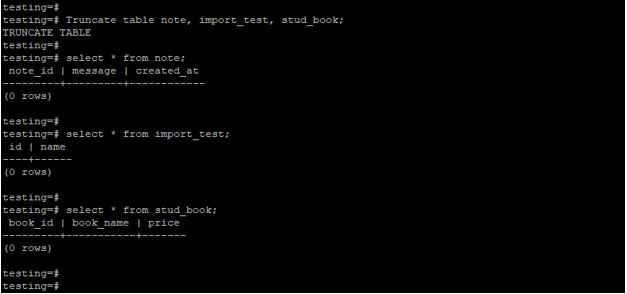
The below example shows the truncate multiple tables in PostgreSQL. We have a truncated note, import_testand stud_book table.
Code:
Truncate table note, import_test, stud_book;
select * from note;
select * from import_test;
select * from stud_book;Output:
3. Truncate a single table using the restart identity
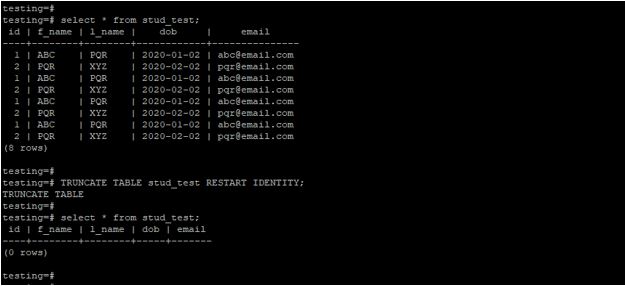
The below example shows a truncate single table using restart identity in PostgreSQL. We have a truncated stud_test table.
Code:
select * from stud_test;
TRUNCATE TABLE stud_test RESTART IDENTITY;
select * from stud_test;Output:
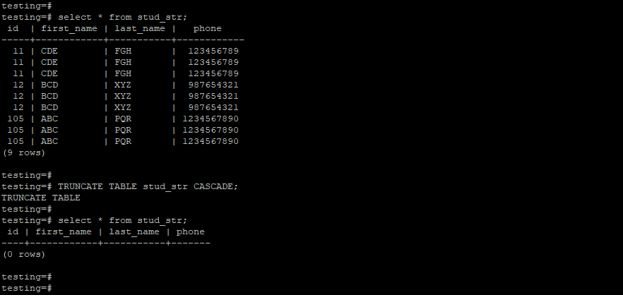
4. Truncate a single table using a cascade
The below example shows a truncate single table using cascade in PostgreSQL. We have a truncated stud_str table.
Code:
select * from stud_str;
TRUNCATE TABLE stud_str RESTART IDENTITY;
select * from stud_str;Output:
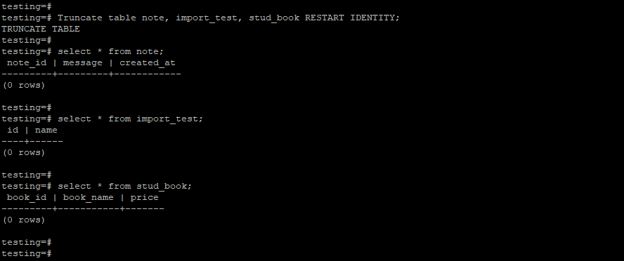
5. Truncate multiple tables using restart identity
The below example shows truncate multiple tables using restart identity in PostgreSQL. We have a truncated note, import_test, and stud_book table.
Code:
Truncate table note, import_test, stud_bookRESTART IDENTITY;
select * from note;
select * from import_test;
select * from stud_book;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL TRUNCATE TABLE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.