Updated August 31, 2023
Table of Contents
- Introduction
- Listing Out Tables in PostgreSQL
- Using psql meta-commands
- Using SELECT query
- Conclusion
Introduction to PostgreSQL List Tables
When working with a database, retrieving information about the tables and their structure is common. This gives us a general idea of the entities stored in the database. When creating a new database, PostgreSQL automatically generates default tables known as system tables. The database uses these tables internally to perform operations and store system variables, operators, and functions. In this PostgreSQL List Tables article, you will learn different methods that you can use to retrieve and list out the tables present in your database.
In addition, the system tables also store data about SQL and strategic parameters that determine how the system executes any operation and considers primary constraints while executing any command. Furthermore, the system tables maintain information about which tables are currently locked for updation if any retrieval query is executed on that table. Besides the system tables, we can create many user-defined tables for our usage.
Listing Out Tables in PostgreSQL
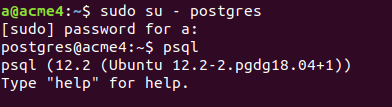
If you are familiar with MySQL before then, you must consider using the SHOW TABLES query to retrieve the list of all the tables in the current database. However, in PostgreSQL, there is no such query. In PostgreSQL, we can retrieve the list of tables by either using the \dt command when you are using psql or retrieving the list of tables using the SELECt query from the pg_tables table of pg_catalog schema. We will see how we can use both of these methods one by one. You must first open the terminal, log in to PostgreSQL with your username and command,
sudo su – postgresand then enter your password. Press enter. Then open the psql shell by typing the command
psqland click on enter. The output will be somewhat like the one below.
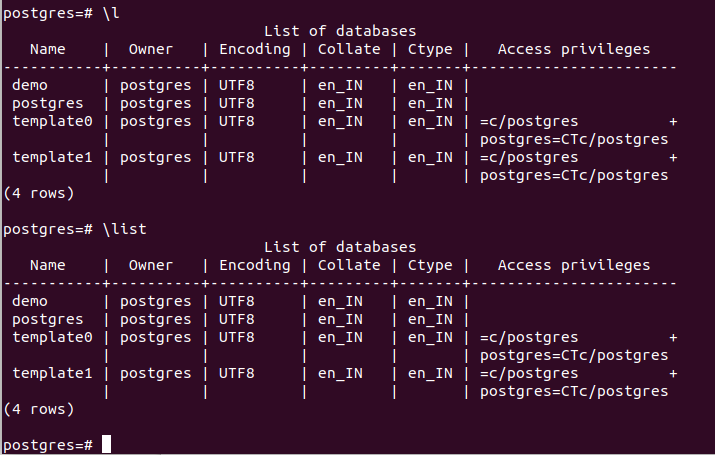
The next step is to check all the databases present in your current database server. You can type
\l or \listthe command to list all databases and schemas for this. It will list all the schemas and databases, and the output will be like this.
The default databases are Postgres, template0, and template1, while I created the demo database previously. You can create a new database using the command createdb and the name. For example, let us create a database named educational_platform. For this, we will fire the following command.
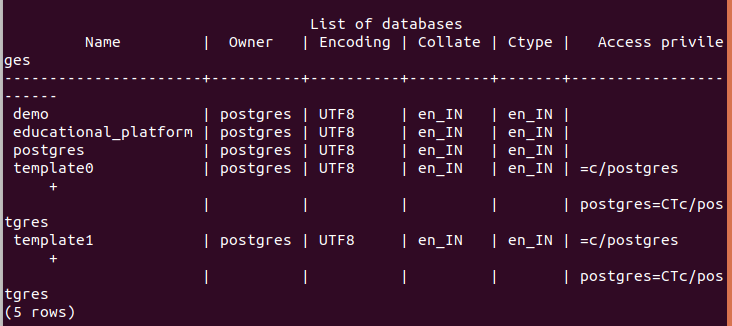
createdb educational_platformLet’s verify if our database has been created by entering the \l command.
\lNow, to switch between databases and use the database of your choice, you can use the command \c or \connect and the name of the database to which you want to connect. Now, fire command
\c educational_platformThe output will be as follows:
Listing Out Tables using psql meta-commands
Now, we will learn how to list the tables using psql metacommands. Metacommands are short commands that are compact and easy for database administrators as the psql evaluates them and converts them to SQL queries if required and stored in system tables. We can use either
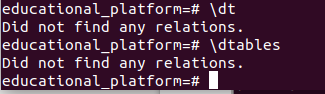
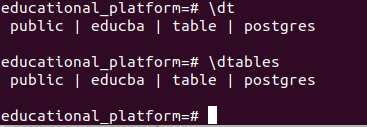
\dt or \dtablesmetacommand to list out the user-created or user-defined tables. The output will be as follows –
Since no tables are present in our newly created database, the system states that it did not find any relations. Let’s create a new table and check if we can retrieve it.
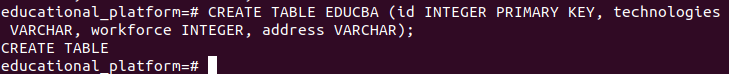
CREATE TABLE educba
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
technologies VARCHAR,
workforce INTEGER,
address VARCHAR);We can check if the table was added by entering the command:
\dt or \dtablesSo we can see now that our table has been added successfully.
Listing Out Tables using SELECT query
Now, we will learn how to use the simple SQL query of SELECT to retrieve information about all the tables in our current database. All table information is stored in the pg_tables table of the pg_catalog schema. When querying a table located in a different database or schema than the one we are currently connected to, we need to explicitly specify the schema name followed by a dot (.) and the table name to retrieve the list of tables. So our query should be like this.
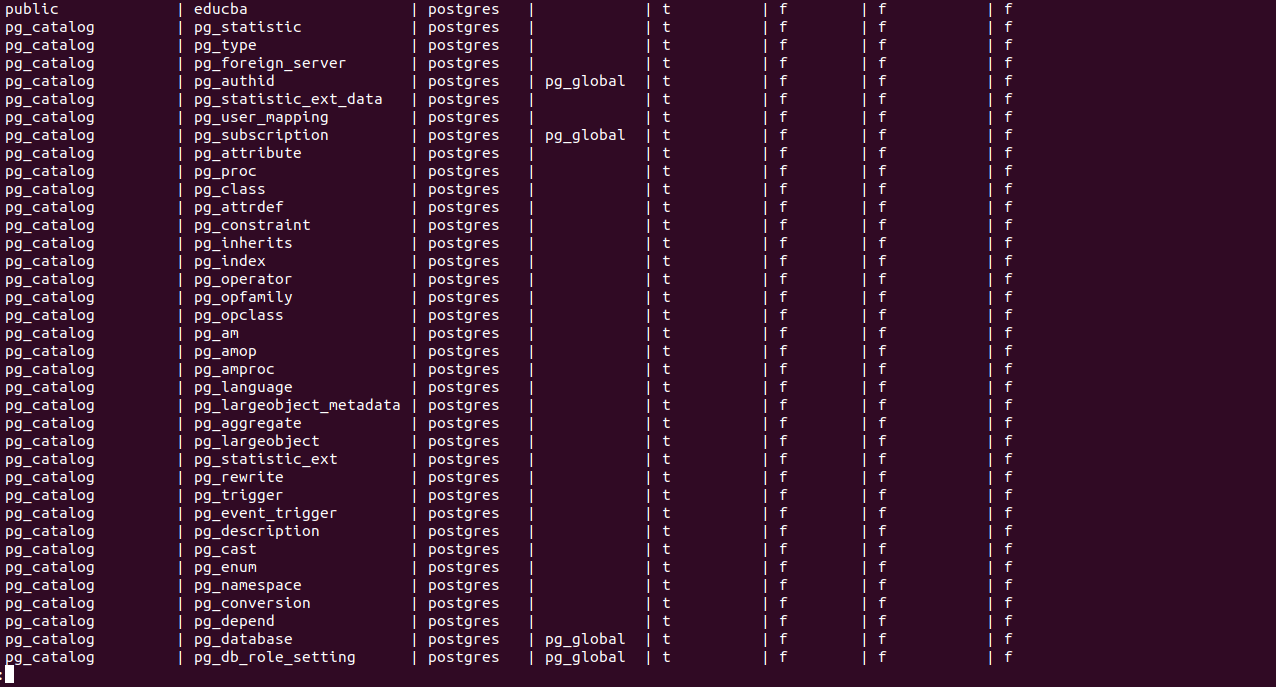
select * from pg_catalog.pg_tables;The above query will produce an output similar to the one shown below.
It will be a long list displaying all the tables that are system tables and user-defined tables. What if we only want to retrieve user-defined tables, not system tables? We must apply the constraint in the WHERE clause specifying that the tables should not belong to pg_catalog or information_schema schemas, as these two schemas only have internal system tables. We should arrange our query in the following manner:
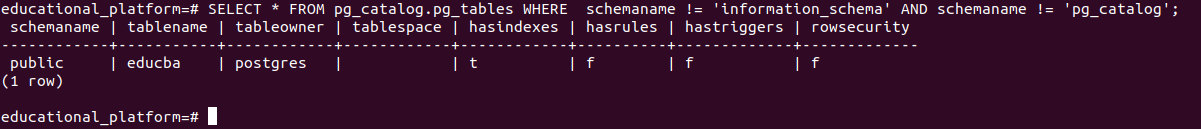
SELECT * FROM pg_catalog.pg_tables
WHERE schemaname != 'information_schema' AND
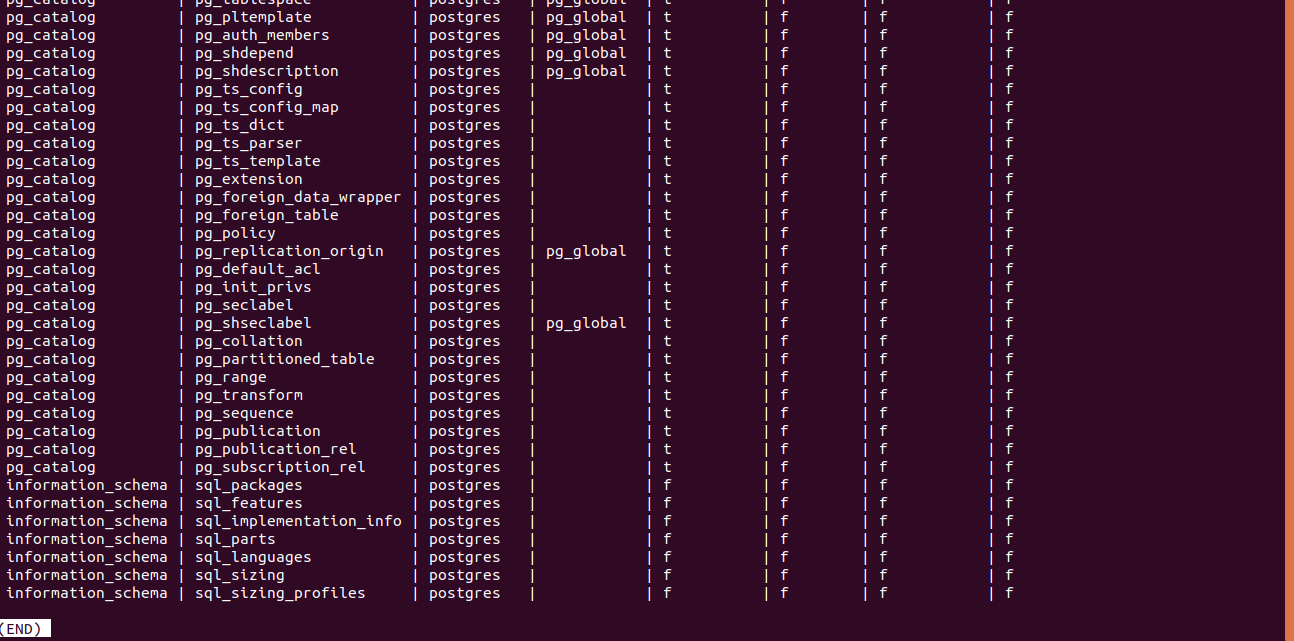
schemaname != 'pg_catalog';The output of the above query will be as shown below.
We can only expect to retrieve the user-defined table “educba,” which we created. The pg_tables table displays the table name and many properties related to the table, which include schemaname, tableowner, tablespace, hasindexes, hasrules, hastriggers, and rowsecurity. Most of the fields’ answers have the values t and f, which are boolean-type parameters specifying whether the table has that property. For example, in our table, the column hastriggers have the value f, which means that the current table educba does not define any triggers. Similar is the case for other columns. Besides this, the columns schemaname and tableowner contain the table that belongs to which schema type and who owns this table.
Conclusion
In PostgreSQL, we can list the tables in two ways: using the psql meta-commands of simple SELECT clause query on the table pg_tables of pg_catalog schema. Both these queries result in the same output. The metacommand returns only user-created tables, while the SELECT query includes system and user-defined tables. We must apply constraints to the SELECT query to list only user-created tables.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL List Tables” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.