Updated May 30, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL TO_CHAR
PostgreSQL provides a set of powerful tools that can help in converting different data types. These can be a date, integer, float, to formatted strings. One of the functions which is widely used for this purpose is the TO_CHAR function. The TO_CHAR function in PostgreSQL is used to convert various data types like date or time, integer, floating-point to formatted strings, and also, they can be used to convert formatted strings to specific data types. They are a part of Data type formatting functions. Let us have a look in detail.
Syntax
The syntax for to_char() is as follows:
to_char(expression, format)Explanation: The to_char() function has two arguments, as mentioned above. Both of these arguments are mandatory. The first argument is expression. You can convert the data to any desired format by specifying an appropriate value for this argument. The available formats are explained below:. The expression can be a decimal, date, or any numeric value that requires conversion to a character.
The second argument is the format. This argument signifies the format which is needed for the resultant string.
Return Value: The To_Char() function’s outcome is a text string. You can use the specified format to format the first argument, which should be a string. Furthermore, it is essential to note that additional formats are available apart from the ones mentioned above. Let us have a look at them as well.
Various Formats
The main conversion which TO_CHAR does is for dates. The format for it can be as below:
TO_CHAR(datetime, format)The format specifiers are as below,
| Oracle TO_CHAR | Format Specifier |
| YYYY | The year which can be used in 4 digit |
| YY | The year which can be used in 4 digit |
| MON | Abbreviation of Months in a three-letter word like Jan, Feb, etc |
| MONTH | Name of the entire month |
| MM | Numerical format for a month, like 1 to 12 |
| DY | Abbreviated day (Sun-Sat) |
| DD | Numerical format for a day like a day from 1 to 31 |
| HH24 | Time in the 24-hour format, which can be 00 to 24 |
| HH or HH12 | Time in the 12-hour format like |
| MI | Minutes which will be displayed between 0 to 59 |
| SS | Seconds which will be displayed between 0 to 59 |
In addition to these, different patterns which can be used are as below:
Y, YYY, or 9,99,999: The year in digits with a comma. This can also be used with numbers. It will return the comma at the mentioned position. Multiple commas can also be given in a given number
Month: The month should be specified in this format: the camel case.
MONTH: The month should be specified in all capital letters
WW: Week number of the year
9 and 0: The numeric values represent the number of digits specified and the leading zeroes, respectively.
D: It will return the specified position of the decimal character.
RN: It signifies the Roman numbers, which can range from 1 to 3999
L: This can be used as a currency symbol.
MI: The minus sign has a specified place for numbers less than 0.
PL: The plus sign has a specified place for numbers that are more than 0.
How does the PostgreSQL TO_CHAR function work?
Let us have a look at how the TO_CHAR() function works.
TO_CHAR(
TIMESTAMP '2017-08-18 22:30:59',
'HH24:MI:SS'
)Here the function converts the timestamp to a character string with the format of the 24-hour clock.
Code:
TO_CHAR(TIMESTAMP '2017-08-18 22:30:59', 'HH24:MI:SS')
TIMESTAMP '2017-08-18 22:30:59'
TO_CHAR()Output: 22:30:59
Explanation: Consider the timestamp, which inputs the date and time. Then, you pass this timestamp to the TO_CHAR() function. This function then converts to the format specified. The format mentioned here is HH24:MI: SS. This indicates the 24-hour clock time format. It converts it to the string format having an output as 22:30:59.
Example to Implement TO_CHAR in PostgreSQL
Below are examples of implementing TO_CHAR in PostgreSQL using various methods:
We now know the to_char() function and how it works. To understand better, let us have a look at some examples.
Example #1
Let us convert a date variable to a string that uses the 24-hour format:
Code:
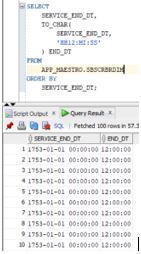
SELECT
SERVICE_END_DT,
TO_CHAR(
SERVICE_END_DT,
'HH12:MI: SS'
) END_DT
FROM
APP_MAESTRO.SBSCRBRDIM
ORDER BY
SERVICE_END_DT;Output:
Explanation: Here, the SERVICE_END_DT is being converted to time. The variable which will be for this converted time is END_DT. Above is the output of the query that we have run. It converts the time from 00:00:00 to 12:00:00 as we have specified the 24-hour format.
Example #2
Let us now convert an entire timestamp value into a different format:
Code:
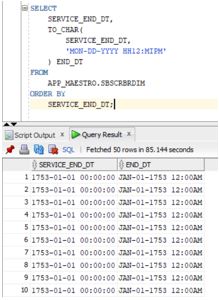
SELECT
SERVICE_END_DT,
TO_CHAR(
SERVICE_END_DT,
'MON-DD-YYYY HH12: MIPM'
) END_DT
FROM
APP_MAESTRO.SBSCRBRDIM
ORDER BY
SERVICE_END_DT;Output:
Explanation: The above code converts the service_end_dt to a completely different format. It takes the Month in three-letter abbreviations, the day in a numbered format, and the year in 4 digit number format. The time is also being taken in the 12-hour format with the specified AM or PM. The output that you see is JAN-01-1753 12:00 AM. It is as per the format we have specified.
Example #3
Let us add a currency symbol to the amount present in the table in this example:
Code:
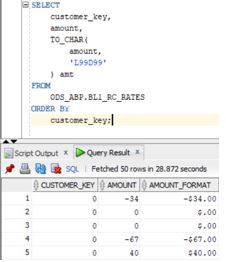
SELECT
customer_key,
amount,
TO_CHAR(
amount,
'L99D99'
) amt
FROM
ODS_ABP.BL1_RC_RATES
ORDER BY
customer_key;Output:
Explanation: The above example is selecting a customer key amount. Then, we convert the amount to the value preceding the $ symbol. If you observe the format in the to_char() function, you will see that it specifies ‘L99D99’. This adds a ‘$’ in front of the amount specified. The output is hence -$34.00. Here we have used ‘L’ and ‘D’, specified in the formats. By using these, we have also added the currency symbol and the digit position.
Conclusion
Like all the functions, the to_char() function is a very helpful formatting string function. It helps in formatting the numerical or date values to characters or strings in the specified format. This ensures that the entire dataset has a consistent format. The different formats and patterns make it easy to use and convert the data to a string and use it or even compare if required.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL TO_CHAR” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.