Updated May 18, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL Sort
The following article provides an outline for PostgreSQL Sort. PostgreSQL provides a sorting function to users. The sorting function plays an important role in database management systems. With the help of the sorting function, we can arrange data as per our requirement, such as ascending or descending Order. We can apply sort functions on single or multiple columns using group by and Order by clause. Before execution of the sort function, we must need a table with records. For the execution purpose of the sort function, we use Order by clause in the select statement to sort table records. We can also implement sort functions with different arithmetic operators.
Syntax:
select column named1, column named2…… column namedN from table name order by column name1, column name2,…………. column nameN;Explanation:
- In the above syntax, we use Order by clause in a select statement where column named1, column named2, and column namedn is used to display the column in the table where table name means specified table name in database and column name1, column name2 and column namen is used to apply for Order by clause.
How Sort Function Works in PostgreSQL?
- We must install PostgreSql in our system.
- Required basic knowledge about PostgreSql.
- We must require tables to perform the Sort function.
- Need basic knowledge about Order by a clause, that means how it is used.
Examples to Implement Sort Function in PostgreSQL
Different ways to implement the sort function are given below:
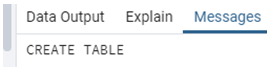
Basically sorting technique, we use Order by clause to sort the record from a database table, so first, we create a table by using the following statement.
create table company (emp_id int primary key not null,
emp_name text not null, emp_age int not null,
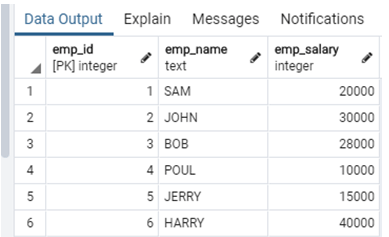
emp_salary int not null);Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
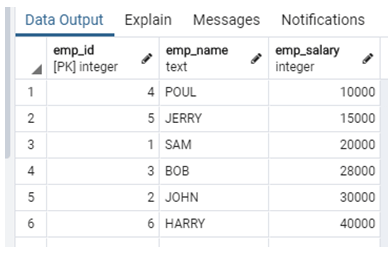
1. Sort by Ascending Order
In this method, we sort records in the database table in ascending Order.
For more details, see the following example.
Example:
Select emp_id, emp_name, emp_salary from company order by
emp_salary asc;Explanation:
- In the above example, suppose we need to sort employee salary in ascending Order, at that time, use the above statement to sort employee salary. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
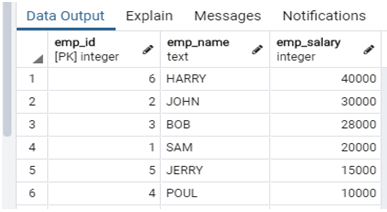
2. Sort by Descending Order
In this method, we sort database table records in descending Order.
For more details, see the following example.
Example:
select emp_id, emp_name, emp_salary from company order by emp_salary desc;Explanation:
- In the above example, suppose we need to sort employee salary in descending Order. At that time, we use the above statement to sort employee salary. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
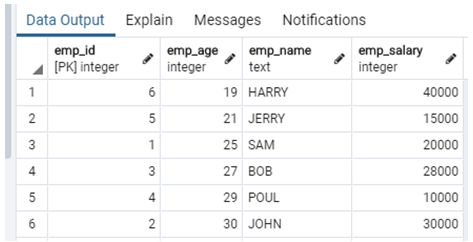
3. Sort by Multiple Column in Ascending Order
In this method, we sort multiple columns in ascending Order by using the following statement.
Example:
select emp_id, emp_age, emp_name, emp_salary from company order by emp_age, emp_salary asc;Explanation:
- In the above example, suppose we need to sort multiple columns in ascending Order, in this example, we sort emp_age and emp_salary in ascending Order by using the above statement. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
4. Sort by Multiple Column in Descending Order
In this method, we sort one or more columns in descending Order of the database table.
For details, see the following example:
Example:
select emp_name, emp_age, emp_salary from company order by emp_id, emp_salary desc;Explanation:
- In the above example, suppose we need to sort emp_id and emp_salary in descending Order by using the above statement. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
5. Sort Column by Using Arithmetic Operators
In this method, we sort columns of the database table by using arithmetic operators on specified columns.
Example:
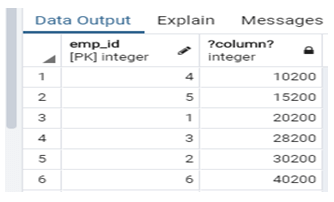
select emp_id, emp_salary+200 from company order by emp_salary+200 asc;Explanation:
- In this example, suppose we need to add Rs. 200 in each employee and need to order in ascending Order at that time, we use the above statement. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
6. Sort by Using Column Alias
In this method, we sort records from the database table using alias.
For more details, see the following example.
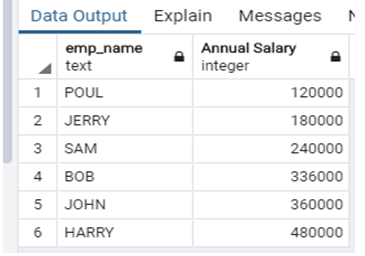
select emp_name, emp_salary*12 "Annual Salary" from company order by "Annual Salary";Explanation:
- In the above example, suppose we need to calculate an employee’s annual salary and arrange them in ascending Order using an alias. By default order of Order by clause is ascending Order. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
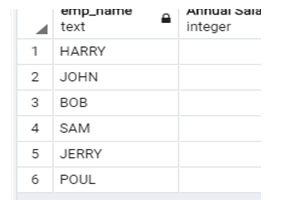
In the same example, we arrange the record of the database table in descending Order by using the following statement.
select emp_name, emp_salary*12 "Annual Salary" from company order by "Annual Salary" desc;Explanation:
- In the above example, we need to arrange employee annual salary by using aliases and need to arrange them in the descending Order. See here we also use an arithmetic operator. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
7. Sort by Using Group by And Order By
In this method, we arrange records by using Group by and Order by clause for details, see the following example.
Example:
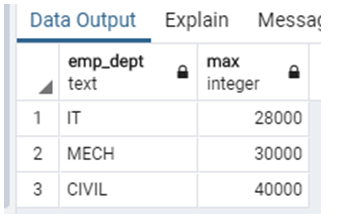
select emp_dept, max(emp_salary) from company group by emp_dept order by max(emp_salary) ;Explanation:
- In the above example, suppose we need to calculate the max salary of an employee in each department by using group by and Order by clause at that time, we use the above statement. In this example max salary of the IT dept is 28000, the max salary of the MECH dept is 30000, and the max salary of the CIVIL dept is 40000. Illustrate the end result of the above declaration by using the use of the following snapshot.
Conclusion
We hope from this article, you have understood the PostgreSQL Sort statement. From the above article, we learn the basic syntax of the sort, such as Order by clause, and we also learn how we can implement the sort function using different methods with the group by clause. From this article, we learn how we can handle sorting tables of databases.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Sort” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.