Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL SUM()
PostgreSQL sum() function returns the distinct value or sum of values; the sum function ignores null values from a table column. It states that the null value from the column will not be considered in the sum function; if we have used a distinct operator using the sum function, then the sum function is only considered the distinct values from the table column on which we have used the Sum function. The sum function in PostgreSQL is very useful and essential to return the sum of all values from the column or the sum of distinct values from the column. We use the sum function to calculate the addition of a numeric column.
Syntax
Below is the syntax of the sum function in PostgreSQL.
1. Sum (Distinct column_name (Name of a column which was used with sum function to get the addition of values.))
OR
2. Select column_name1, column_name2, …, sum (column_name or aggregate expression) from table_name [ where condition ] group by column_name;
OR
3. Select sum (column_name or aggregate expression) from table_name [ where condition]
OR
4. Sum (column_name (Name of the column which was used with sum function to get the addition of values.))
Below is the parameter description syntax of the sum function in PostgreSQL.
1. Sum – This function is used to get the addition of all values from a numeric column in PostgreSQL. We use the sum function in PostgreSQL when adding the numeric table column.
2. Distinct – This keyword is used to get the addition of distinct values for the numeric column in PostgreSQL. It is an optional parameter of the sum function in PostgreSQL.
3. Column name – It is defined as the name of the column on which we have performed a sum operation to get the addition of all values. The column name is a very important parameter in the sum function.
4. Table name – It is defined as the name of the table from which column we have performed the sum operation and get the result of adding all values. We can use a numeric column table name for the sum function in PostgreSQL.
5. Select – This operation retrieves data from the table. We have to retrieve data using the sum function in PostgreSQL. We have used the sum function using select operations.
6. Where condition – We have filtered the result of select operations in PostgreSQL. We have got specific results by selecting conditions using the where clause in PostgreSQL.
7. Group by – We have used group by clause with sum function in PostgreSQL. We have to retrieve results as per group by the condition in PostgreSQL.
How does the SUM() function works in PostgreSQL?
- Below is the working of the sum function in PostgreSQL. We have used the sum function to get the sum of the numeric column in PostgreSQL.
- The sum function will exclude the null values from the column if the column contains the null value, and we have to perform the sum function operation on the same; then, the sum function will exclude the null values from the column.
- After excluding null values, it will provide the result of the sum function. The below example shows that the sum function will exclude the null values from the column.
Command:
Command:
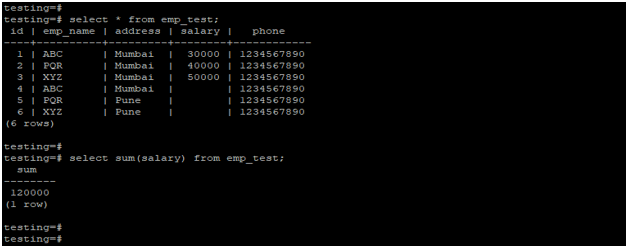
select * from emp_test;
select sum(salary) from emp_test;Output:
- In the above example, we have performed sum function operation on the salary column, after performing sum function operation on the salary column it will return the sum of all values from the salary column.
- When performing a sum operation, it will exclude the null values from the salary column in PostgreSQL.
- Using a distinct clause with a sum function will only get the sum of distinct values in PostgreSQL.
- In the below example, we have used the sum function with a distinct clause; it will only return the sum of the result of the column, which contains only the distinct values.
Command:
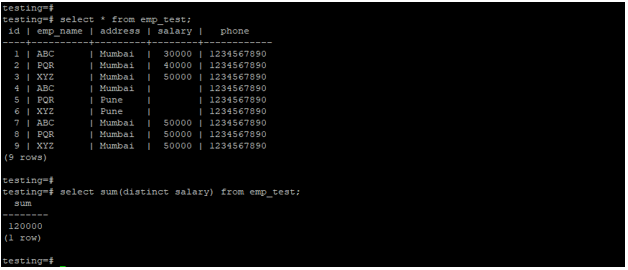
select * from emp_test;
select sum(distinct salary) from emp_test;Output:
- In the above example, we have used the sum function on the salary column with a distinct clause. Distinct clause only returns the result of the only emp id of 1, 2, and 3 because that value is distinct in the salary column.
- We have used the sum function in an application where we have to retrieve data of the sum of the calculation of the result.
- Column name and table name is the important parameter of the sum function.
- We have used some functions with where having and group by clause.
- If we want the sum of unique records from the PostgreSQL table, we have used the sum function with the where clause.
Examples of PostgreSQL SUM()
- Below is an example of the sum function.
- We have used emp_test to describe the example of the sum function in PostgreSQL as follows.
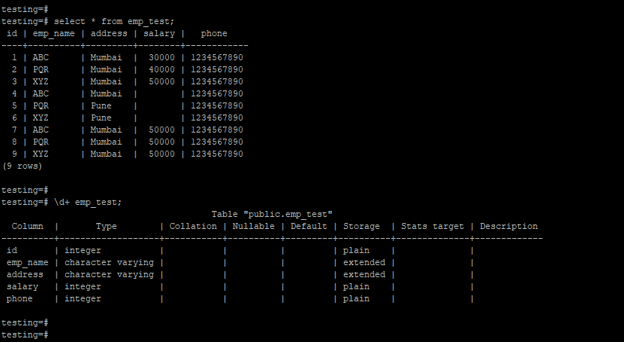
- Below is the data and table description of the emp_test table.
Command:
select * from emp_test;
\d+ emp_test;Output:
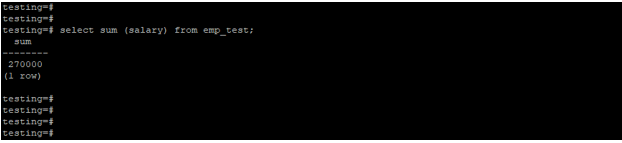
Example #1 – Sum function without using any clause
In the example below, we have used the sum function without any clause. We have applied the sum function to the salary column.
select sum (salary) from emp_test;Output:
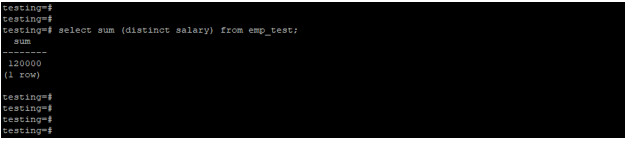
Example #2 – Sum function using distinct clause
We used the sum function with a distinct clause in the example below. We have applied the sum function with a distinct clause on the salary column.
select sum (distinct salary) from emp_test;Output:
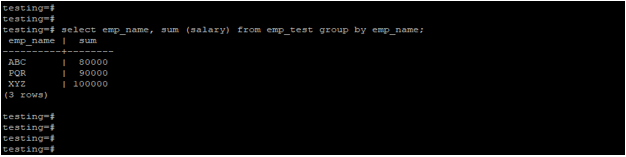
Example #3 – Sum function using group by clause
In the below example, we have used the sum function with the group by clause. We have applied the salary column’s sum function and group by clause on the emp_name column.
select emp_name, sum (salary) from emp_test group by emp_name;Output:
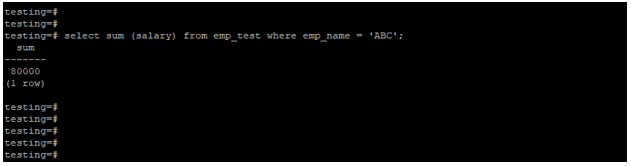
Example #4 – Sum function using where the condition
We used the sum function with the where condition in the example below. We have applied the sum function on the salary column and where condition on the emp_name column.
select sum (salary) from emp_test where emp_name = 'ABC';Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL SUM()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.