Updated May 4, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL ROLLUP
The PostgreSQL ROLLUP is an extension of the GROUP BY clause. Generally, the PostgreSQL GROUP BY ROLLUP is used for data analytics operations. For performing data analytics related operations, so many tools or software are available in the market. PostgreSQL is not made for Data Analytics purpose; with the help of the operations like ROLLUP, we can support data analytics operations on real-time data.
Syntax:
SELECT
c1, c2, c3, aggregate_function(c4)
FROM
table
GROUP BY ROLLUP (c1, c2, c3);The columns defined in the ROLLUP option get considered for generating hierarchy. Consider the above syntax where we have input columns (c1, c2, c3). The ROLLUP generates all grouping sets considering the hierarchy c1 > c2 > c3. So for reporting sub-total and grand-total, we use the ROLLUP.
In the syntax above, ROLLUP(c1,c2,c3) generates three following grouping sets:
- (c1, c2, c3)
- (c1,c2)
- (c1)
- ()
We can also perform a partial roll up to reduce the count of sub-totals created.
SELECT
c1, c2, c3, aggregate(c4)
FROM
table_name
GROUP BY
c1, ROLLUP (c2, c3);How ROLLUP works in PostgreSQL?
- We can use a single statement to generate multiple grouping sets with the help of the PostgreSQL ROLLUP option.
- The PostgreSQL ROLLUP option adds extra rows in the result set, allowing us to get total and super-aggregate rows.
- In order to analyze the hierarchical data like creating grand-total or sub-total, we use the PostgreSQL ROLLUP option.
Examples of ROLLUP in PostgreSQL
Let’s create a table named Furniture.
Code:
CREATE table furniture
(
furniture_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
furniture_name VARCHAR (256) NOT null,
furniture_type VARCHAR (256) NOT null,
furniture_price int NULL
);Now, insert some data in the furniture table to execute SQL statements.
INSERT INTO furniture (furniture_name,furniture_type,furniture_price)
VALUES
('Chair','Wood',2500),
('Chair','Plastic',2000),
('Table','Wood',5000),
('Table','Plastic',4000),
('Sofa','Wood',10000),
('Sofa','Plastic',8000),
('Bed','Wood',15000),
('Bed','Plastic',13000);Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot and the SELECT statement.
SELECT * FROM furniture;Example #1 – ROLLUP with one column
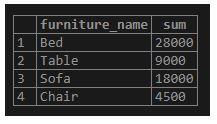
The following SQL statement uses the GROUP BY clause and the SUM() function to find the total furniture price from furniture_name.
Code:
SELECT
furniture_name, SUM(furniture_price)
FROM
furniture
GROUP BY furniture_name;Output:
Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
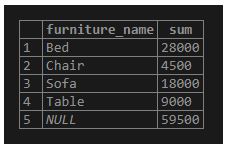
To fetch the total furniture price of all Furniture, we can use the PostgreSQL ROLLUP to the GROUP BY clause as follows:
SELECT
furniture_name, SUM(furniture_price)
FROM
furniture
GROUP BY ROLLUP (furniture_name);Output:
Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
You can see the NULL value in the furniture_name column, which shows the grand total super-aggregate result.
In this above example, the PostgreSQL ROLLUP option allows the statement to add an extra row showing the total furniture price.
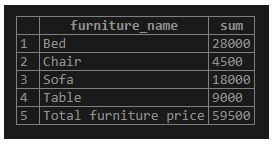
As we have seen, the output shows a NULL value in a newly produced row, which we can make more readable using the COALESCE() function.
Here we will substitute the NULL value by the ‘Total furniture price’ as follows:
Code:
SELECT
COALESCE(furniture_name, 'Total furniture price') AS furniture_name,
SUM(furniture_price)
FROM
furniture
GROUP BY ROLLUP (furniture_name);Output:
Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
Example #2 – ROLLUP with multiple columns
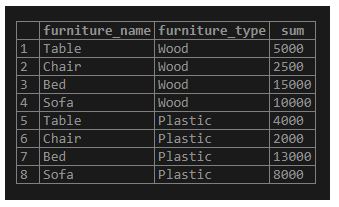
The following SQL statement generates the furniture result by furniture_name and furniture_type:
Code:
SELECT
furniture_name, furniture_type, SUM(furniture_price)
FROM
furniture
GROUP BY furniture_name, furniture_type;Output:
Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
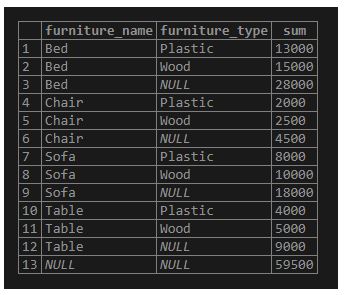
Now add the ROLLUP to the GROUP BY clause as follows:
Code:
SELECT
furniture_name, furniture_type, SUM(furniture_price)
FROM
furniture
GROUP BY ROLLUP (furniture_name , furniture_type);Output:
Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
Explanation:
- The set of furniture_type rows for a specified furniture_name, an additional summary row, generates the total furniture price. The values in the furniture_type column are set to NULL in the newly added row.
- Following all rows, an additional summary row generates the total furniture price of all furniture names and furniture types. The values in the furniture_name and furniture_type columns are set to NULL in the newly added rows.
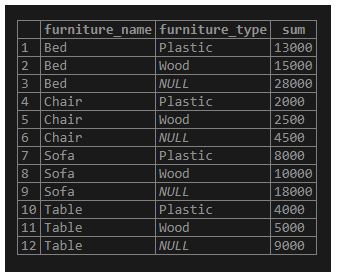
Example #3 – ROLLUP with a partial rollup
We can use it to do a partial rollup which reduces the count of sub-totals generated, as shown in the following example:
Code:
SELECT
furniture_name, furniture_type, SUM(furniture_price)
FROM
furniture
GROUP BY furniture_name, ROLLUP (furniture_type);Output:
Illustrate the result of the above statement with the help of the following snapshot.
The above example generates an aggregate summary for the furniture_type column, not the furniture_name column.
Conclusion
From the above article, you have seen how to use it. Also, we have added some examples of PostgreSQL ROLLUP to understand it in depth.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL ROLLUP” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.