Updated May 6, 2023

Introduction to LEFT JOIN in PostgreSQL
In SQL, joining is a technique used to operate on multiple tables simultaneously. It involves combining two or more tables to retrieve desired results. As a result, the left joint operation returns all rows from the left-hand side table and only matched rows from the right-hand side table where the ON clause satisfies the condition. The LEFT JOIN and LEFT OUTER JOIN are similar terms. This topic will teach you how to use PostgreSQL LEFT JOIN to combine two tables.
Syntax
The PostgreSQL LEFT [OUTER] JOIN syntax:
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, column_name3....
FROM table_name1
LEFT [OUTER] JOIN table_name2
ON table_name1.column_name = table_name2.column_name;Explanation:
- Define the list of column names from which you want to retrieve the data.
- Define the first (left) table from where you want to fetch all rows in the FROM clause, like table_name1.
- Define the LEFT JOIN clause’s second (right) table like table_name2.
- Define the condition to join both tables.
Visualize the following diagram to understand the result set of the PostgreSQL LEFT [OUTER] JOIN.
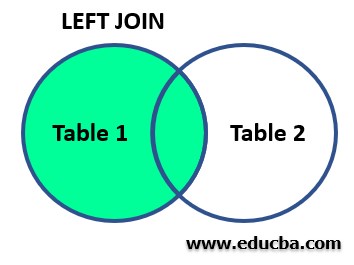
It returns the highlighted area as a result of the join operation:
How LEFT JOIN works in PostgreSQL?
In PostgreSQL, the LEFT JOIN is a method used for combining two tables. It returns the result set containing all rows from the first (left) table defined in the JOIN clause and all matched rows from the second_table based on a condition.
Consider a syntax as
first_table LEFT JOIN second_table JOIN CONDITIONUnderstand table dependency.
- The second_table depends on the first_table and all tables on which the first_table is depended on.
- The first table uses all tables that are involved in the LEFT JOIN, except for the second table.
Condition:
The condition specified in the LEFT JOIN clause determines how rows are retrieved from the second_table.
If a row in the first table matches the condition specified in the WHERE clause but no matching row in the second table based on the ON condition, then the resulting rows for the second table will contain NULL values for all columns.
The PostgreSQL LEFT JOIN, or LEFT OUTER JOIN operation returns the result as:
- Fetches all values from the first (left) table.
- Combines them with the column names defined in the condition from the second (right) table
- Fetch the matched rows from both the first (left) table and the second (right) table.
- When the left table’s rows do not have a matching row in the right table, each column in the right table will have a NULL value for those rows.
Examples of PostgreSQL LEFT JOIN
Let’s create two tables named’ transaction’ and ‘invoices’ in order to understand the PostgreSQL NATURAL JOIN examples.
The following CREATE TABLE statements will create the transaction and invoices table.
CREATE TABLE transaction (
transaction_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
transaction_data VARCHAR (256) NOT NULL
);
CREATE TABLE invoices (
invoice_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
transaction_id INT NOT NULL,
invoice_data VARCHAR (256) NOT NULL,
FOREIGN KEY (transaction_id) REFERENCES transaction (transaction_id)
);The transaction table’s primary key is the transaction_id, and the invoices table references it as a foreign key. So while performing the natural join operation, we will use the transaction_id column as it is the common column for both tables. The transaction may have zero or more invoices, and the invoice will belong to one and only one transaction.
Now insert some data into the transaction and invoices tables using the INSERT statement as follows:
INSERT INTO transaction (transaction_data)
VALUES
('Purchase of Mobile'),
('Purchase of PC'),
('Purchase of Headphone');
INSERT INTO invoices (invoice_data, transaction_id)
VALUES
('Purchase of Mobile', 1),
('Purchase of Mobile', 1),
('Purchase of PC', 2),
('Purchase of PC', 2),
('Purchase of Headphone', 3),
('Purchase of Headphone', 3);Illustrate the content of the transaction table using the following statement and snapshot.
select * from transaction;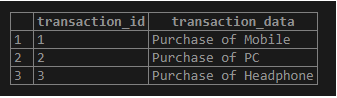
Illustrate the content of the invoices table using the following statement and snapshot.
select * from invoices;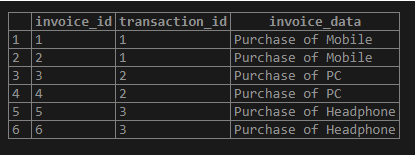
Example of LEFT JOIN clause to join the transaction table to the invoices table as follows:
SELECT
transaction.transaction_id,
transaction.transaction_data,
invoice_data
FROM
transaction
LEFT JOIN invoices ON invoices.transaction_id = transaction.transaction_id;Illustrate the result of the above statement using the following snapshot.
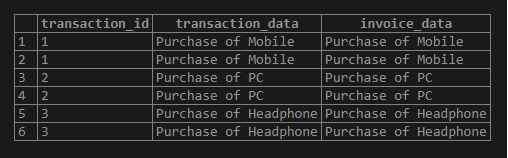
We can use the WHERE clause to select only invoices whose transaction_id is not (1 and 2) as follows:
SELECT
transaction.transaction_id,
transaction.transaction_data,
invoice_data
FROM
transaction
LEFT JOIN invoices ON invoices.transaction_id = transaction.transaction_id
where invoices.transaction_id not in ( 1,2);Illustrate the result of the above statement using the following snapshot.
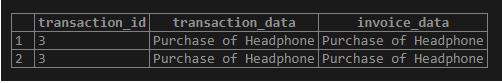
Using a where clause, you can filter out data you want to retrieve from one table which matches other tables.
Conclusion
From the above article, we hope you have learned about the PostgreSQL LEFT JOIN and how the PostgreSQL LEFT JOIN works. We have also added some examples to demonstrate how to use the LEFT JOIN to query data from the tables mentioned.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL LEFT JOIN” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

