Updated May 4, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL LAG()
PostgreSQL lag () is a function in which the row will come before the current rows as an output or a specified query offset. In general, this function states that for the current row value, the lag function will access the data from previous rows; it will always access the data from previous rows to display the query output. This function is essential and useful in PostgreSQL to compare values or data for current and previous rows. It is used to compare the values of the current and previous rows.
Syntax
Below are the syntaxes as follows.
1. Using Partition by Clause
Syntax:
LAG (expression (Expression is column name of table) [, offset (Which specifies the rows number that comes before current row) [, default_value (Default value of lag function)]]) OVER (
[PARTITION BY (It will divides rows into partition) partition_expression (Partition column name), ... ]
ORDER BY (Order by clause is used to sort the data) sort_expression [ASC | DESC], ... (Sort column row by ascending or descending order))2. Default Value of Partition by Clause
Syntax:
LAG (expression (Expression is column name of table) [, offset (Which specifies the rows number that comes before current row) [, default_value (Default value of lag function)]]) OVER (
ORDER BY (Order by clause is used to sort the data) sort_expression [ASC | DESC], ... (Sort column row by ascending or descending order))Parameter
Below is the parameter description of the above syntax as follows.
- Expression: Expression is a column name used in a lag function to display the specified column data. This is a column or a Subquery. It will return a single value in the lag function.
- Lag(): PostgreSQL lag () function is a function that row will come before the current rows as an output or a specified query offset.
- Offset: An offset is an integer number in a lag function specifying the number before the current row. The default value of offset in the lag function is 1. If we do not specify the offset value, it will take 1 by default.
- Default value: This is a default value of a lag function; the PostgreSQL lag function will return the default value if the offset goes above the partition’s scope value.
- Partition by: When using the lag function in PostgreSQL, the ‘partition by’ clause can be used to divide the rows into partitions to which the lag function is applied. If no partition by clause is specified, the function will consider the entire table as a single partition.
- Partition expression: You can use a column name as the partition expression in the ‘partition by’ clause to divide the values in a table into partitions.
- Order by: In PostgreSQL, you can use the order by clause with the lag function to fetch data in ascending or descending order. Use “ASC” to retrieve data in ascending order or “DESC” to retrieve data in descending order.
- ASC: To fetch data in ascending order using the lag function, you can specify the ‘order by’ clause with the default ascending order
- DESC: The lag function uses the ‘order by’ clause along with ‘descending’ to retrieve data in descending order
- Sort expression: This is the column name we have used in order by clause to fetch the data using ascending or descending order.
How PostgreSQL LAG () Function Work?
Below is the working of the lag function as follows.
- The lag function works by its names that lag behind the current rows; it will fetch the data from previous rows.
- The PostgreSQL lag () function is a row that will come before the current rows as an output or a specified query offset.
- PostgreSQL lag function will state that for the current row, the PostgreSQL lag function will access the data from previous rows; it will always access the data from previous rows to display the query output.
- We have used partition by clause in the lag function; partition by the clause in the PostgreSQL lag function will divide rows into a partition on which the lag function was applied. If we didn’t specify a partition by clause, it would consider the whole partition of a table. If we specify a partition, data will be fetched as per order.
- The lag function is essential and useful in PostgreSQL to compare current rows and previous rows’ values or data. It is used to compare the values of the current and previous rows.
- In PostgreSQL, one can use the lag function combined with an order by clause to display or fetch data in ascending or descending order.
- The lag function compares the current row with the previous rows of a table. If we need to compare two tables simultaneously, we use the lag function in PostgreSQL.
- The lag function is more important for comparing current and previous rows.
Examples to Implement LAG() Function
- Below is an example of implementing a lag function in PostgreSQL.
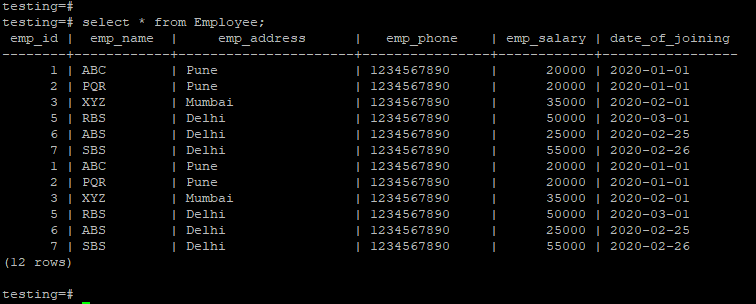
- We have used the employee table to describe the example of a lag function in PostgreSQL; the below image shows the employee table’s data.
testing=# select * from Employee;1. Lag Function Default Partition by Clause
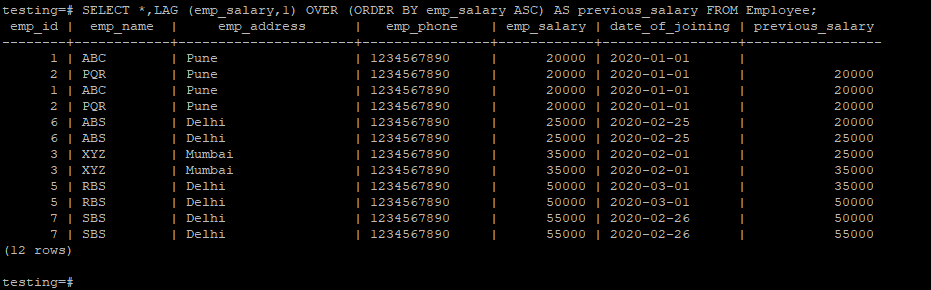
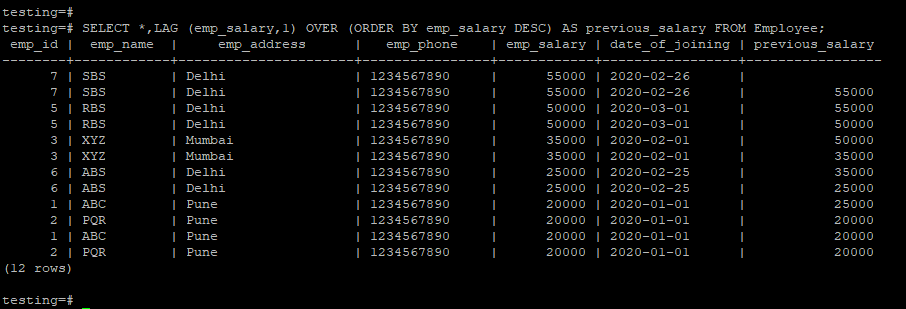
The below example shows the lag function default partition by clause.
testing=# SELECT *,LAG (emp_salary,1) OVER (ORDER BY emp_salary ASC) AS previous_salary FROM Employee;testing=# SELECT *,LAG (emp_salary,1) OVER (ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) AS previous_salary FROM Employee;2. Lag Function with Partition by Clause
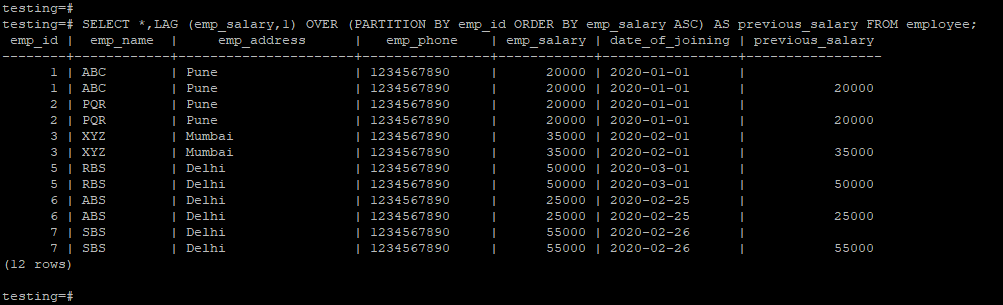
The below example shows the Lag function with partition by clause.
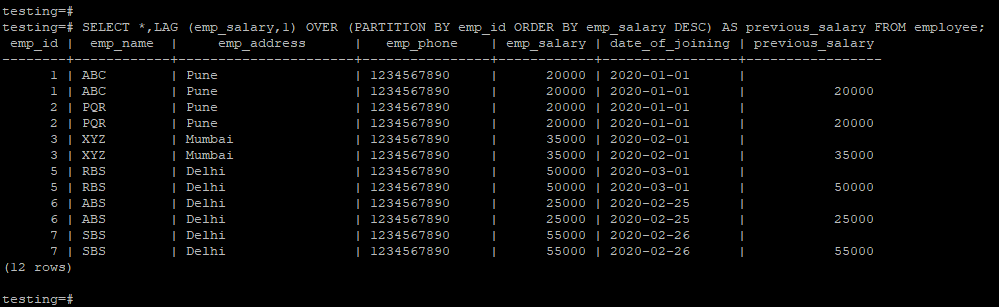
testing=# SELECT *,LAG (emp_salary,1) OVER (PARTITION BY emp_id ORDER BY emp_salary ASC) AS previous_salary FROM employee;testing=# SELECT *,LAG (emp_salary,1) OVER (PARTITION BY emp_id ORDER BY emp_salary DESC) AS previous_salary FROM employee;Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL LAG()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.