Updated May 6, 2023
Introduction to Wildcards in PostgreSQL
Wildcards in PostgreSQL is used to find matching rows values from tables; it is also used to find matching patterns rows from tables, Wildcards is also used to find matching rows, column, and tables names; the output of the wildcard operator will return matching name, which was table name, column name or rows, In PostgreSQL, the “like” operator compares text values to a pattern by utilizing wildcards. PostgreSQL requires the wildcard operator when the pattern expression matches the search expression in the query.
Explain all Wildcards in PostgreSQL
We will explain all wildcards in PostgreSQL one by one as follows. The wildcard operators used by PostgreSQL are as follows.
- Using percentage (%) wildcard
- Using Underscore (_) wildcard
1. Using % Wildcard
- To match text values based on patterns in PostgreSQL, you can use wildcard operators. To search for matching text values in a table based on a pattern, the LIKE operator is commonly used in PostgreSQL.
- PostgreSQL utilizes two types of wildcard operators.
- Percentage (%) wildcard
- Underscore (_) wildcard
- The percentage (%) sign represents one, zero, or multiple no of characters, which have used percentage in different form to retrieve the output.
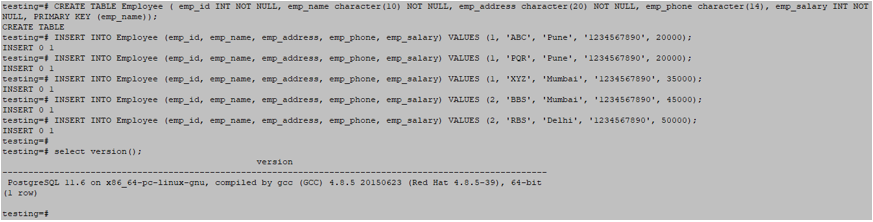
- We have used the employee table to describe the wildcard operator in PostgreSQL.
Table Example
testing=# CREATE TABLE Employee ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (emp_name));
testing=# INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000);
testing=# INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary) VALUES (1, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000);
testing=# INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary) VALUES (1, 'XYZ', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 35000);
testing=# INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary) VALUES (2, 'BBS', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 45000);
testing=# INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary) VALUES (2, 'RBS', 'Delhi', '1234567890', 50000);Output:
Syntax
Please find below the syntax of percentage (%) wildcard operators are as follows.
- %xxx% : Select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name where column_name like ‘%xxx%’;
- xxx% : Select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name where column_name like ‘xxx%’;
- %xxx : Select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name where column_name like ‘%xxx’;
- xxx : Select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name where column_name like ‘xxx’;
Please find below the parameter description of the above syntax are as follows.
- Column1 to column – Column is used in the query to fetch data from the table.
- Table name – Table name used in the query to fetch data from that table.
- Percentage (%) – Percentage wildcard (%) operator used to fetch matching data from the table.
- Like – Like operator is used to fetch data from the table.
- Where – Where clause is used to fetch data from the table.
Example
Please find below an example of the percentage (%) wildcard operator is as follows.
1. Like ‘%xxxx%.’
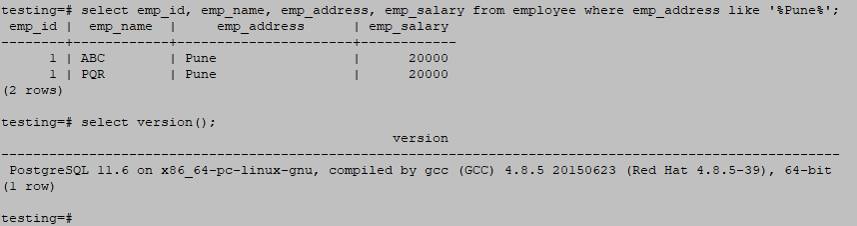
The example below returns all rows matching Pune text from the employee address from the employee table.
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_salary from employee where emp_address like '%Pune%';Output:
2. Like ‘%xx.’
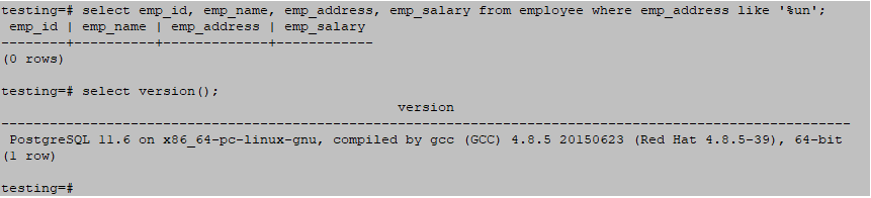
The below example returns all rows which matching the “un” text from the employee address from the employee table.
Which starts matching patterns from the right side.
The below query has no matching rows, so it will return an empty set.
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_salary from employee where emp_address like '%un'Output:
3. Like ‘xx%.’
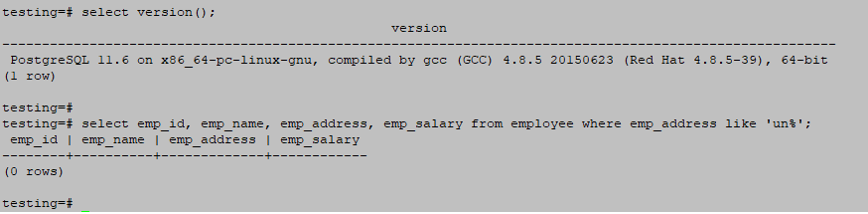
The below example returns all rows which matching the “un” text from the employee address from the employee table.
Which starts matching patterns from the left side.
The below query has no matching rows, so it will return an empty set.
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_salary from employee where emp_address like 'un%';Output:
4. Like ‘xxx.’
The below example returns all rows which matching the “une” text from the employee address from the employee table.
Which starts matching patterns from both side.
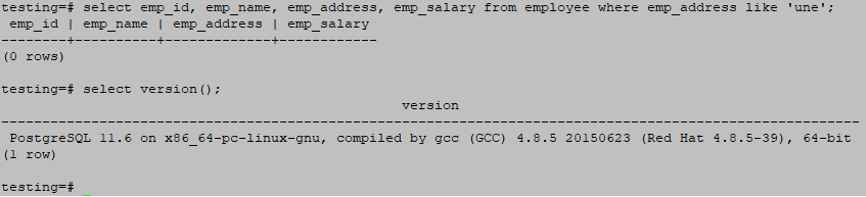
There is no matching in the below query, so it will return an empty set.
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_salary from employee where emp_address like 'une';Output:
Using the Underscore, (_) operator
Please find syntax and examples of Underscore (_) wildcard operators below.
Syntax
Please find below the syntax of the Underscore (_) wildcard operator is as follows.
- _xxx_ : Select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name where column_name like ‘_xxx_’;
- xxx_ : Select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name where column_name like ‘xxx_’;
- _xxx : Select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name where column_name like ‘_xxx’;
- xxx : Select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name where column_name like ‘xxx’;
Please find the parameter description of the above syntax are as follows.
- Column1 to columnN – Column is used to fetch data from a query.
- Table name – Table name used in the query to fetch data from a table.
- Underscore (_) – Underscore wildcard (_) operator fetches matching data from the table.
- Like – Like operator is used to fetch data from the table.
- Where – We use the WHERE clause to fetch data from a table.
Example
Here are the following examples mention below
1. Like ‘_xxx_.’
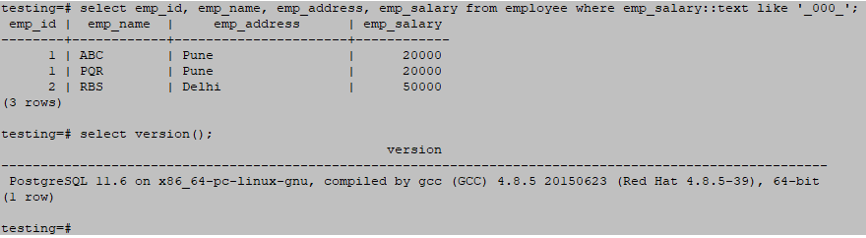
Below is an example of a like ‘_xxx_’ wildcard operator is as follows.
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_salary from employee where emp_salary::text like '_000_';Output:
2. Like ‘_xxxx.’
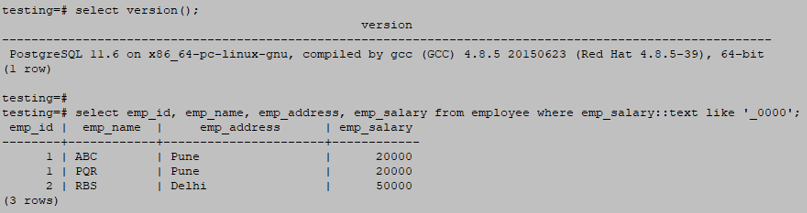
Below is an example of a like ‘_xxxx’ wildcard operator as follows.
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_salary from employee where emp_salary::text like '_0000';Output:
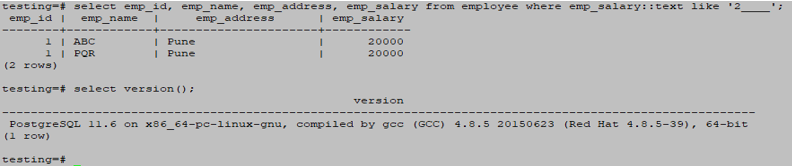
3. Like ‘x____.’
Below is an example of a like ‘x____’ wildcard operator is as follows.
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_salary from employee where emp_salary::text like '2____';Output:
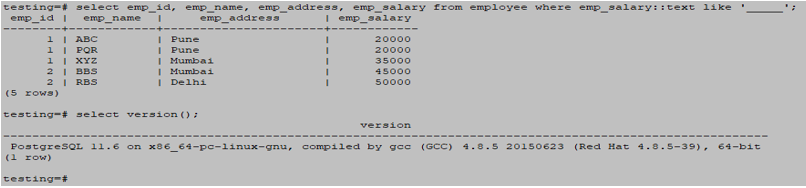
4. Like ‘_____.’
Below is an example of a like ‘_____’ wildcard operator is as follows.
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_salary from employee where emp_salary::text like '_____';Output:
Conclusion
The Wildcard operator is essential in PostgreSQL. We used percentage (%) and underscore (_) wildcard operators to fetch matching rows from the table. There are many ways to retrieve data from the table using wildcard operator like (‘%xxx%’, ‘%xxx’, ‘xxx%’, ‘xxx’, ‘____’, ‘_xxx’, ‘xxx_’ and ‘_xx_’).
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Wildcards in PostgreSQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.