Updated September 1, 2023

Table of Contents
- What is the PostgreSQL Function?
- How do PostgreSQL Functions work?
- Examples of PostgreSQL Functions
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is the PostgreSQL Function?
PostgreSQL functions are also called stored procedures in PostgreSQL; You set a PostgreSQL stored procedure or function within SQL statements. Create a statement to create a new function; we can create a PostgreSQL function in many languages like C, Python, SQL, and PL/pgsql. Before PostgreSQL version 11, PostgreSQL relied heavily on functions, but after that, the database differentiated between functions and procedures. Its function name will be unique, which means it will not be the same as other names of a function that was already created in the database.
Syntax
Below given is the syntax:
CREATE [OR REPLACE (Replace the function if already exist)] FUNCTION
name (Name of function) ( [ [ argmode (Mode of argument)] [ argname(Name of argument) ] argtype (Type of argument)[ { DEFAULT | = } default_expr (Default expression of function) ] [, ...] ] )
[RETURNS rettype (Return type of functions)
| RETURNS TABLE (Table name which we have used to return from function)(column_name (Name of column) column_type (Data type of column)[, ...] ) ]
{LANGUAGE lang_name (Language name which was used to create function)
| WINDOW (Window function)
| IMMUTABLE | STABLE | VOLATILE (Attribute of function)
| COST execution_cost (Execution costs)
| ROWS result_rows (No of rows returned from function)
| SET configuration_parameter (Specified configuration parameter) {TO value | = value | FROM CURRENT}
| AS 'definition' (Definition of function)
} ...
[WITH (attribute [, ...] ) ] (Display optional function information)Below is the parameter description of the above syntax:
- Create: Creates a new function.
- Function name: Name of function that we are creating. The function name should be unique.
- Replace: Replace the function name which is already present in the database.
- Argmode: The mode of argument used in a function; the default argument mode of function is IN.
- Argname: Name of argument which we have used to create a function.
- Argtype: The type of argument used to create a function.
- Default: The default behavior is to use a default value if no argument is given.
- Rettype: This is defined as a return type of function. The return type can be anything composite, base, or table column.
- Table: Table name which column we have returned from a function.
- Column name: This defines the name of columns that we have a return in return table syntax.
- Column type: This is a data type of column we have returned in the return table syntax.
- Language name: We define the language used to create a function by specifying its name. The language can be Python, pl/pgsql, or C.
- Window: This is defined as creating a window function instead of a plain one.
- Execution cost: This parameter defines the total time required to execute the function; it shows the positive number.
- Cost: The cost parameter defines the execution cost of the function.
- Rows: The rows parameter defines the total rows returned from the function.
- Result rows: Result of rows that have returned from the function.
- Configuration parameter: This defines a configuration parameter set as a different value.
- Definition: This parameter defines a definition of a function.
- Attribute: This will display extra information about a function.
How do PostgreSQL Functions work?
- In PostgreSQL, people refer to functions as stored procedures or stored functions.
- A PostgreSQL stored procedure or function consists of a set of SQL or PL/SQL statements.
- Its name will be unique, which means it will not be the same as other function names already created in the database.
- Create a statement is used in a function to create a new function; also, we can replace the existing function using the replace keyword at the time of new function creation.
- We can create a new function in various languages such as C, Python, SQL, and PL/pgSQL in PostgreSQL. To define a new function in PostgreSQL, we use the CREATE statement.
- Before version 11, a function in PostgreSQL was required to behave like a PostgreSQL procedure. However, starting from version 11, functions and procedures are distinguished.
- In PostgreSQL, a stored procedure or function refers to a set of SQL statements stored on the database server and invoked through an SQL interface.
- In PostgreSQL, we use a function to execute multiple SQL queries and return the results in the format specified in the function definition.
- We can check all functions from the database by using a “\df”. This command is used to display all functions from a database.
- We can implement it in different languages. It will choose the default language if we do not define the language during function creation.
- It uses an interface that defines an argument and returns the function type, as stated in the function’s syntax.
Examples of PostgreSQL Functions
Given below is the example to create, modify, and drop a function:
Example #1: Create a PostgreSQL function
Below is an example of creating a new function.
Code
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION Func_Test ()
RETURNS integer AS $test$
declare
test integer;
BEGIN
SELECT count (1) into test FROM EMP;
RETURN test;
END;
$test$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
\dfOutput
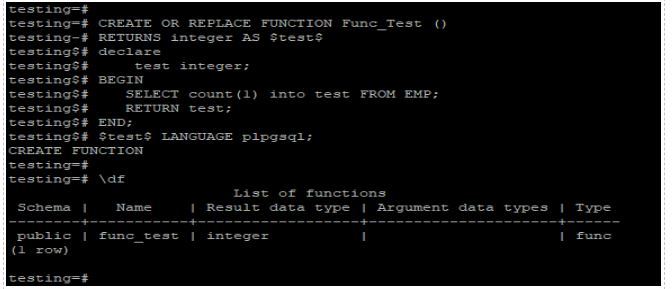
In the above example, we have created a function named Func_Test. We have used the pl/pgsql language to create a new function.
A count record from the EMP table is available. The commands we can use to call or run Func_Test are as follows.
Code
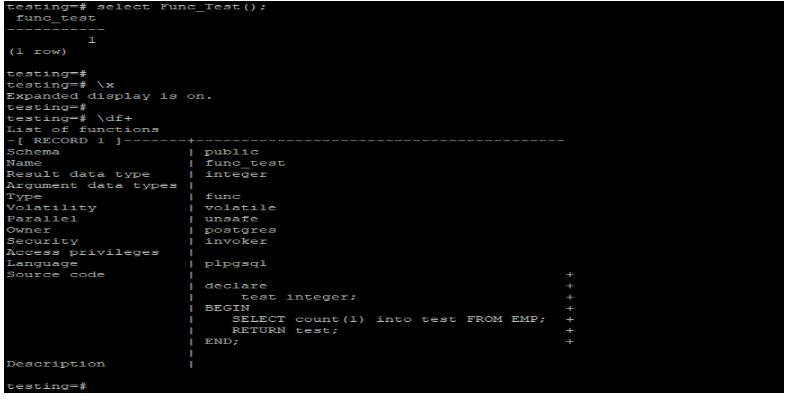
select Func_Test();
\df+Output
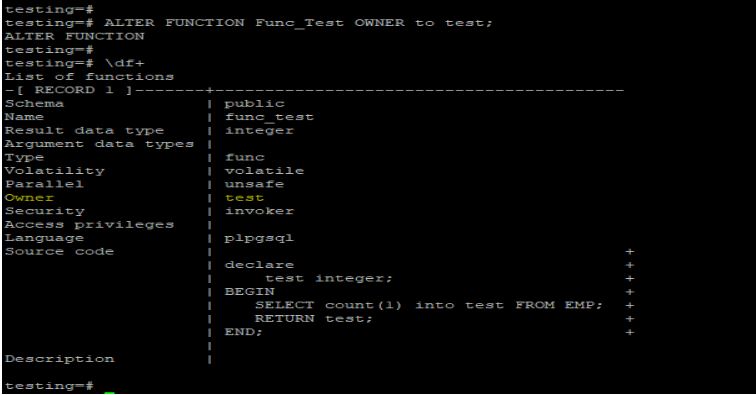
Example #2: Modify the PostgreSQL function
We are changing the owner of the Func_Test function from Postgres to a test user.
Code
ALTER FUNCTION Func_Test OWNER to test;
\df+Output
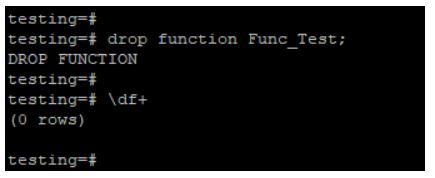
Example #3: Drop the PostgreSQL function
We can drop by using a drop command. We are dropping the Func_Test function.
Code
drop function Func_Test;
\df+Output
Conclusion
A PostgreSQL function or stored procedure is a set of SQL statements stored on the database server and invoked through an SQL interface. The create statement is used to create a new function in PostgreSQL. We can implement this function in C, Python, and pl/pgsql.
FAQs
Q1. What is $1 in the Postgres function?
Ans: In PostgreSQL, the dollar sign ($) is often used as a delimiter in dollar-quoted strings within SQL functions. It allows you to create multiline string literals without escaping special characters. For example:
CREATE FUNCTION my_function() RETURNS text AS $$
BEGIN
RETURN 'This is a dollar-quoted string with $1 in it';
END;
$$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;In this context, “$1” is simply a part of the string and has no special meaning within the function.
Q2. How to check functions in PostgreSQL?
Ans: To check functions in PostgreSQL, you can use the following SQL commands:
To list all functions in a schema:
SELECT * FROM pg_catalog.pg_proc WHERE pronamespace = 'your_schema'::regnamespace;To describe a specific function:
\df+ function_nameReplace ‘your_schema’ with the schema name and ‘function_name’ with the function name you want to check.
Q3. How to check all functions in PostgreSQL?
Ans: To check all functions in PostgreSQL, you can use SQL queries to access the system catalog. You can query the “pg_proc” catalog table, which stores information about all functions in the database. Here’s a simple SQL query to list all functions:
SELECT proname
FROM pg_proc;This query will return the names of all functions in the current database. You can customize it further to retrieve additional information about the functions if needed.
Q4. How to get a function script in PostgreSQL?
Ans: In PostgreSQL, you can obtain the source code or definition of a function using the \df command in the psql command-line tool. Simply type \df function_name to display the script of a specific function named “function_name.” This command will provide the function’s source code, allowing you to view and analyze its implementation.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Functions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

