Updated May 22, 2023
Introduction to Postgres DROP Table
In this Postgres DROP Table article, we will learn about how we can manage to drop a table and deleting the table in the PostgreSQL database. Only the owner of the table can drop the table using the DROP TABLE command. This command entirely deletes the table structure, its records, associated objects like Views defined on that table, its indexes, constraints, and restrictions. In case if you just want to delete the contents of the table, you can use the TRUNCATE or DELETE command. Both these commands will keep everything intact related to the target table and remove the records present in the target table. Let us begin with the help of the syntax of the DROP TABLE command.
Syntax:
DROP TABLE [IF EXISTS] name_of_the_table [CASCADE | RESTRICT];- IF EXISTS– It is an optional parameter. The “IF EXISTS” keyword can be used to prevent any errors that may occur when executing the above command in case there is no table with the specified name (“name_of_the_table”) in the current database. When you use the “IF EXISTS” keyword in the query and no table with the specified name “name_of_the_table” is found in the current server, the system will actively display a notification to inform you about it. This operation will not generate any errors.
- name_of_the_table– It is the name of the table that you wish to drop and is located in the current database.
- CASCADE– This is used when a foreign key constraint is involved. To handle the target table’s foreign constraints over other tables or its usage in views, you need to specify the CASCADE property. When CASCADE is used, all the related views to the target table are permanently deleted. However, in the case of foreign key constraints, the related table remains unaffected. All its contents remain intact in the table.
- RESTRICT– The default behavior in the DROP TABLE query is to prevent the dropping of a table if the “CASCADE” or “RESTRICT” options are not specified. In such cases, if other tables reference the table with foreign constraints or if the table is being used in any views, the system will prohibit the dropping of the table.
Example of Postgres DROP Table
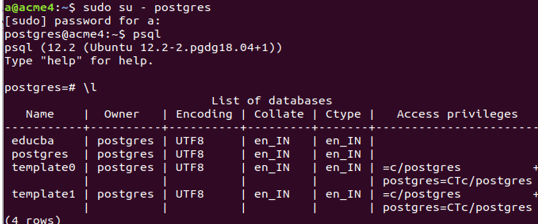
sudo su - postgres
psql
\lWe can check all the databases present in our database server using the query \l, which results in the following output currently for my server –
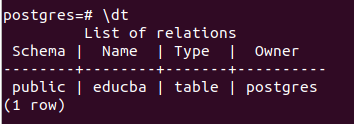
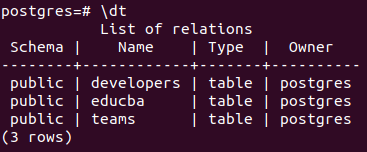
Now, to check what are all the tables present in the Postgres database, we can use \dt command. Here’s how they result in –
\dtLet us try to delete a certain table in postgres database, say a table named demo. As it does not contain any table named demo, it will throw the error when we fire the query statement –
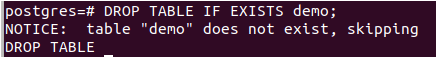
DROP TABLE demo;As can be seen, it gives the error saying table “demo” does not exist. Now, is we use IF EXISTS in our above query in the following way, then instead of an error, it will display a notice shown below –
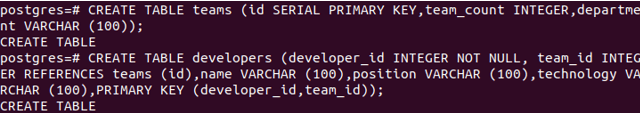
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS demo;Let us insert some tables in it. The example will contain two tables, namely teams, and developers. Each developer is a member of one team or another, and one team consists of many developers. While maintaining both records in the database, we will first create tables for each one. Firstly let us create a table for teams which will be our main referenced parent table.
CREATE TABLE teams (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
team_count INTEGER,
department VARCHAR (100)
);Now, we will create a table for developers which will act as the referencing or child table. There will be one to many relationships between teams and developers table. team_id will be our referencing key, which will refer to the id of the team’s table.
CREATE TABLE developers (
developer_id INTEGER NOT NULL,
team_id INTEGER REFERENCES teams (id),
name VARCHAR (100),
position VARCHAR (100),
technology VARCHAR (100),
PRIMARY KEY (developer_id,team_id)
);The output of the above two tables is as follows –
Let us verify the table creation by using \dt command that now results in –
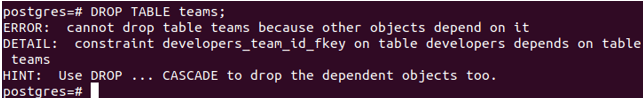
\dtThe above query will create just a referencing table ‘developers’ for teams. But while dropping table teams, it will restrict us to drop and not allow if any of the referencing tables are present such as the developers table for the field id of the team’s record, as the default CASCADE/RESTRICT value is RESTRICT. Let us see the query for dropping the table teams –
DROP TABLE teams;The above query results in the following output, which suggests us use CASCADE.
Now, if we want to delete the table teams with a particular id along with the foreign constraint referencing table developers, then we will use option CASCADE. Here is the syntax using which we can do so while dropping the table teams.
DROP TABLE teams CASCADE;that gives the following output –
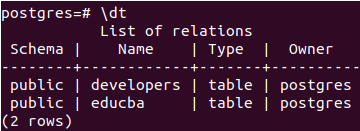
In contrast to the previous case, the execution does not result in an error. In contrast, the execution results in the dropping of the “teams” table, along with the foreign constraint associated with the “developer’s” table. After successfully deleting the foreign constraint, the system generates a notice to inform us of the successful removal. Now, if we check all the tables in postgres database using \dt, then it gives the output –
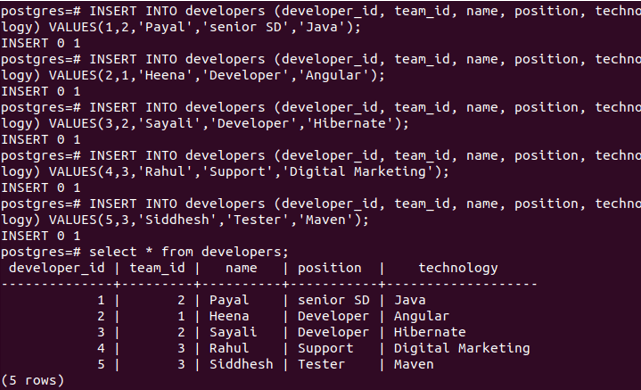
\dtNow, we will insert some records in the developers table.
INSERT INTO developers (developer_id, team_id, name, position, technology) VALUES(1,2,'Payal','senior SD','Java');
INSERT INTO developers (developer_id, team_id, name, position, technology) VALUES(2,1,'Heena','Developer','Angular');
INSERT INTO developers (developer_id, team_id, name, position, technology) VALUES(3,2,'Sayali','Developer','Hibernate');
INSERT INTO developers (developer_id, team_id, name, position, technology) VALUES(4,3,'Rahul','Support','Digital Marketing');
INSERT INTO developers (developer_id, team_id, name, position, technology) VALUES(5,3,'Siddhesh','Tester','Maven');and check by selecting records of the developer’s table.
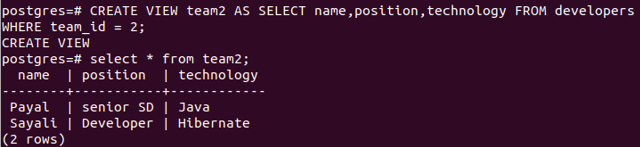
Let us create a view on the table developers named
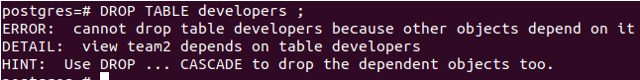
CREATE VIEW team2 AS SELECT name,position,technology FROM developers WHERE team_id = 2;After selecting from the view team2, you can see that two records are retrieved. Now, if we drop the table developers using the command
DROP TABLE developers ;It gives us an error saying a view named team2 exists, and when we use CASCADE in the following manner –
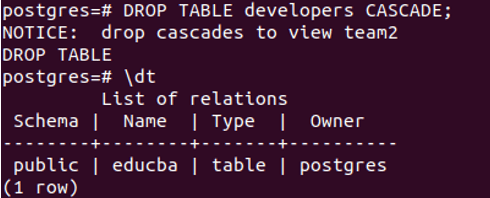
DROP TABLE developers CASCADE;and select the tables using \dt command, then the output is –
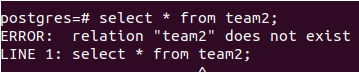
You can confirm the deletion of the table developers and the view team2 by retrieving values from the view using the following query.
SELECT * from team2;which gives output –
Conclusion- Postgres DROP Table
We can use the DROP TABLE query to completely delete a table in PostgreSQL, including its existence, structure, records, restrictions, and indexes. We can utilize the CASCADE option to handle dependencies associated with the target table in PostgreSQL. This includes managing foreign constraints of other tables that reference the target table or its related views. IF EXISTS helps us to throw a notice instead of an error.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on the “Postgres DROP Table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.