Updated May 6, 2023

Introduction to PostgreSQL Date Functions
In PostgreSQL, a variety of date functions are available that are used to manipulate timestamps. The date function is very useful and important in PostgreSQL; in date functions, inputs come in two formats:
- one is time with time zone or timestamp with time zone and
- another input comes with time without a time zone or timestamp without a time zone
The most commonly used date function in PostgreSQL is now (), date_part (), age (), extract (), date_trunc (), to_char (), and to_timestamp ().
All PostgreSQL Date Functions
Below are the common date functions that are as follows.
- Now ()
- Now ():: date
- date_part ()
- age ()
- extract ()
- date_trunc ()
- current_date ()
- to_timestamp ()
- justify ()
We have using an employee table to describe the date function. Please find below the example to create an employee table.
CREATE TABLE Employee ( emp_id INT NOT NULL, emp_name character(10) NOT NULL, emp_address character(20) NOT NULL, emp_phone character(14), emp_salary INT NOT NULL, date_of_joining date NOT NULL, PRIMARY KEY (emp_id));INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (1, 'ABC', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (2, 'PQR', 'Pune', '1234567890', 20000, '01-01-2020');INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (3, 'XYZ', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 35000, '02-01-2020');INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (4, 'BBS', 'Mumbai', '1234567890', 45000, '02-01-2020');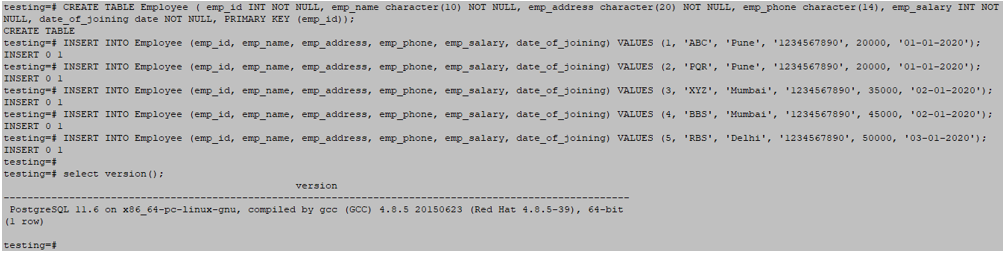
1. NOW ()
- We have used the now () function to select the current date.
- Now the function will return the date and time with the time zone from which the current transaction started.
- The return type of the now () function is timestamptz.
- Below are the syntax and examples of the now () function.
Syntax
Select now ();Example
INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (7, 'RBS', 'Delhi', '1234567890', 50000, now());
select now();
select * from Employee where emp_id = 7;
select now() - date_of_joining as no_of_day from employee;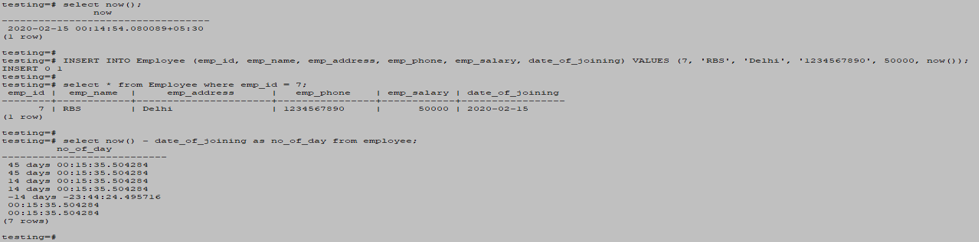
2. Now ():: date
To select the date without a timestamp at the same time, we have to use the now ():: date function.
Below are the example and syntax of the now ():: date function.
Syntax
Select now ():: date;Example
select now()::date;
INSERT INTO Employee (emp_id, emp_name, emp_address, emp_phone, emp_salary, date_of_joining) VALUES (8, 'RBS', 'Delhi', '1234567890', 50000, now()::date);
select now()::date - date_of_joining as no_of_day from employee where emp_id=1;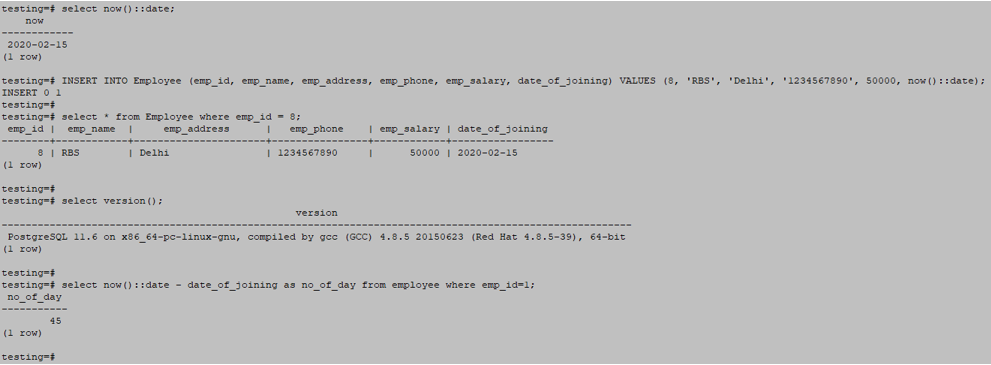
3. Date_part ()
The return type of the date_part () function is a double-precision value.
To get the timestamp field or an interval like the year, month, or day of that time, we use the date_part () function.
Below is the example, and the syntax of the date_part () function is as follows.
Syntax
Date_part (subfield (month, day, year) from timestamp)Example
select date_part('days', now() - date_of_joining) as days from employee limit 3;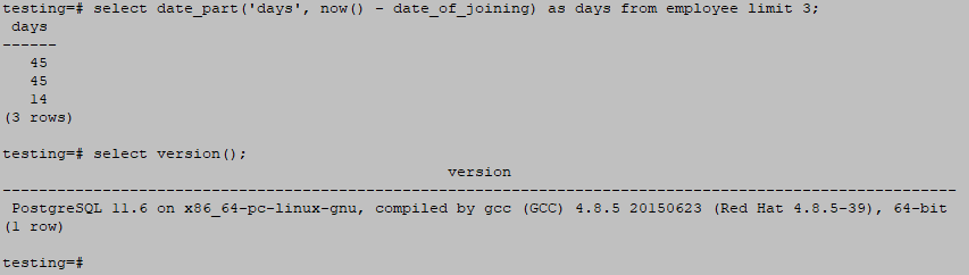
4. Age ()
We have found an interval between two dates using the age () function in PostgreSQL.
The return type of the age () function is an interval.
It will calculate ages between two timestamps’ current date and timestamps; after calculating, it returns symbolic results.
Below is the example and syntax of PostgreSQL’s age () function.
Syntax
Age (timestamp)Example
select age(date_of_joining) from employee limit 3;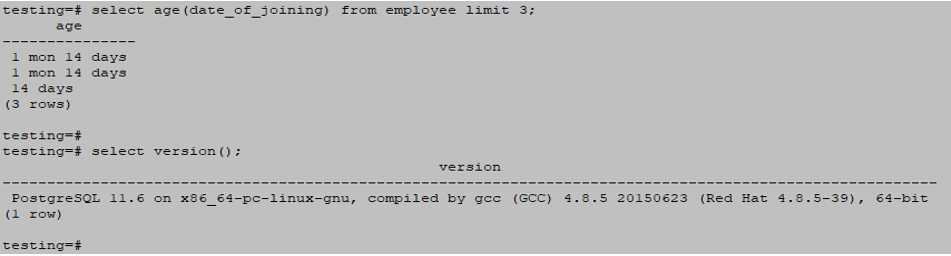
5. extract ()
The return type of the extract function is a double-precision value.
The extract () date function is the same as PostgreSQL’s date_part () function.
This function allows us to isolate the date between the date, month, and year fields. The extract () function isolates the date between different parts.
Below are the syntax and examples of PostgreSQL’s extract () function.
Syntax
Extract(subfield(month, day, year) from timestamp)Example
select extract (year from date_of_joining) from employee limit 3;
select extract (month from date_of_joining) from employee limit 3;
select extract (day from date_of_joining) from employee limit 3;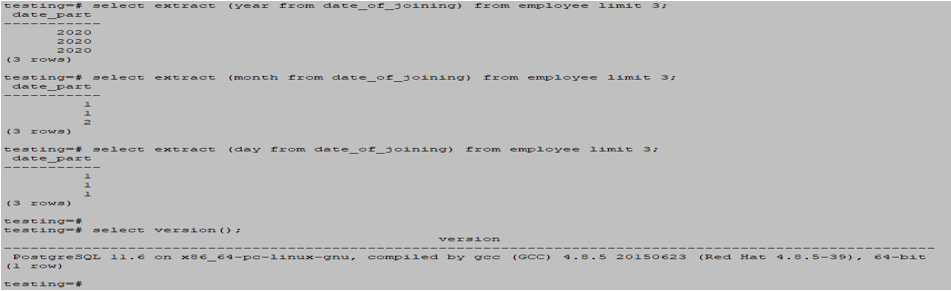
6. date_trunc ()
- The return type of the date_trunc () function is a timestamp. Date_trunc () function timestamp truncated to a specific precision.
- Below is the example, and the syntax of the date_trunc () function is as follows.
- Date_trunc () function is used to truncate in specified precision.
Syntax
Date_trunc (field (month, day, year) from timestamp)Example
SELECT date_trunc ('year', timestamp '2020-02-15 11:30:45');
SELECT date_trunc ('month', timestamp '2020-02-15 11:30:45');
SELECT date_trunc ('day', timestamp '2020-02-15 11:30:45');
SELECT date_trunc ('hour', timestamp '2020-02-15 11:30:45');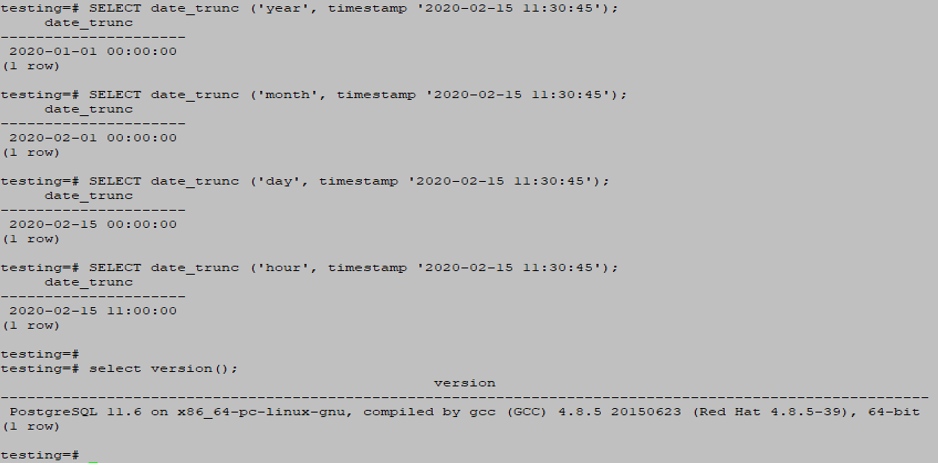
7. current_date ()
- The return type of the current date function is the date. Below is an example of the current_date () function in PostgreSQL as follows.
Syntax
select current_date;Example
select current_date;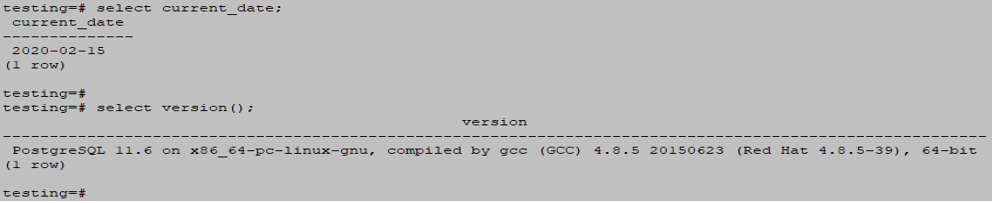
8. to_timestamp ()
- PostgreSQL will convert a string value into proper date format using the to_timestamp () date function in PostgreSQL.
- Below are the example and syntax of the to_timestamp date function in PostgreSQL.
Syntax
to_timestamp ()Example
select to_timestamp('202015FEB', 'YYYYDDMon') as valid_date;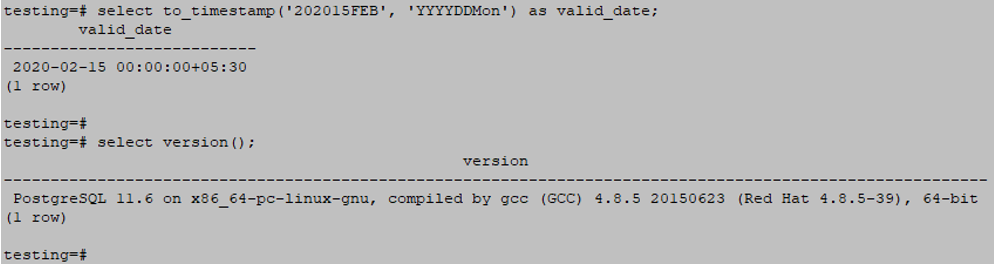
9. Justify ()
Below is the adjust interval of justifying the date function in PostgreSQL.
- JUSTIFY_DAYS (interval) – Adjust interval with 30 days time period.
- JUSTIFY_HOURS (interval) – Adjust the interval with 24 hours time period.
- JUSTIFY_INTERVAL(interval) – Adjust interval with days, hours, and additional sign adjustments.
Below is the syntax, and examples of justifying intervals are as follows.
Syntax
JUSTIFY_DAYS (interval)Example
SELECT justify_days (interval '65 days');
JUSTIFY_HOURS (interval)Example
SELECT justify_hours (interval '55 hours');
JUSTIFY_INTERVAL(interval)Example
SELECT justify_interval (interval '2 mon -5 hour');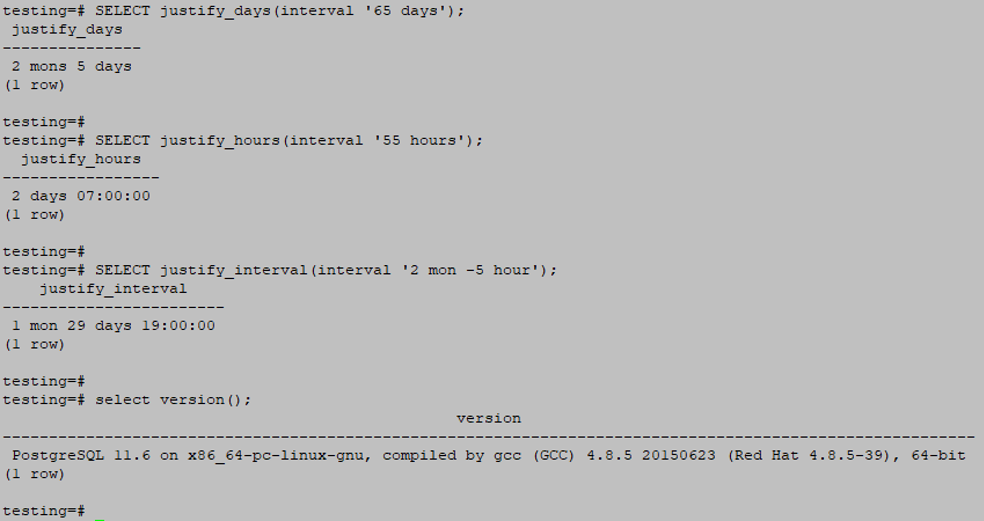
Conclusion
Date functions are very important and useful. In PostgreSQL variety of date functions are available, but mainly now (), current_date (), date_part (), extract (), age (), justify (), date_trunc (), to_timestamp (), and to_char () date functions used.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Date Functions” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.

