Updated May 22, 2023
Introduction to Postgres Rename Table
Whenever we perform manipulations on the table in the PostgreSQL database, we often feel the necessity to perform some changes on the existing table. We can add more columns to the table, modify the existing column and its related properties, add or remove the constraints, remove columns, rename the table or assign the default value to certain columns of the table, add or remove primary and foreign key constraints and rename the table. We can perform all these operations using the ALTER TABLE command in PostgreSQL. In this article, we will study the syntax of the ALTER TABLE command and view a few examples to understand how we can change the name of the table in the PostgreSQL database.
Syntax:
ALTER TABLE tableName
RENAME TO alteredTableName- tableName – This is the name of the table that exists in your current PostgreSQL database that you wish to rename.
- AlteredTableName – This is the name you want to assign to the table with tableName and rename the same.
Example of Postgres Rename Table
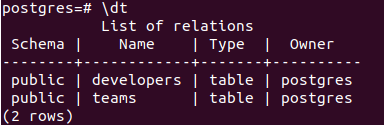
Let us begin by creating a new table named educba, which will store the data related to the corporation after checking all the present tables in our current DB by using \dt command –
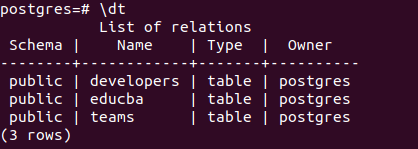
\dtCREATE TABLE educba
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
technologies VARCHAR,
workforce INTEGER,
address VARCHAR);Check whether the table is created by \dt command that gives output –
\dtWe can rename the name of the table using the alter table command. To rename the name of the table educba to educational_platforms, we can use the syntax mentioned above of alter table command in the following way –
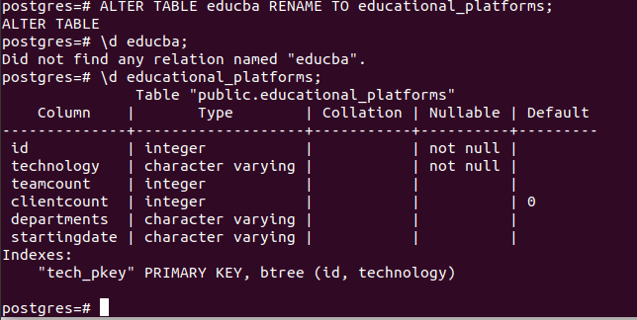
ALTER TABLE educba RENAME TO educational_platforms;Let us check using \d command after firing the above command to describe the educba and educational_platforms table. This gives the following output –
\d educba;
\d educational_platforms;
As can be seen that the educba table cannot be described as it has been renamed, and now none of the tables named educba exists in our database. After describing the educational_platforms, it contains the same structure and keys as that of our previously created educba table. Hence, we can conclude that our table has been renamed successfully.
Let us see what happens if we try to alter the table not in our database, say SQL demo.
ALTER TABLE SQL demo RENAME TO education;This will result in the error after executing the above command output as follows –
Error saying relation name SQL demo does not exist given as the output of executing the above command. To avoid such an error, we can use the IF EXISTS statement in our alter table syntax in the following way –
ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS tableName
RENAME TO alteredTableName;This will prevent the system from throwing an error if none of the tables named tableName exists in the current database. Instead, the system will raise the notice saying no such table exists. Let us try to execute the following query statement –
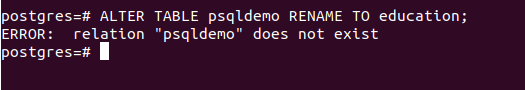
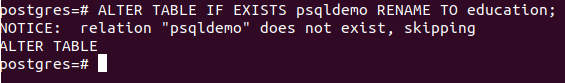
ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS psqldemo RENAME TO education;Execution of the above query statement gives the following output –
As the tables are referred to as the relations in the PostgreSQL database server, a notice saying – “relation name psqldemo does not exist and hence the alter table command execution is being skipped” is produced.
Let us create a table name psqldemo and then try to alter it using the above-mentioned syntax, including IF EXISTS.
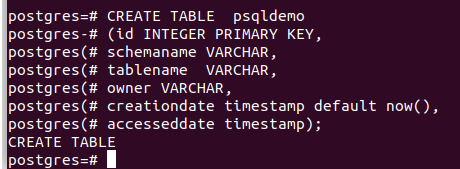
Create a table named psqldemo containing columns such as id, schemaname, tablename, owner, creationdate, and accesseddate using the following query statement –
CREATE TABLE psqldemo
(id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,
schemaname VARCHAR,
tablename VARCHAR,
owner VARCHAR,
creationdate timestamp default now(),
accesseddate timestamp);Executing the above command on the PostgreSQL command prompt gives the following output –
Let us now try to rename the psqldemo table to education using the alter table syntax ith if exists a statement in it. The query statement will be as follows –
ALTER TABLE IF EXISTS psqldemo RENAME TO education;after executing the query, the output is as follows –
Let us try describing the psqldemo and education tables and see the output –
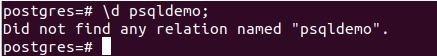
For describing the psqldemo, fire the following command –
\d psqldemo;that now results in the following output –
Output saying that none of the relation named psqldemo exists in the current database.
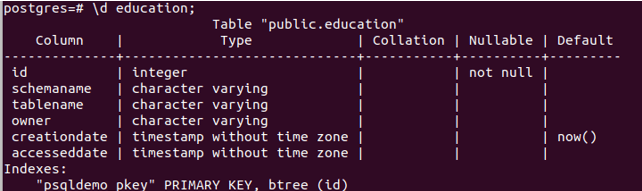
Describing the education table using the following query statement
\d education;gives the following output –
which resembles the structure and keys we assigned to the psqldemo table that we created and later renamed. Hence, our table is renamed successfully.
Points to Remember
There are some points that you should keep in your mind while renaming any table in PostgreSQL. They are as listed below –
- Whenever we rename the table, the dependent objects on the table, such as views in which that table was used, any foreign keys the table has, and all other constraints and indexes, are automatically updated.
- If you want to rename multiple database tables, we cannot fire a single alter command for them. Each of the tables needs to be renamed separately using an altered query for each table.
- When you rename a table, all the contents of the table remain unaffected and unchanged.
- Whenever the table that does not exist is tried to be renamed using the if exists statement, the execution flow does not go for renaming the table. It first checks the presence of the table and raises the notice in its absence, and terminates execution.
Conclusion
We have a versatile and variable ALTER TABLE command in the PostgreSQL database that can add, remove, and modify the columns, their datatypes, and constraints such as not null, default, etc. We can use this method to rename the name of the table present in our current Postgres database. To avoid throwing the error when attempting to rename the table that does not exist in our database, we can use the IF EXISTS statement that helps raise a notice saying no such relation, i.e, the table exists in the database with the specified name. We should maximize the utilization of such commands available in PostgreSQL to prepare efficient, robust, and consistent PostgreSQL databases.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Postgres Rename Table” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.