Updated May 18, 2023
Definition of PostgreSQL Current Date
We can get the current date by using the PostgreSQL current_date function. The PostgreSQL current_date function does’t accept any arguments or parameters. Even if the PostgreSQL current_date is a function but it is not required to add parentheses () after the PostgreSQL current_date function. The PostgreSQL current_date function will return the current date, which is in a ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ format. We can use the PostgreSQL current_date function with the versions of PostgreSQL such as PostgreSQL 8.4, PostgreSQL 9.0, PostgreSQL 9.1, PostgreSQL 9.2, PostgreSQL 9.3, and PostgreSQL 9.4 etc. The PostgreSQL current_date function will have different dates as per the execution date of the PostgreSQL current_date function.
How does the PostgreSQL Current_date function work?
As we know, the PostgreSQL Current_date function returns the current date, which is in a ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ format which means,
- YYYY defines the year, which is four-digit.
- MM defines the month which is two-digit,
- DD defines the day on which is two-digit.’
In order to understand the working of the PostgreSQL Current_date function, let’s consider the following examples of the PostgreSQL current_date function.
- Consider the following, which will return the current date in the ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ format.
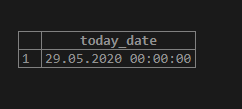
SELECT current_date AS today_date;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot:
In the above example, we will get the format which works as follows :
- YYYY defines the year which is four-digit ‘2020’,
- MM defines the month which is two-digit ’05’,
- DD defines the day, which is a two-digit ’29.’
- We can perform arithmetic operations like add or subtracts on the current date, Consider the following example to understand the PostgreSQL current_date function with add or subtracts.
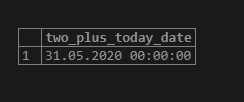
SELECT current_date + 2 AS two_plus_today_date;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot:
In the above example, we will get the format which works as follows :
- YYYY defines the year which is four-digit ‘2020’,
- MM defines the month which is two-digit ’05’,
- DD defines the day, which is a two-digit ’31.’
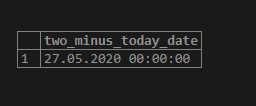
SELECT current_date - 2 AS two_minus_today_date;Illustrate the result of the above statement by using the following snapshot:
In the above example, we will get the format which works as follows :
- YYYY defines the year which is four-digit ‘2020’,
- MM defines the month which is two-digit ’05’,
- DD defines the day which is two-digit ’27.’
In the above examples, we can see the PostgreSQL current_date function returns a current date by adding or subtracting days which is equal to the number mentioned after (-) or (+) sign.
- We can use the PostgreSQL current_date function in table creation as well. We can give a default value to the column by using the PostgreSQL current_date function. The PostgreSQL current_date function will have different dates as per the execution date of the PostgreSQL current_date function.
Consider the following example where we will create a table named ‘Employee’, and this table will have column ‘joining_date’ with data type as DATE. The column ‘joining_date’ will have a default value set to the current date as we are using the PostgreSQL current_date function to set a default value, which is the result of the PostgreSQL current_date function.
Consider the following CREATE TABLE statement, which will create a table named ‘Employee’.
CREATE TABLE Employee(
Employee_id serial PRIMARY KEY,
Employee_name varchar(255) NOT NULL,
joining_date DATE DEFAULT CURRENT_DATE
);Now, we will insert a row into the Employee table by using the INSERT INTO statement as follows:
INSERT INTO Employee(Employee_name)
VALUES('Jacob Petter');In the above INSERT INTO statement, we have not specified the joining date, hence the PostgreSQL sets default value as the current date.
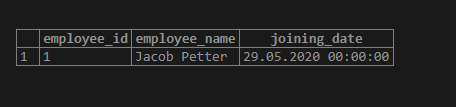
Illustrate the result of the Employee table by using the following currency symbol and a snapshot.
SELECT * FROM Employee;In the above example, for the date of joining, we have used CURRENT_DATE, the format which works as follows :
- YYYY defines the year which is four-digit ‘2020’,
- MM defines the month which is two-digit ’05’,
- DD defines the day which is two-digit ’29’
As per the SQL query execution date, the Employee table will have different dates inserted in the ‘joining_date’ column. Like, if someone is joining a company tomorrow and we execute the insert into a SQL statement, as explained above, the date of joining will be tomorrow’s date.
Conclusion – PostgreSQL Current Date
We hope from the above article, you have understood how to use the PostgreSQL Current date and how the PostgreSQL PostgreSQL Current date works. Also, we have added several examples of PostgreSQL PostgreSQL Current date to understand it in detail.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL Current Date” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.