Updated May 22, 2023
Introduction to Postgres Dump Database
If you are using the PostgreSQL database in the production environment for your clients, you need to ensure that your database is always working fine and is available 24 * 7. For the availability of the database, you must often keep a backup of your client’s database. You should have the ability to restore the data in the database in case of corruption, crashes, or loss. For this reason, PostgreSQL provides us with a facility to dump the database using the pg_dump utility. The advantage of this utility is that it is not server-side version specific and can work even on the machine having different architectures. For example, if you dump your database from a 32-bit architecture machine and then use it in a 64-bit machine, it will work fine.
To maintain an updated database backup, it is advisable to regularly perform database dumps. Restoring the backup brings the database back to the state it had at the time of creating the dump file using pg_dump. One more advantage of using the pg_dump utility instead of file-level backups and archiving is that it is not specific to the version of the PostgreSQL server.
Additionally, while pg_dump is running, it does not lock the database operations, allowing them to continue running in the background. However, the execution of certain operations related to structural changes, like ALTER TABLE, faces restrictions. You will have to specify external -o in the pg_dump command in case if your database schema depends on OIDs such as foreign keys. For this, you will also need to dump the OIDs.
Syntax for Postgres Dump Database:
pg_dump databaseName > outputFile- pg_dump – It is the utility program provided in PostgreSQL to store the current state of the database into a file containing commands which, when run on the database server, will recreate the state of the database when it was dumped using the same. It is a client-side program that must be run through the Linux command line prompt.
- databaseName – It is the database name you want to dump.
- outputFile – It is the file name that must be created after the dumping is finished.
Only the superuser login has the exclusive privilege to execute the pg_dump process, as it holds the required permissions to read all databases and tables. Although, you do have a facility to dump the database remotely. By default, when connecting to the database, the system considers the environment variables PGHOST, PGPORT, and PGUSER as localhost, 5432, and the username, respectively. These values correspond to the operating system username.
You can change the PGHOST and PGPORT by using the options -h for the host and -p for the port in the pg_dump command. To change and override the PGUSER variable, you can use the -U option in the statement. The client authentication mechanisms verify and confirm all these factors.
For example
pg_dump postgres > myBackupFile
lsCheck whether the file is created successfully. Let us use the ls command, which lists all the files in the current directory –
Now, we have a prepared backup file named myBackupFile.
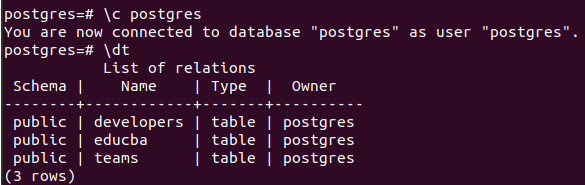
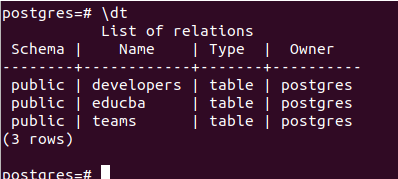
Let us see the contents of the Postgres database by checking all its tables with the help of \dt command.
\c postgres
\dtSo, it contains three tables which we will drop one by one. By using the commands
drop table educba;
drop table teams cascade;
drop table developers;
\dtand then further check whether all of them are deleted by \dt command.
So, now my database Postgres does not contain any tables in it. Now, we will learn how we can restore the data into the database.
Restoring the dump
Now, if we possess a backup file, we can restore the database at any time in case of corruption or loss. Before proceeding with the restoration, it is advisable to consider certain factors. The database you are trying to restore should be on the server. If not, then you should create the database with the help of the command
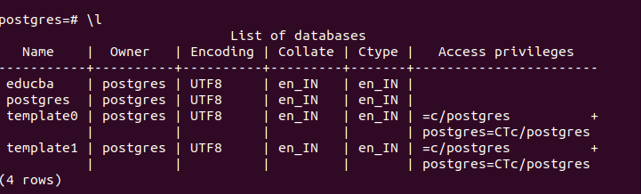
createdb -T template0 Postgresin our case. Since the database already exists, you can verify this by using the command \l, which will yield the following result from the database server. Therefore, there is no need to execute the createdb command now.
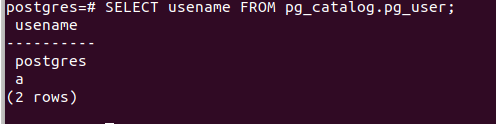
\lThe other thing is to ensure that the database you are restoring should already consist of all the users with the right to it. In our case, the Postgres user owns the Postgres database. Hence, a database server should already have a user named Postgres, or it will give an error while restoring. You can check this by firing the command –
SELECT usename FROM pg_catalog.pg_user;which results in the following –
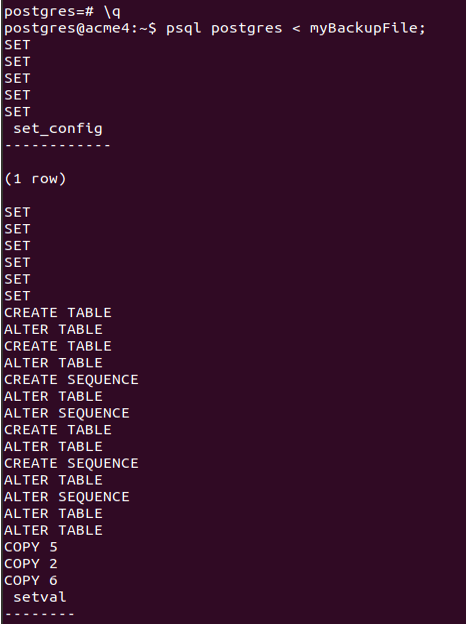
The Postgres database and user are already present on my server. I can go for restoring the database using the command –
psql postgres < myBackupFile;the syntax of restoring the dump is
psql empty_database < backup_filewhere empty_database is the database you want to restore, and backup_file is the file resulting from the pg_dump command.
psql postgres < myBackupFile;gives the output as follows.
Now, if we check the contents of the Postgres database using the command \dt, it gives the output as –
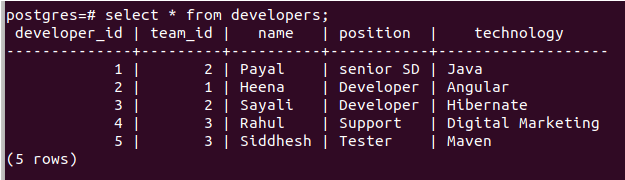
Also, the contents of all the tables are restored correctly –
select * from developers;Handling restoration errors
PostgreSQL continues the restoration process of the database even if any error occurs in between. It only tells about them at the end of the completion of restore. In this case, the database is restored incompletely. If you want to stop the restoration process on error occurrence, you can use –
psql --set ON_ERROR_STOP=on postgres < myBackupFileON_ERROR_STOP option helps you to stop the restoration process whenever the error occurs. You can establish the restoration process in a transactional manner by using the -1 or –single-transaction option. By using this option, you ensure that the restoration process restores the entire database either entirely or not at all.
psql -1 postgres < myBackupFileFor dumping all the databases in the current database server to a file, you can use the pg_dumpall utility program and provide the default database while restoration.
Conclusion: Postgres Dump Database
We can dump our database so that a backup is available in the near future to restore the database in case of any problem with data available from the database using pg_dump in PostgreSQL.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on the “Postgres Dump Database” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.