Updated May 22, 2023
Introduction to Postgres DROP Database
Whenever the data in the database is not important and not necessary to store it anymore or is an empty database that you wish to delete, you can delete that database completely using the DROP Database command or one available utility for that named dropdb. Deleting or dropping a database results in the permanent removal of the entire directory associated with that database, as well as the permanent deletion of its related information from the catalog entries. There is no way to rollback this query, hence you have to be very much sure and careful while using these commands.
In this article, we will learn how we can delete the database completely using available two methods of DROP Database statement and dropdb utility program one by one.
Syntax:
DROP DATABASE [IF EXISTS] nameOfTheDb;The above syntax contains the query statements DROP Database and other parameters in it can be explained in the following manner –
- IF EXISTS – It is an optional parameter. This keyword can be used to prevent any error resulting from using the above command when there is no database in the current database server with the name “nameOfTheDb”. If you use the “IF EXISTS” keyword in your query and none of the databases named “nameOfTheDb” exist in the current server, it will notify you about the absence without causing any errors.
- nameOfTheDb – It is the database name you wish to delete or drop and is located in the current database.
Notes:
To drop a database and comprehend its behavior, it is important to consider a few factors.
- We cannot delete the database if the database we are deleting has any active sessions associated with it.
- Furthermore, only the owner of the database can delete it.
- One more thing to remember is that the drop database query statement cannot be executed for the same database you are connected to.
- Once you delete the database, the actions cannot be undone. So be more cautious while doing so.
Example
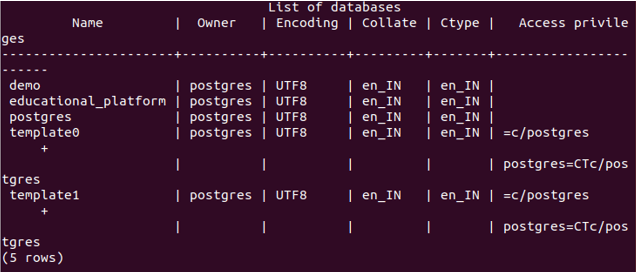
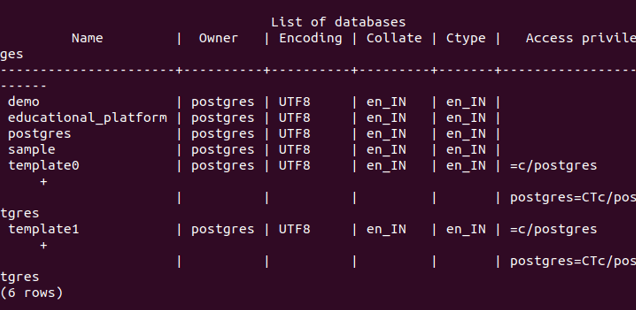
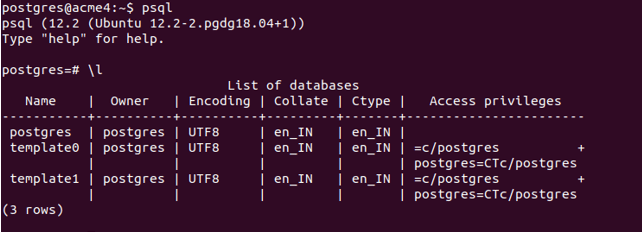
We can check all the databases present in our database server using the query \l, which results in the following output currently for my server –
\lAs can be seen, no database named sample is present in our database server.
Let us understand how we can use this command with the help of an example. First, we need to open our psql command prompt and then execute our statement. Suppose we want to drop the database named “sample”. So, my query statement will be as follows –
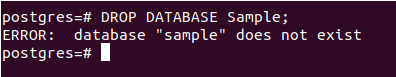
DROP DATABASE sample;It will result in the following output –
Upon observation, an error is generated indicating that there is no database named “sample” in the current database server.
Now what will be output if we use IF EXISTS for the same command like –
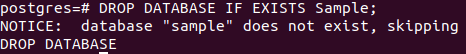
DROP DATABASE IF EXISTS sample;It will result in the following output –
We can see that instead of an error, it has thrown a notice to inform us that such a database does not exist.
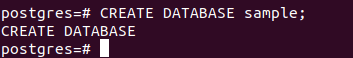
Let us create a “sample” database and perform the above query. We can use this command to create a new database for our purpose –
CREATE DATABASE sample;that will result in the following output –
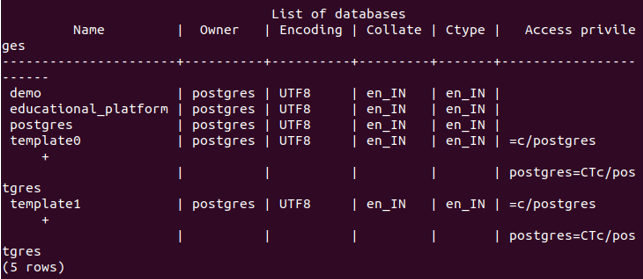
Let us check whether it is created successfully with the help of command \l, which results as follows –
So, our database now exists. This means running any of the above DROP commands won’t result in an error or notice. Let us check the output by firing the query itself.
DROP DATABASE sample;now results in –
Let us verify by checking all databases.\l gives the following output –
This means that our database is dropped successfully.
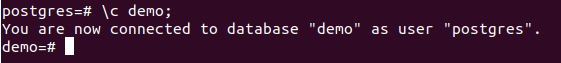
Let us try deleting a database with active connections. In this example, we will drop the database demo which already exists. You can even create a new database and try deleting it. For the database o have active connections, then we will open a new terminal with a psql prompt and then connect to the demo database using the \c demo; command.
\c demo;Now, returning back to my previous terminal, we will try to drop the demo database.
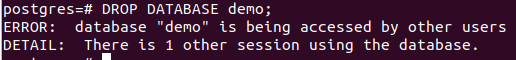
DROP DATABASE demo;As can be seen, it shows an error saying one session is already using the database named demo. Hence, it cannot be deleted. In such cases, we can drop the database by first checking all the activities associated with it and terminating them. We can see all the activities of the database from table pg_stat_activity.
Let us fire the following query –
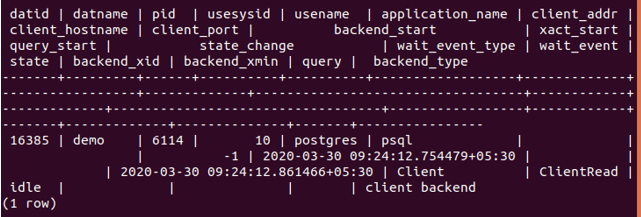
SELECT * FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE datname = 'demo';that give output –
One session is associated with the demo database. We can terminate all of them by using the query –
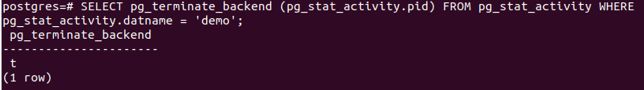
SELECT pg_terminate_backend (pg_stat_activity.pid) FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE pg_stat_activity.datname = 'demo';Let us drop our demo db now.
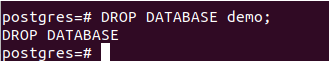
DROP DATABASE demo;And \l command now results in –
Hence, our database is dropped successfully.
dropdb command -We can even use the dropdb command for deleting the database. It works similarly to the DROP DATABASE statement. The advantage is that we can drop the database remotely using dropdb functionality, but it is necessary to be the owner of the database we are trying to drop. the syntax is as follows –
Dropdb [option.] nameOfTheDb;- nameOfTheDb – It is the name of the database that you wish to delete or drop and is located in the current database.
Options can be any of the following –
| Option | Description |
| -e | Echo commands. |
| -i | Whether to display the verification prompt |
| -V | For printing the dropdb version |
| –help | For getting help |
| -h host | Specify the host of the current system |
| -p port | Socket used by current established connections. |
| –if exists | Whether to show notice instead of error if the database does not exists. |
| -U username | User name using which to connect the database. |
| -w | If no password prompt required to be ask. |
| -W | If a password prompt is required to be ask before droping Database. |
| maintenance db-=dbname | Name od datbase to connect to for droping target database. |
Example of Postgres DROP Database
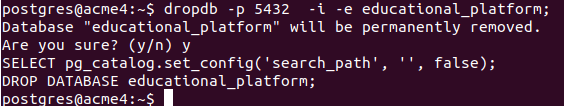
dropdb -p 5432 -i -e educational_platform;Note that dropdb command is shell command and not psql. You can open the psql command and execute the “\l” command to check whether a database has been deleted.
So, our database educational_platform is deleted successfully.
Conclusion- Postgres DROP Database
We can drop our database either by using the DROP Database statement or the dropdb utility. Be careful while doing so, as action cannot be undone.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on the “Postgres DROP Database” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.