Updated May 6, 2023
Introduction to PostgreSQL OFFSET
PostgreSQL offset is used to skip rows before returning a result of the query; suppose we have 100 records in the employee table, and we need to fetch the last 50 records from the table at that time we used to offset. The offset will skip the first 50 records and display the last 50 records as required. Offset is very important to skip rows before returning a query result. If we use the offset value as zero, it will return the same value; the offset condition is not used in this type of scenario.
Syntax
Below are some of the syntax.
Syntax #1 – PostgreSQL offset clause
select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name OFFSET N (Number of rows that we have skipping in query result)select * (select all table columns) from table_name OFFSET N (Number of rows that we have skipping in query result)Syntax #2 – Offset clause using limit clause
select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name OFFSET N (Number of rows that we have skipping in query result) LIMIT Nselect * (select all table columns) from table_name OFFSET N (Number of rows that we have skipping in query result) LIMIT NSyntax #3 – PostgreSQL Offset using order by clause
select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name ORDER BY column_name OFFSET N (Number of rows that we have skipping in query result)select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name ORDER BY column_name OFFSET N (Number of rows that we have skipping in query result) LIMIT Nselect column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name ORDER BY column_name DESC OFFSET N (Number of rows that we have skipping in query result)select column_name1, …, column_nameN from table_name ORDER BY column_name ASC OFFSET N (Number of rows that we have skipping in query result)Parameter
Below is the parameter description of the above syntax are as follows:
- Select: You can use the SELECT statement along with the OFFSET clause in PostgreSQL to retrieve no rows from a table.
- Column_name1 to column_nameN: We have selected a column to fetch data from the table using the offset clause.
- From: Keyword used to select the specified table to fetch data using the offset clause.
- Table name: Table used to fetch a specified record from the table using an offset clause.
- Asterisk (*): Asterisk is used to select all columns from the table to fetch data.
- Offset N: Offset clause used in PostgreSQL to skip the rows before returning the date.
- Limit N: You can use the LIMIT clause with the OFFSET clause in PostgreSQL to select a specified number of rows from a table.
- Order by: Order by clause used with an offset clause to fetch a record in ascending or descending order.
- ASC: Fetch data in ascending order by using order by an OFFSET clause in PostgreSQL.
- DESC: Fetch data in descending order by using order by an OFFSET clause in PostgreSQL.
How does OFFSET Clause work in PostgreSQL?
- In PostgreSQL, you can use the OFFSET clause to skip a specified number of rows before returning the query result.
- Suppose we have 1000 records in the student table, and we need to fetch the last 100 records from the table. At that time, we used offset in PostgreSQL.
- The offset will skip the first 900 records and display the last 100 records as required.
- Offset is very important to skip rows before returning a query result.
- If we use the offset value as zero, it will return the same value; the offset condition is not used in this type of scenario in PostgreSQL.
Examples to Implement PostgreSQL OFFSET
Below is an example of implementing offset as follows. We have used an employee table to describe the example.
Example #1
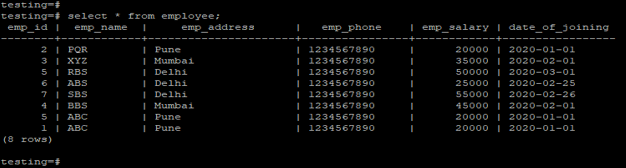
Employee table to describe the example of offset in PostgreSQL.
Code:
testing=# select * from employee;Output:
Example #2
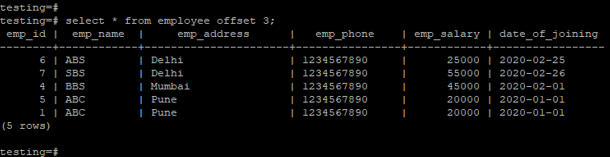
Example of offset by fetching data from all columns and skipping the first three columns. In the below example, we have fetched records from all columns and skipping the first three rows using offset.
Code:
testing=# select * from employee offset 3;Output:
Example #3
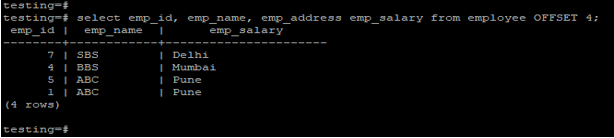
Example of offset by fetching data from a specified column and skipping the first four rows. In the example below, we have fetched records from specified columns and retrieved only from four columns using PostgreSQL limits.
Code:
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address emp_salary from employee OFFSET 4;Output:
Example #4
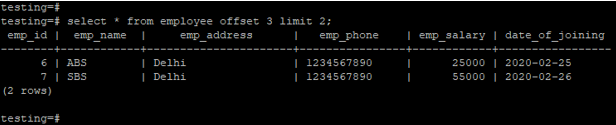
Offset clause by using a limit clause to fetch two records and skipping the first three rows. In the below example, we have to retrieve data from all columns and skipping the first three rows. We have used a limit clause with the offset clause.
Code:
testing=# select * from employee offset 3 limit 2;Output:
Example #5
Offset clause by using a limit clause to fetch data from the specified column and skipping the first three rows. In the example below, we retrieved data from the specified column and skipped the first three rows using the limit and offset clause.
Code:
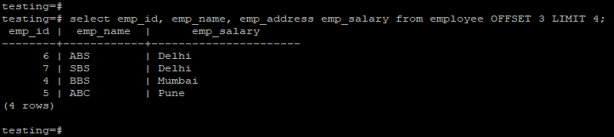
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address emp_salary from employee OFFSET 3 LIMIT 4;Output:
Example #6 – Offset using order by clause
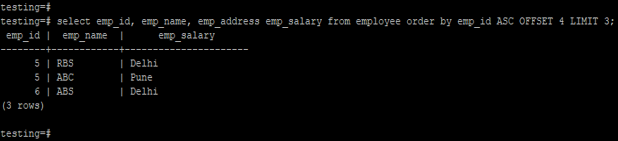
1. Fetch the data in ascending order by using order by.
Code:
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address emp_salary from employee order by emp_id ASC OFFSET 4 LIMIT 3;Output:
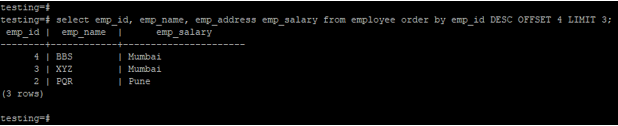
2. Fetch the data in descending order by using order by.
Code:
testing=# select emp_id, emp_name, emp_address emp_salary from employee order by emp_id DESC OFFSET 4 LIMIT 3;Output:
Advantages
Below are the advantages of offset are as follows.
- We can skip the rows using the offset clause before returning an output.
- The offset clause is used with the limit clause.
- The offset clause is used with an order by clause to fetch a record in ascending and descending order.
- Offset is very important in PostgreSQL.
- The offset clause is to skip specified rows and return the query result.
Conclusion
PostgreSQL offset clause is essential to skip the number of rows before returning the query’s output. The offset clause is used with a limit clause to fetch the specific number of rows. We can fetch data in ascending and descending order in the offset clause using order by clause.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PostgreSQL OFFSET” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.