Updated April 5, 2023

Introduction to PL/ SQL Formatter
Pl/ SQL formatter is basically used for restructuring and reorganizing the code which is written in PL/ SQL. Usually, this code, program, or set of instructions in PL/ SQL are referred to as the source code. In order to make the code more indented, properly spaced, beautified, and easy to read the formatter tools available format the source code, parse through the code, find out any syntactical errors if present and gives the proper spacings and the new lines wherever needed to make the code well-indented which results into an easy understanding and reading of code by the user. In this article, we will have a look at some of the formatting tools available on the internet which can help you to indent your PL/ SQL source code. We will also list out the features provided by each of the tools. At last, we will study an example of formatting the source code of Pl/ SQL by using an online editor.
Features of PL/ SQL Formatters
The general features provided by each of the formatting tools of PL/ SQL includes the following specified points –
- Execution is not affected after formatting the code which means the code executes in the same manner as it was doing before formatting.
- Even if you don’t have the oracle connection, you can still do a complete check over your syntax of the source code with the help of a formatter.
- We can customize the spacing and step distance while performing the indentation with the help of a formatter.
Tab column positions for arbitrary input can be specified in a formatter. - UNICODE, ASCII, and European ASCII encoding is followed by the output.
- Some of the formatters even provide the feature which can obfuscate the source code which scrambles the code and makes it difficult for another person to encode it. This feature is mainly used for security reasons.
- We can even pass the files which include the PL/ SQL source code instead of the raw queries, procedures, functions, etc.
Formatter Tools
There are many online formatting tools available that can beautify and indent your PL/ SQL source code. Let us have a look at some of them here listing the specialties of each of them and links to access them.
- Code Beautify – This formatter tool comes with the provision to download the formatted code and we can even remove the comments and minify the SQL code by using this tool available online. Link used for accessing this tool is this one.
- Red Gate SQL prompt – It comes with various options of styling including collapsed, default, commas before, right-aligned, and indented. The prominent features of this tool are that it creates completely sharable and customized formatting, a library of code snippets is provided, we can refactor the SQL code, analysis of code can be dome very comprehensively, tab history and coloring and code completion of advanced IntelliSense-style. Link used for accessing this tool is this one.
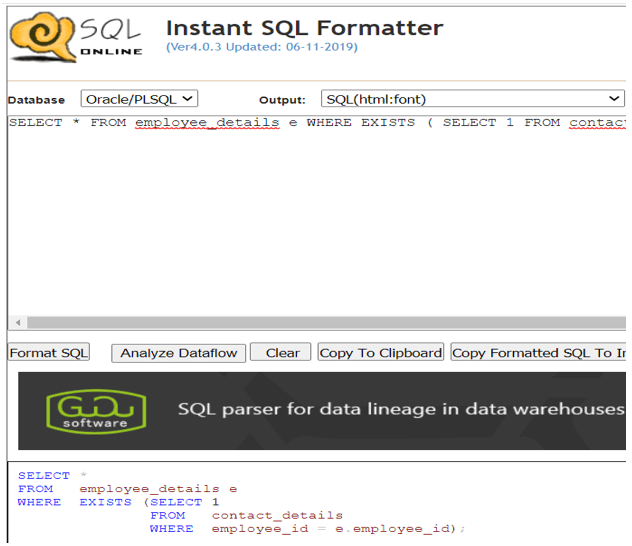
- Instant SQL formatter – This formatting tool comes along with the provision to choose the database you are using such as MSACCESS, MYSQL, MSSQL, Oracle/ PLSQL, etc. As we want the formatter for PL/ SQL code, we can choose the option of the database as Oracle/ PLSQL. Along with that this formatter also asks you to choose the output type, you can choose any of your preferred formats from the drop-down list and paste the PL/ SQL source code that you want to format. After clicking on the Format SQL button the formatted PL/ SQL code will be generated which you can copy to the clipboard if you want. Link used for accessing this tool is this one.
Example
Let us consider one example for the same. Suppose that, we have the following PL/ SQL code to be formatted by this formatter.
SELECT * FROM employee_details e WHERE EXISTS ( SELECT 1 FROM contact_details WHERE employee_id = e.employee_id);After we paste this code on that formatter and format it, we will get the following output shown in the below image. We can see how clear and easy it becomes to read and understand the formatted code.
Allround Automation’s Pl/ SQL Beautifier – This beautifier comes with the provision of defining the set of rules at the user level which will be in turn used while formatting and beautifying the coed. We can even make the settings that will format and beautify the code automatically while the file is opened or while saving your code or while compiling the PL/ SQL source code. Link used for accessing this tool is this one.
SQL formatter – The important feature of this editor is that it provides you the feature to choose the file which includes your Pl/ SQL code to be formatted. Link used for accessing this tool is this one.
Tutorials point online SQL formatter – This tool also provides you the feature of directly specifying your source code or uploading the file containing the same. After formatting, you can even download the formatted code. Link used for accessing this tool is this one.
Advantages
The advantage of using a formatter for your PL/ SQL source code is that when you are working on a project which includes multiple persons working on the same application. IF over there, you spend a lot of time understanding the code and the program written in Pl/ SQL by any of your colleagues. Then most often you try to reformat the code to understand and read it better.
If you go for doing the reformatting manually, it will consume your unnecessary time of yours. Instead, you can make use of any of the above-mentioned formatters and get your source code formatted instantly. Along with the above-mentioned tools, there are many other tools available out there that will help you in formatting your Pl/ SQL code.
Conclusion
We can beautify and format our PL/SQL source code to make it properly spaced, well indented, and beautified in order to read and understand the code easily and quickly. There are many tools available online which can beautify and format the PL/ SQL code along with the syntax check. You can either directly specify your Pl/SQL source code there or can upload a file containing your PL/ SQL program.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “PL/ SQL Formatter” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


