Updated February 28, 2023
Introduction to Oracle Window Functions
Window Functions in Oracle performs aggregate function like operation but like in case of aggregate functions the result set groups query rows into a single row whereas if window function is applied the window function returns a result for each query row (query rows are rows on which function will be applied) meaning window operations do not collapse group of query rows into a single row but the result set returned by the window function contains result for each row which helps in performing data analysis calculations which gives it an edge over aggregate functions.
Oracle Window Functions
Below are the functions
OVER clause
The over clause is permitted for many aggregated functions. In the first example, we have a table named sales which consist of sales details based on the country and the year. If we use the aggregate function SUM (), it will return us a result set with a single row but we do not want the output to be of the single row instead we want it to have a result for each row. Let us look at the query for the same.
Code:
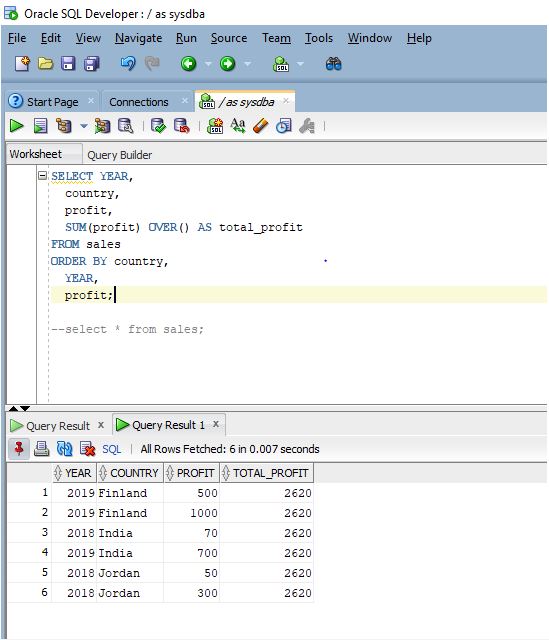
SELECT YEAR,
country,
profit,
SUM(profit) OVER() AS total_profit
FROM sales
ORDER BY country,
YEAR,
profit;
Output:
Explanation: In the above query if you see we have used over clause which treats the query set as a single row meaning the query calculates the total sum but it does for each row as it will display the total sum with each row. As we can see in the output screenshot the window function produces a global sum but for each row.
PARTITION BY
This clause is used to split the result set into partitions on which window function is applied. In this example, we will use the PARTITION BY clause with the OVER BY clause. The aim of this example is to get the total profit from the sales table based on the country using a window function along with the aggregate function SUM(). We will use our previous table sales from the first example. Let us look at the query for the same.
Code:
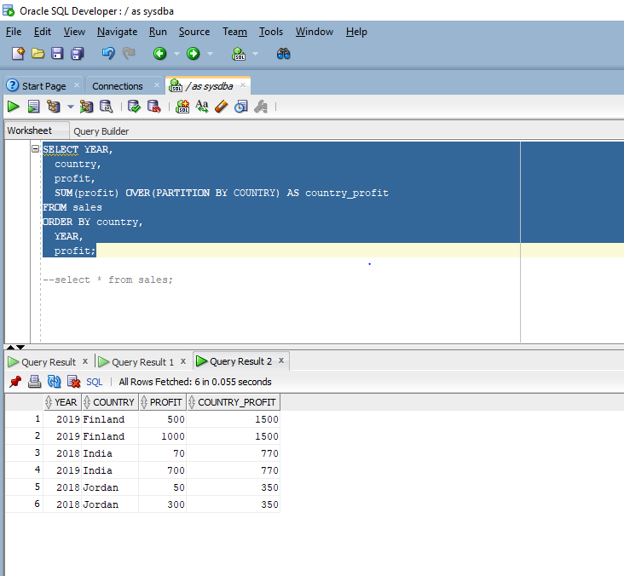
SELECT year,
country,
profit,
SUM(profit) OVER(PARTITION BY COUNTRY) AS country_profit
FROM sales
ORDER BY country,
year,
profit;
Output:
Explanation: If we see the above query, there is a slight difference from the one we used in the first example. Here we have used the PARTITION BY clause inside the OVER clause. This partition clause splits the rows by country and then producing the sum per country unlike in the previous case where it was producing a global sum for each row. The Partition BY clause allows the function to produce the sum for each partition row. As we can see in the output screenshot the window function produces the sum based on each country or for each partition row.
Row_Number ( )
This is a ranking type window function that assigns incrementing integers to each row or each row of the partition to which it is applied. We can use row_number function with non- aggregating functions also. In this example, we will use row_number function to find the rank/row number of profit based on the year and partitioned on the basis of country. So, each country is a partition. Let us look at the query.
Code:
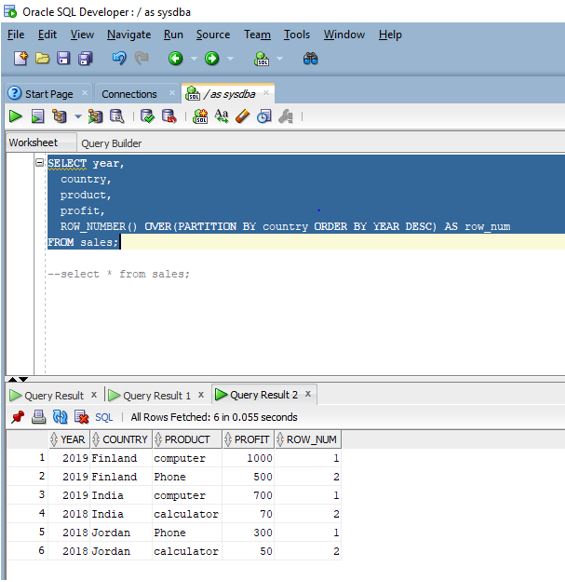
SELECT year,
country,
product,
profit,
ROW_NUMBER() OVER(PARTITION BY country ORDER BY YEAR DESC) AS row_num
FROM sales;
Output:
Explanation: As we can see in the query the partition by clause is used to partition the row set based on the country and then we are using order_by clause to sort the partition rows based on the year in descending order. The row_number () function then generates a unique incremental rank number. As per the above output screenshot we can see that in the result set, the row number is displayed for each row of each partition.
RANK ( ) function
The rank ( ) function is also a type of ranking function also used as an analytical function. It calculates the rank of a value in a set of values. The rank is same for the same values. In this example, we are going to use the RANK ( ) function to calculate the rank based on the profit. For this we first partitioned the rows on the basis of the country so each country is one unique partition and then we use order by clause to sort it into descending order based on the profit column and then apply the rank () window function on that. Let us look at the query below
Code:
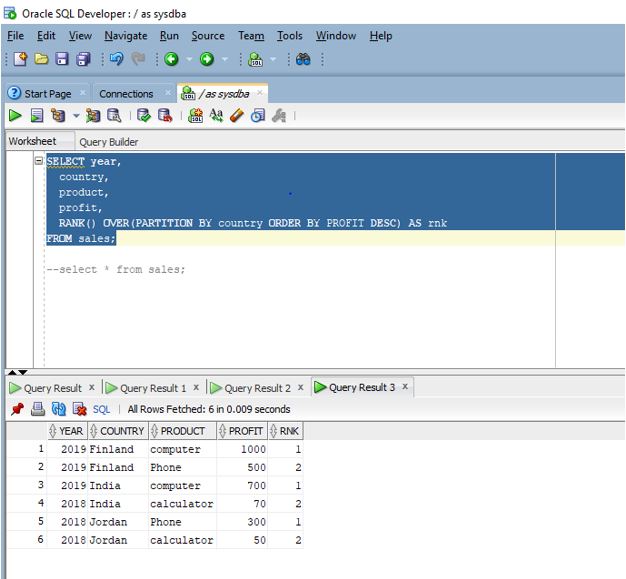
SELECT year,
country,
product,
profit,
RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY country ORDER BY PROFIT DESC) AS rnk
FROM sales;
Output:
Explanation: As we can see in the above screenshot each row is provided with a rank.
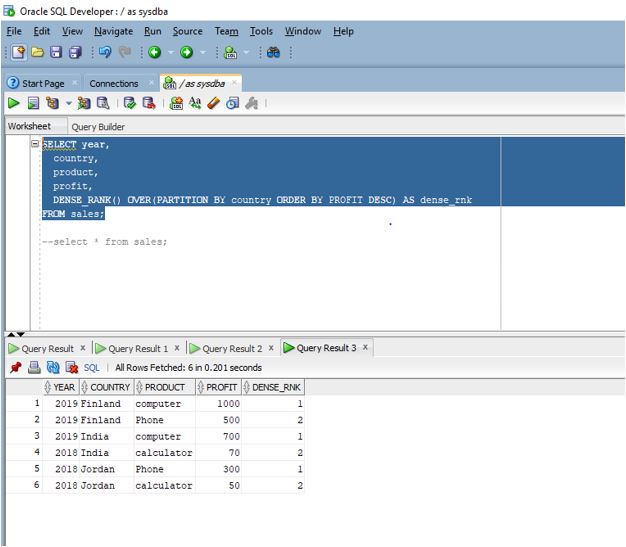
DENSE_RANK ( ) function
The DENSE_RANK ( ) function is also a type of ranking function which calculates the rank of a value in a set of value and same values gets the same rank. The difference between rank () and dense_rank () is that in case of dense_rank () function, we get rank values as consecutive integers meaning that the next consecutive rank is not skipped in case of ties. Let us rerun the previous example with dense_rank () function instead of rank () function
Code:
SELECT year,
country,
product,
profit,
DENSE_RANK() OVER(PARTITION BY country ORDER BY PROFIT DESC) AS dense_rnk
FROM sales;
Let us execute the query in SQL developer.
Output:
Explanation: As we can see in the above screenshot each row is provided with a rank.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the definition of windows function, and then we discussed about the various types of windows function that are available in the oracle and also went through the various examples based on those cases to help us understand better.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle Window Functions. Here we discuss an introduction to Oracle Window functions, examples with code and output. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –