Updated February 14, 2023
Introduction to Oracle SYSDATE()
The Oracle SYSDATE( ) function can be defined as a built-in function with no arguments in Oracle database which is used to return the current date and time set for the operating system on which the particular oracle database is installed and the data type returned in the output is of type DATE with the format which depends on the value of NLS_DATE_FORMAT initialization parameter and this function cannot be used with any CHECK constraint.
Syntax
So, after discussing the definition of the SYSDATE function, we will now look at the syntax of the function. The syntax is simple.
SYSDATE
As, we can see in the above syntax there are no arguments associated with the SYSDATE function.
How does Sysdate Function Work in Oracle?
The SYSDATE function is one of the basic functions in oracle to find out the date based on the local system date. So, we can use SYSDATE function with SELECT statements in Oracle. One important point that we need to remember while using SYSDATE is that it cannot be used in the condition of the check constraint. So, when we execute a SELECT query having SYSDATE function. It extracts the system date which is the current date and time as shown in the local system or laptop where the Oracle database is installed and the same is returned in the output.
Examples to Implement Oracle SYSDATE()
Let us now look into various examples for Oracle SYSDATE function:
1. Sysdate Function to Get Date
In this scenario we will use the SYSDATE function to get the date of the current system in which the database is stored. So in this example we will see the current date of the system in which the database is stored. We are going to use a select statement with a dual table. Dual table as we know is a one-row one-column table present by default in the oracle database. Let us create a simple query for it.
Code:
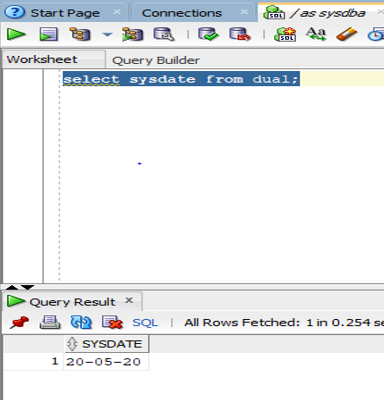
select SYSDATE from dual;
Output: Let us now run the query in SQL developer and check the result.
As we can see that the data is displayed in the output.
2. Using Sysdate to Calculate Age
In this scenario we will see how we can calculate the age of any person using the SYSDATE function. In order to do that we will see an example in which suppose the date of birth of a person is 12th April 1992. So we are going to use the SYSDATE function to calculate the age of the person on the present day. So, let us create a simple query using SYSDATE to get the age of the person.
Code:
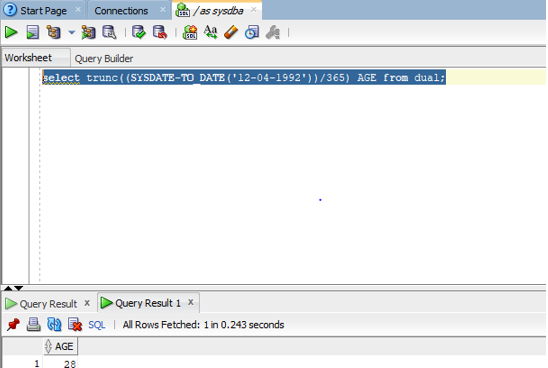
select trunc((SYSDATE-TO_DATE('12-04-1992'))/365) AGE from dual;
Explanation: In the above query first we are converting the string type date of birth to DATE type as SYSDATE is DATE type value. After converting we subtract them and then divide the whole difference by 365 as there are 365 days in a year and TRUNC function which is a built-in function helps us to return the year.
Output: Let us run the query in SQL developer and check the result.
As we can see in the above output screenshot the YEAR is returned in the output after the function is executed successfully
3. Sysdate Function Used with Where Condition
In this scenario we will discuss the fact that we can use SYSDATE function with conditional statements like WHERE clause with the SELECT statement. The example, in this case, will be extracting the employee id, employee name, and the SYSDATE when the query is being executed where the condition is that the employee should be from the Union Territory of ‘Delhi’. Let us create a query for this scenario.
Code:
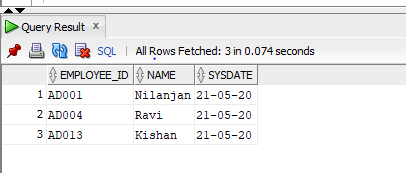
select employee_id, name, sysdate from employee where city ='Delhi';
Output: Let us now execute the query in SQL developer and check the result.
4. Using TO_CHAR with Sysdate to Extract only The Day of The Date
In the previous scenario and its examples we have seen how we can use the SYSDATE function with SELECT statement along with WHERE condition. In this scenario we will see how we can use a TO_CHAR function along with SYSDATE function to extract only the day from the SYSDATE function. One important note is that the value returned will not be DATE value as we are using TO_CHAR function. It will be a string value. The example is to extract the employee name, employee id and current day from the employee table where the city of the employee is ‘Mumbai’. Let us create a SELECT query for this task.
Code:
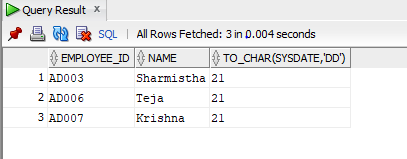
select employee_id, name, TO_CHAR(SYSDATE, ‘DD’) from employee where city ='Mumbai';
Output: Let us now execute the query in SQL developer and check the result.
As we can see in the above screenshot it shows only the day in the third column of the result set.
5. Using Sysdate with Insert Statement
In the previous examples we have used only SELECT statements. In this case we are going to use a DML statement like INSERT statement as the SYSDATE function can be used to insert current date and time in the columns of the employee table. In this example we will insert date and time into the column of a table employee. Let us create a DML query for the same.
Code:
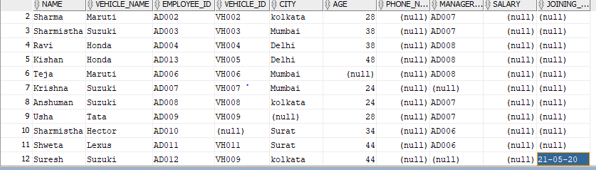
INSERT INTO employee VALUES('Suresh',Suzuki,'AD012', 'VH002', 'kolkata', '44', null, null , null, sysdate);
Explanation: As we can see in the above query the sysdate function is used in the insert statement. This function will insert the current date in the last column of the employee table.
Output: Let us run the query in SQL developer and check the result.
As we can see in the output the SYSDATE function inserts the current date and time in the table.
Conclusion
In this article we discussed the definition and syntax of the SYSDATE function and how it works in the Oracle database. Later on, in the article we discussed the various scenarios along with an example for each scenario to understand better.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle SYSDATE(). Here we discuss an syntax, how does Oracle SYSDATE() work with examples to implement. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –