Updated March 3, 2023
Introduction to Oracle Bitmap Index
Oracle Bitmap Index is a schema object which contains an entry for each value that appears in the indexed column(s) of the Table or Cluster. It provides direct and fast access to rows.
- An index is a schema object.
- An index is used by the Oracle server to speed up retrieval of rows by using a pointer.
- Indexes are independent of the table it Indexes, both logically and physically.
- The index is used and maintained automatically by the Oracle server.
- Indexes can be created or dropped at any time and do not affect the base tables or other indexes.
- When a table is dropped, the corresponding indexes are also dropped automatically.
- On one table more than one Index can be created, but this does not mean that more indexes lead to faster performance.
- Each DML operation that is committed on a table with Index means that the Index must be updated.
- Index reduces the disk I/O by using a rapid path access method to locate the data quickly.
Points of Concentration
- The Table or Cluster to be indexed must be in the OWN schema.
- Index object privilege should be available on the table to be indexed.
- Create an Index system privilege that must be available for the user who needs to create an index.
- Unlimited tablespace system privilege or space quota on space quota on tablespaces must be available.
- The Bitmap index stores ROWID’S associated with a key-value as a bitmap.
- Bitmap index can be a composite bitmap index.
- Composite Bitmap index gets created on multiple columns of a table.
- The composite bitmap index can be created upon a table to the maximum collection of 32 columns.
- Specify Bitmap to indicate that the index has to be created with a Bitmap Distinct Key in the table.
- Each BIT in the Bitmap corresponds to a possible ROWID.
- These indexes are used to tune queries that use non-selective columns in their limiting conditions.
- Bitmap index should be used only when the data is infrequently updated.
- Bitmap indexes add to the cost of all data manipulation transactions against the tables they index.
- The Oracle optimizer can dynamically convert Bitmap index entries to ROWID’s during the query processing.
Restriction on BITMAP Index
- Bitmap cannot be specified when creating a global partitioned index.
- Bitmap secondary index cannot be created on an index-organized table has a mapping table associated with it.
- Bitmap and Unique index cannot be specified at a time.
- Bitmap index cannot be specified for a Domain index.
- Bitmap indexes should not be used for tables involved in OLTP.
- Bitmap indexes increase the load factor on the internal mechanisms of Oracle to maintain them.
- Restricted with usage to tables involved in batch transactions.
Syntax
Creating an Index:
CREATE BITMAP INDEX IndexName ON Table (ColumnName) TABLESPACE
TableSpaceName;
Dropping an Index:
DROP INDEX IndexName;
Description
- IndexName: It can be any name of that Index object according to the Oracle naming convention.
- TableSpaceName: It is a logical storage name where that index object will be stored.
Examples of Oracle Bitmap Index
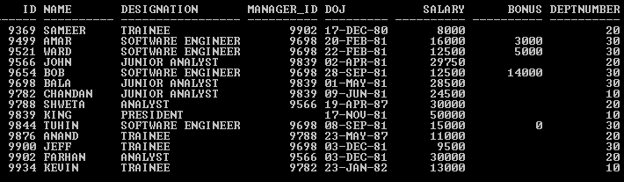
In this section, we’ll see the implementation of the Oracle BITMAP Index and its behavior. For that, we will use the below sample table (Employee) with 14 records to understand the Oracle BITMAP Index behavior.
SELECT * FROM Employee;
Output:
Example #1 – BITMAP Index
CREATE BITMAP INDEX EmpBitIndex ON Employee (Deptnumber);
Output:
The above create statement creates a Bitmap Index on Deptnumber.
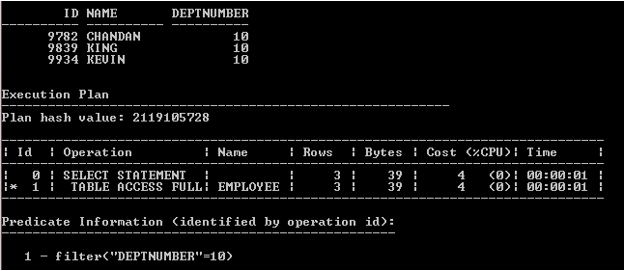
SELECT ID,Name,Deptnumber FROM Employee WHERE Deptnumber=10;
Output:
The execution plan clearly shows that the above statement does not use Index to access the rows because the oracle optimizer decides that when to use the Index.
Bitmap index adds only one bit to each row in the table being indexed to the size of the Bitmap pattern.
Each distinct value adds another row to the Bitmap index.
Example #2 – How to check Indexes
The index can be checked from the USER_INDEXES data dictionary.
SELECT Table_Name,Index_Name FROM USER_INDEXES WHERE
TABLE_NAME='EMPLOYEE';
Output:
Example #3 – Dropping Bitmap Index
The index can be dropped at any time but User needs to have drop privilege.
DROP INDEX EmpBitIndex;
Output:
In the above example, using a drop index syntax index gets dropped. So now the Employee table does not have any Index.
SELECT Table_Name,Index_Name FROM USER_INDEXES WHERE
TABLE_NAME='EMPLOYEE';
Output:
Example #4 – When to Use BITMAP Index
- Low cardinality column: It means any column which consists of less than 100 distinct values.
- Infrequently updated or Read-only tables: Bitmap indexes are good for the read-only tables or tables that do not get updated frequently. It is extensively being used in the data warehouse.
Tip:
- It is an expensive Index to maintain if distinct key values increase.
- It reduces performance if the distinct key values increases.
Conclusion
Oracle BITMAP Indexes are very useful for the static table or static column. It is also useful for the Materialized view. Need to take extra care about distinct key values to create a BITMAP index.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle Bitmap Index. Here we discuss the points of concentration, restriction on BITMAP Index with query examples. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –