Updated July 1, 2023
Introduction to Oracle UNIQUE Index
Oracle Unique Index (Index creates an entry in the database for each value that has been stored in the indexed column of a table to allow faster retrieval of data) can be defined as a unique index that does not allow the entry of duplicate values in that particular column which has been created with unique constraint as whenever we create a unique constraint on a column or create a primary key; the Oracle database automatically creates a unique index.
Syntax
Let us now look into the SYNTAX of the Oracle UNIQUE INDEX. The syntax is similar and almost similar to creating index syntax.
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX indexName ON
tableName (column1, column2, …);
Parameters
Below are the parameters of the Oracle UNIQUE Index:
indexName refers to the name of the Index the user wants to create.
tableName: It refers to the name of the table on which the user wants to create a unique index.
column1, column2, ..: It refers to the column names of the table on which a unique index will be created.
How does UNIQUE Index work in Oracle?
In the previous section of the article, we discussed the definition of the UNIQUE index. In this section, we are going to discuss how the Unique Index works in Oracle. A unique index is automatically created when we create a table with a unique constraint, but in case we want to explicitly create a UNIQUE index, we have to run the CREATE INDEX query. Once we execute the CREATE INDEX query, the particular column entry is provided in the database for all values assigned in the column, or, in other words, indexes are created. When a UNIQUE INDEX is created in a column of a table, the index does not allow any other duplicate index to be created for that column because since the column of the table already has a Unique constraint associated with it, the unique constraint does not allow any duplicate values to be inserted for that column.
Examples to Implement Oracle UNIQUE Index
In this section, we are going to discuss how we can create and use UNIQUE Index with the help of examples.
Example #1
ORACLE AUTOMATICALLY CREATES UNIQUE INDEX: Whenever we associate a column or columns with a primary key or unique constraint, the Oracle database automatically creates a unique index on the primary key or the unique key columns. In this example, we will create a table with two columns and assign unique constraints to one of them and then check whether UNIQUE INDEX has been created on it or not. Let us first create a table with a unique constraint.
Code:
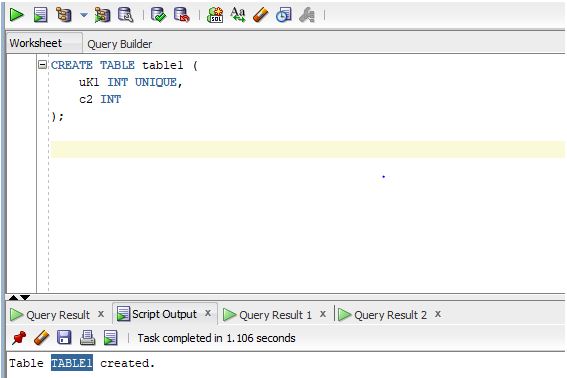
CREATE TABLE table1 (
uK1 INT UNIQUE,
c2 INT
);
Output:
We have added a unique constraint on one of the columns. So, let us prepare a SELECT query to check whether the unique index has been created or not.
Code:
SELECT
index_name,
index_type,
visibility,
status
FROM
all_indexes
WHERE
table_name = 'TABLE1';
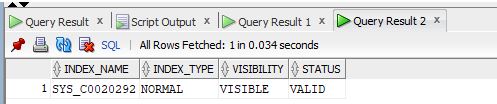
Output:
Explanation: As we can see in the above screenshot, the unique index SYS_C0020292 has been created automatically.
Example #2
ORACLE UNIQUE INDEX WHEN ONLY ONE COLUMN: In this section, we will discuss we can create a unique index on one column in a table with the help of an example. We have already gone through the syntax earlier. In this example, we will create a UNIQUE INDEX on the column customer name, which is present inside the table customers, and then we will try to insert duplicate values and check whether it is allowed or not. So, let us first create the index.
Code:
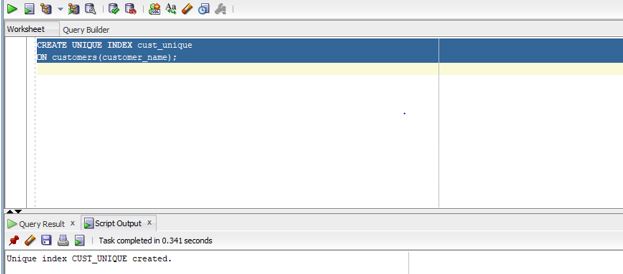
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX cust_unique
ON customers(customer_name);
Output:
Explanation: The column is customer_name, for which a unique index will be created. As we can see in the above screenshot that the unique index has been created.
Now let us look at the existing values present in the table.
Code:
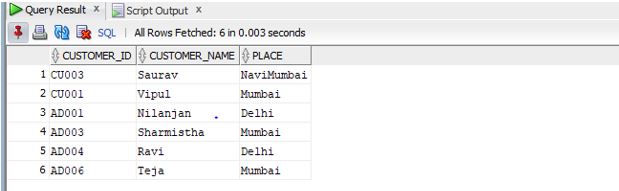
SELECT * from customers;
Output:
As we can see there are six rows in the table. Let us now check the unique index by trying to enter a duplicate value. Let us prepare an INSERT query for the same.
Code:
INSERT INTO customers
VALUES('AD002','Nilanjan','New Delhi');
Output:
Explanation: As we can see that it throws ORA-00001 Unique Constraint error.
Example #3
ORACLE UNIQUE INDEX WHEN MORE THAN ONE COLUMN: In this section, we will discuss how to create a unique index on more than one column in a table with the help of an example. We have already gone through the syntax earlier. In this example, we will create a UNIQUE INDEX on two columns, city and vehicle name, which is present inside the table vehicle, and then we will try to insert duplicate values and check whether it is allowed or not. So, let us first create the index.
Code:
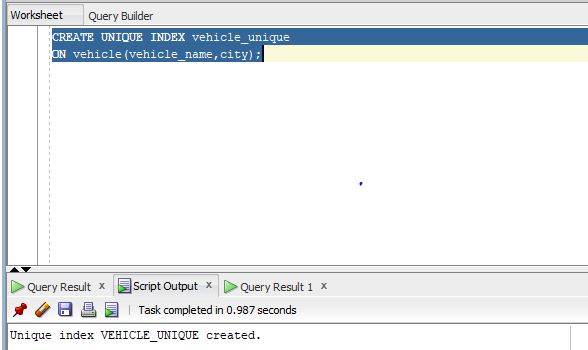
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX vehicle_unique
ON vehicle(vehicle_name, city);
Output:
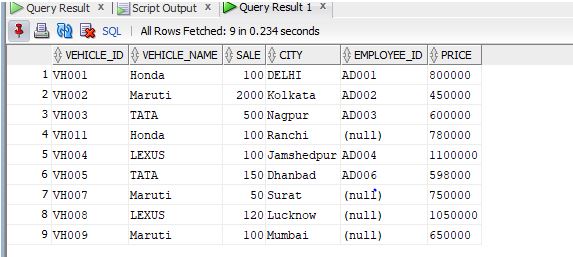
Let us now execute the query in SQL Developer and check the result. Let us now check the contents of the table vehicle.
Code:
SELECT * from vehicle;
Output:
We will now try to insert duplicate values into the column’s vehicle_name and city. Let us now prepare an INSERT query and try to insert duplicate values.
Code:
INSERT INTO vehicle
VALUES('VH013','Honda','100','DELHI','','9000');
Output:
Explanation: As we can see that it throws ORA-00001 Unique Constraint error.
Conclusion
In this article, we discussed the UNIQUE INDEX. We started the article with a discussion about the definition of the UNIQUE INDEX. Later on in the article, we discussed the working of the UNIQUE INDEX with the help of examples.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Oracle UNIQUE Index. Here we discuss an introduction to Oracle UNIQUE Index, its syntax, and how it works with programming examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –