
Introduction on Native keyword in Java
The native keyword acts as a link between the JAVA language and a chunk of code or library written in different languages except for JAVA, which may depend on the machine you are operating on. If the native keyword is applied to a method, then that means the method will be implemented using native code written in some other language (like C or C++) via JNI (JAVA native interface).
Syntax of Native Keyword in Java
The syntax of native code is the same as the normal function definition, with the “native” keyword added at the starting of the function.
For example:
public class testing
{public native String testMethod (String parameter);}Here the public is an access modifier. It should be public so that another file can use it. The string is the return data type of the function. It can be integer, character or Boolean depending upon the keyword. The parameter passed to this function is of data type string as well. Everything should be kept underclass.
After function declaration, we call this function via object created, and library loaded.
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.loadLibrary("testing");
testing testingnew = new testing();
String output = testingnew.stringMethod("NATIVE");
}Library defined above should be loaded first, and the n its object is created. With the help of this object, the native function is called.
How does the Native keyword work?
There should be two files. One containing JAVA code, while the other one should have C/C++ legacy code. Java code will be used to call the legacy code. This legacy code will interact with hardware and return the expected output.
When the legacy code interacts with hardware, then it will not follow the guidelines laid out by JAVA. This code will do the desired processing to get the output and pass the results to JNI. Java native interface will then check in its directory containing all the rules pertaining to native code (This comes under a file called javah.exe in SDK). JNI is designed as part of the Java toolkit. After this processing, the JAVA will publish the outputs in the JAVA language itself. When we are creating the JAVA program, we must make sure that there is a variable/ data flow link between the JAVA file and the legacy file so that there is a smooth flow of data between both.
Steps explaining how to make use of native keywords are given below:
- Write the JAVA code containing the native method, shared library loaded and save it using “filename.JAVA”.
- Compile JAVA code and convert the code to bytecode.
- Create a C/C++ header file containing a native function signature which should be called.
- Write C/C++ code has a native method’s implementation.
- Run JAVA executable file to see the results.
Example
We should write code in Eclipse and run the code to create a library using which then C code will be implemented.
Code: package com.slackerOne;
public class JPP {
public static native void pAccess();
public static native int pRead();
public static native void pWrite(int port, int output);
static{
System.loadLibrary("JPPlibs");
}
public void jAccess(){
JPP.pAccess();
}
public int jRead(){
return JPP.pRead();
}
public void jWrite(int port, int output){
JPP.pWrite(port, output);
}
}After saving this code in the new “class” of the java project, we have to set up a run environment to generate a header file.
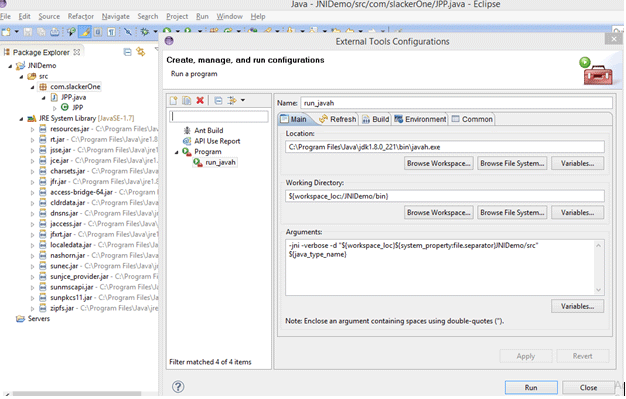
When we will run this, we should get a library generated.
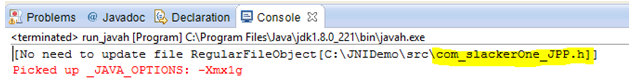
Output:
Here we created the header file from the java code, which will link native code and java language.
Advantages of Native Keyword in Java
Given below are some of the advantages.
- It provides an added advantage to JAVA to interact with the code written in other languages and reduce the work to have the same code written in JAVA, hence reducing the code redundancy.
- It improves the overall code performance. As the code is written in other languages, it may be faster when it works with the machine language than JAVA. We can then use the JAVA program to call this code.
- Using this approach, we can directly give system calls. Reducing the probability of external interference and improving the sped of code execution.
- You can dynamically call a pre-loaded library (written in any language other than JAVA) using an arbitrary driving code written in JAVA and still get a response in JAVA.
- It makes it accessible for JAVA to reach the hardware resources which are available to be used by other languages only.
- In case you have a platform-dependent code already build-up for your application, and whose features are not supported via JAVA, in that case, we can have native code and link this native code to JAVA via native keyword.
Rules
The rules for a native keyword are as follows.
- The native keyword is to be used before the method name.
- Native method declaration does not have a body and should end with a semicolon as these methods are not defined in JAVA but are present in the C/C++ language.
- Native methods can not be declared as abstract method.
- Since there is no surety if the previous old code is written in accordance to IEEE 754 standard (The IEEE Standard for Floating-Point Arithmetic is a technical standard for floating-point arithmetic established in 1985 by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers) so, we can not declare these native methods as strictftp.
- JAVA designs the Java Native Interface (JNI) specification to define the rules and declarations to implement native methods, like conversion of data types between Java and the native code.
Conclusion
The native keyword is which bridges the gap between native languages and JAVA. This can be used as a critical link if our software’s interaction with hardware is more efficient in using pre-existing code. It makes the implementation work lesser in comparison to designing a new application code from scratch wherever it could be avoided.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Native keyword in Java. Here we discuss How does the Native keyword work with the examples, as well as the advantages and the rules. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –


