Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to MySQL WHERE Clause
When working with databases, we use various commands to communicate with the database and perform the required operations. In MySQL, we use SQL, the structured query language that helps us write the query statements in a specific format understandable to the MySQL server. When writing the statements there is often necessary to apply certain conditions and restrictions on certain columns of the tables to retrieve the specific expected result set. Where clause in MySQL helps specify conditions that can filter out the result of the table or filter the result set of combinations of multiple tables through the join.
In this article, we will learn how to use the where clause in MySQL query statements to filter out the result set; further, we will see its syntax, working, and implementation with the help of specific examples.
Syntax:
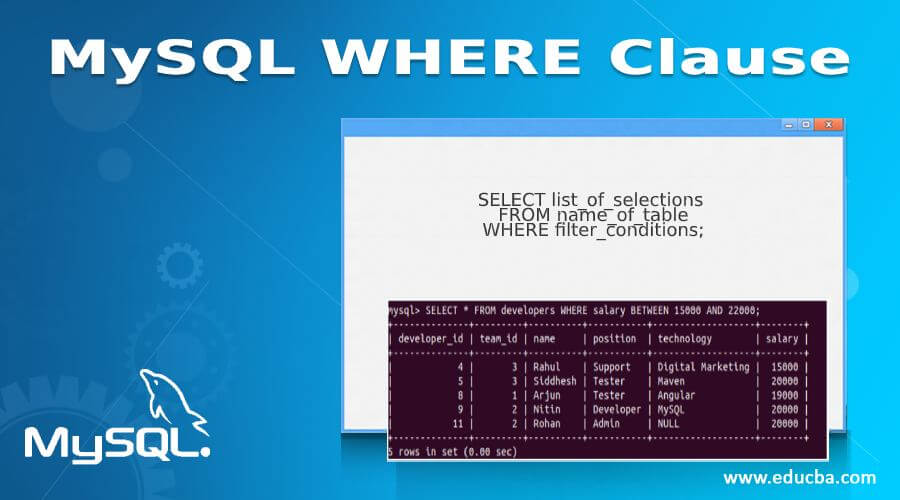
The syntax of the where clause is as defined below:
SELECT list_of_selections FROM name_of_table WHERE filter_conditions;Some of the terms used in the syntax are explained below:
- List_of_selections: this is the list of column names, expressions, aggregate functions on columns, literals, constants, or nearly any value you want to retrieve in the result set.
- Name_of_table: This is the name of the table from which you want to retrieve the result set and whose contents you wish to filter out by specifying certain restrictions.
- Filter_conditions: These are the restrictions or conditions you mention on the table’s columns to get the result set containing records or rows that satisfy those conditions mentioned by you. You can specify one or more conditions with the help of logical operators like AND, OR, and NOT as per your requirement.
Working of MySQL WHERE Clause
This condition is also referred to as the predicate. In MySQL, the predicate will return to a boolean value that is either true, false, or unknown. only and only when the condition mentioned in where clause evaluates to true will the row be added to the final result set.
We can use the WHERE clause in SELECT, DELETE, and UPDATE statements. The evaluation order of the WHERE clause in MySQL query statements is before the SELECT, UPDATE, or DELETE clause, whichever is used in the statement, and after the FROM clause.
Examples to Implement MySQL WHERE Clause
Let us look at examples of using the WHERE clause to learn its implementation. For that, we will consider a table named developers that we will create in an educba database and insert some records.
Example #1
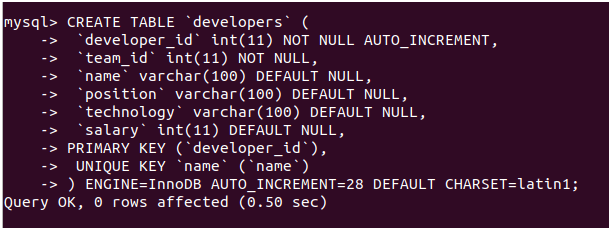
Let us create the developer’s named table in our database educba to hold all the above data.
Query:
CREATE TABLE 'developers' (
'developer_id' int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
'team_id' int(11) NOT NULL,
'name' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'position' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'technology' varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
'salary' int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY ('developer_id'),
UNIQUE KEY 'name' ('name')
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=28 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;Output:
Example #2
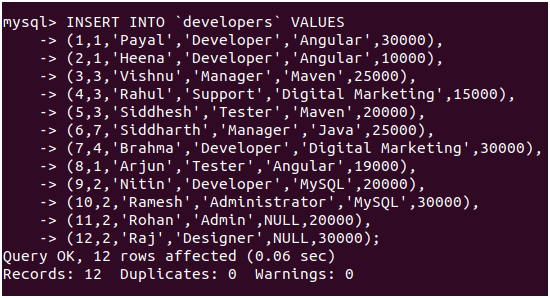
We will insert some records in it using the following query statements.
Query:
INSERT INTO 'developers' VALUES
(1,1,'Payal','Developer','Angular',30000),
(2,1,'Heena','Developer','Angular',10000),
(3,3,'Vishnu','Manager','Maven',25000),
(4,3,'Rahul','Support','Digital Marketing',15000),
(5,3,'Siddhesh','Tester','Maven',20000),
(6,7,'Siddharth','Manager','Java',25000),
(7,4,'Brahma','Developer','Digital Marketing',30000),
(8,1,'Arjun','Tester','Angular',19000),
(9,2,'Nitin','Developer','MySQL',20000),
(10,2,'Ramesh','Administrator','MySQL',30000),
(11,2,'Rohan','Admin',NULL,20000),
(12,2,'Raj','Designer',NULL,30000);Output:
Example #3
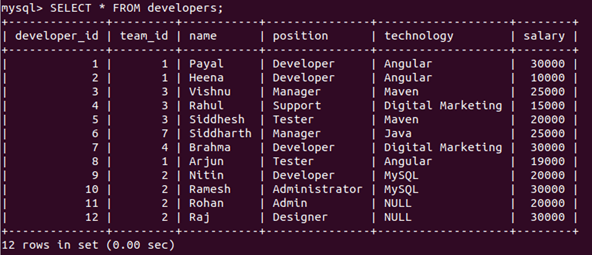
First, Let us retrieve the table’s records using a simple select query statement.
Query:
SELECT * FROM developers;Output:
Example #4
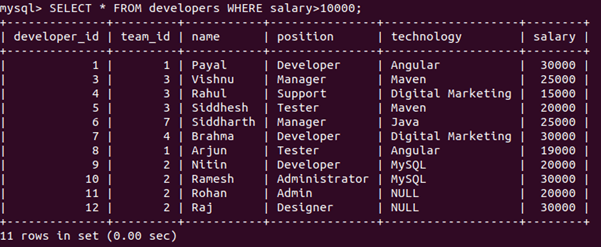
Suppose we want to retrieve only those records from the developer’s tables whose salary is greater than 10000. We must mention a predicate/ condition in the WHERE clause of the SELECT query statement above. Our query statement will be as follows:
Query:
SELECT * FROM developers WHERE salary>10000;Output:
Example #5
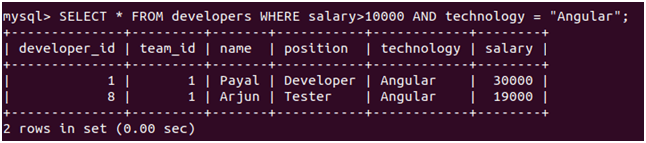
Now, consider a situation where you want to apply multiple conditions on more than one column in a query statement so that when all the specified conditions are fulfilled, only the row should be added into the final resultset of the query. In this case, we can use the AND operator in the WHERE clause. For example, suppose we want to find out the names of all the developers whose technology is angular and whose salary is greater than 10000. Then our query statement will be as follows
Query:
SELECT * FROM developers WHERE salary>10000 AND technology = "Angular";The execution of the above query statement will give the following output, including the records whose salary is greater than ten thousand and who work with angular technology.
Output:
Example #6
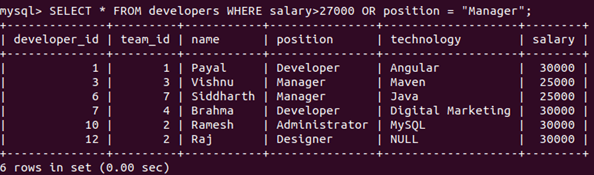
When you have to apply the conditions so that if either of them gets fulfilled, you want that row to be retrieved in the final set, then you can use the OR operator to specify the conditions in the WHERE clause. Consider one example where we want to retrieve the records of table developers having a salary greater than 27000 or in a manager position. Then our query statement will be as follows –
Query:
SELECT * FROM developers WHERE salary>27000 OR position = "Manager";The execution of the above query statement will give the following output, including the records whose salary is greater than 27000 as well records having a position as a manager that might or not have a salary greater than twenty-five thousand –
Output:
Example #7
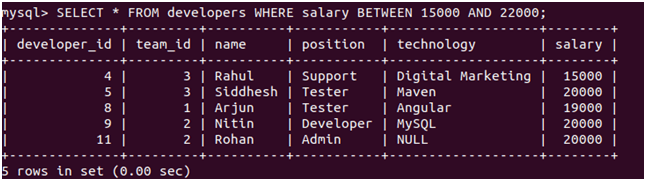
When you want to specify the range of the values allowed for a certain column, you can use the between keyword in the WHERE clause. Considering that we have to find the developers whose salary is between 15000 to 22000, our query statement will be as follows.
Query:
SELECT * FROM developers WHERE salary BETWEEN 15000 AND 22000;Output:
The above query statement gives the following output after execution with all the developers whose salary ranges from 15000 to 22000.
Along with all the operators mentioned above, we can make use of all types of comparative operators that are available such as <,>,<=,>=, etc., along with IS NULL and IS NOT NULL and boolean values like TRUE and FALSE in the WHERE clause. It functions in the same manner as the of with the SELECT statement.
Conclusion
We can use the WHERE clause in MySQL query statements to specify the conditions and predicates related to the table’s columns. If the predicate evaluates to true, the final result set will only include that row. You can use the WHERE clause with SELECT, DELETE, and UPDATE statements, allowing the use of various logical operators, comparative operators, and boolean values. IS NULL and IS NOT NULL constraints and also be specified for certain columns inside the WHERE clause.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL WHERE Clause” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.