Updated May 25, 2023
Introduction to MySQL WITH Clause
MySQL WITH clause defines the CTE (Common table expressions). A common table expression is a named temporary result set that can be used multiple times. The CTE can be defined using WITH clause and can have one or more sub-clauses separated by a comma. The defined sub-clauses consist of each result set associated with a name to it. CTE can be used in other CTEs. We also have recursive CTE, which will be referred to as itself. The result set exists only within the scope of a single statement as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE.
In this session, let us see how CTE will be defined using the WITH clause, along with an example.
Syntax of MySQL WITH
Now let us consider the syntax of declaring the CTE using WITH clause:
1. Declaration of Single CTE
Syntax:
WITH <CTE NAME><COLUMN LIST > AS
<
QUERY STATEMENT
>
SELECT * FROM <CTE NAME>;2. Declaration of Multiple CTE
Syntax:
WITH <CTE NAME1><COLUMN LIST > AS
<
QUERY STATEMENT
>
, <CTE NAME2><COLUMN LIST > AS
<
QUERY STATEMENT
>
SELECT * FROM <CTE NAME1> join <CTE NAME2> ON <Condition>;WITH clause can be used in the beginning as:
- WITH … SELECT …
- WITH … UPDATE …
- WITH … DELETE …
WITH statement can immediately precede as below:
- CREATE TABLE … WITH … SELECT …
- CREATE VIEW … WITH … SELECT …
- INSERT … WITH … SELECT …
- REPLACE … WITH … SELECT …
- DECLARE CURSOR … WITH … SELECT …
- EXPLAIN … WITH … SELECT …
How does WITH Clause Work in MySQL?
Now let us consider the tables that apply the CTE concept using the WITH clause:
1. Let us create a Table, use the above Syntax format, and insert Data into the Table.
create table Order_detail
(
shop_id int,
product_id int,
brand_id int,
Shop_name varchar(20),
quantity int,
price int
);2. Now, let us insert Data into the Table.
insert into Order_detail (shop_id, product_id, brand_id, Shop_name, quantity, price)
values (1,1,1,'Kellogs',45,45);
insert into Order_detail (shop_id, product_id, brand_id, Shop_name, quantity, price)
values (2,7,5,'Fantasy Store',75,145);
insert into Order_detail (shop_id, product_id, brand_id, Shop_name, quantity, price)
values (3,3,2,'Laxshmi store',65,85);
insert into Order_detail (shop_id, product_id, brand_id, Shop_name, quantity, price)
values (4,4,7,'General store',25,65);
insert into Order_detail (shop_id, product_id, brand_id, Shop_name, quantity, price)
values (5,5,8,'Corn store',35,75);Query:
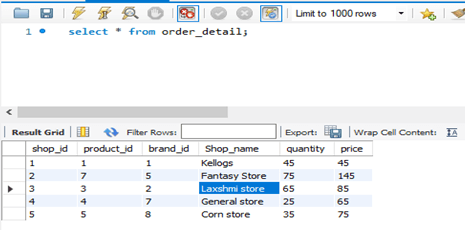
select * from Order_detail;Output:
3. Now let us Perform the Simple CTE Creation on the above Table.
Query:
With CTE_Orders_Store AS
(
Select shop_id,
product_id,
brand_id,
shop_name,
quantity
from order_detail where UPPER(shop_name) like '%store%'
)
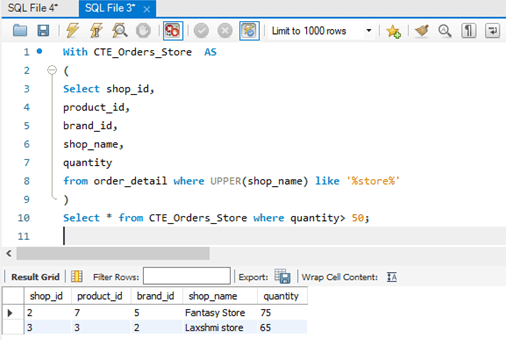
Select * from CTE_Orders_Store where quantity> 50;Output:
Explanation: Here we are finding the shops that have stored in their “shop_name” and the number of products sold exceeds 50.
4. Now let us Perform another Simple CTE on the above Table.
Query:
With CTE_Orders_quantity AS
(
Select shop_id,
product_id,
brand_id,
shop_name,
quantity
from order_detail where quantity> 30
)
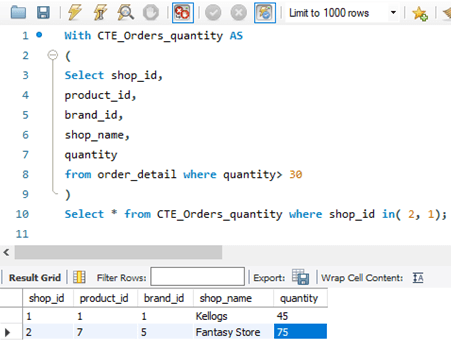
Select * from CTE_Orders_quantity where shop_idin( 2, 1);Output:
Explanation: Here, we are finding the shops with quantity sold > 30 and then filtering the rest and bringing only the shop_id that are (2, 1).
5. Now let us Consider the above-Created table “order_detail” and create another Table as below.
Query:
create table Details_People
(
id int,
name varchar(20),
location varchar(20),
pincodeint,
product_idint
);6. Insert the Below Rows into the Table as below.
Query:
insert into DETAILS_PEOPLE values (1, 'Sam', 'MP', 564321,1);
insert into DETAILS_PEOPLE values (2, 'Sohan', 'Bangalore', 523321,7);
insert into DETAILS_PEOPLE values (3, 'Will', 'Tamilnadu', 523021,3);
insert into DETAILS_PEOPLE values (4, 'Ben', 'UP', 564000,3);
insert into DETAILS_PEOPLE values (5, 'Hamington', 'UP', 564000,4);
insert into DETAILS_PEOPLE values (6, 'Ji eun', 'Bangalore', 523321,2);
insert into DETAILS_PEOPLE values (7, 'Jimin', 'UP', 564000,5);
insert into DETAILS_PEOPLE values (8, 'Jk', 'Bangalore', 523321,4);
insert into DETAILS_PEOPLE values (9, 'V', 'AP', 590001,5);
insert into DETAILS_PEOPLE values (10, 'Jhope', 'Bangalore', 523321,1);7. Now let us Select the Columns from the Table
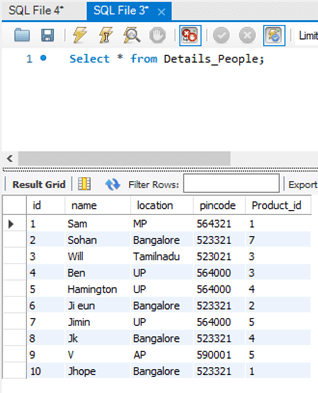
Query:
Select * from Details_People;Output:
8. let us perform the Complex CTE Between the two Tables.
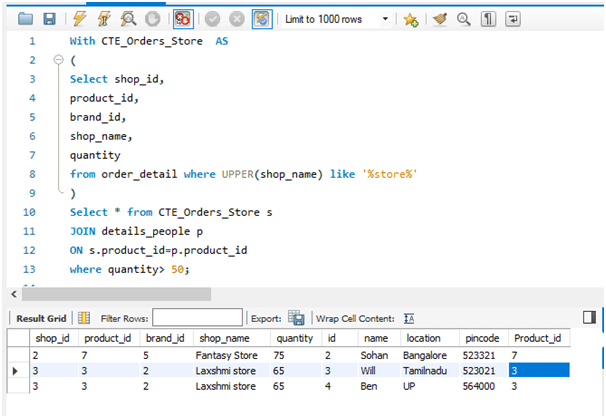
Query:
With CTE_Orders_Store AS
(
Select shop_id,
product_id,
brand_id,
shop_name,
quantity
from order_detail where UPPER(shop_name) like '%store%'
)
Select * from CTE_Orders_Stores
JOIN details_people p
ON s.product_id=p.product_id
where quantity> 50;Output:
Explanation: Here in the above query, we are finding the shops which have stored in their “shop_name” and the number of products sold greater than 50. The output of the CTE we have joined with the “details_people” and got the output.
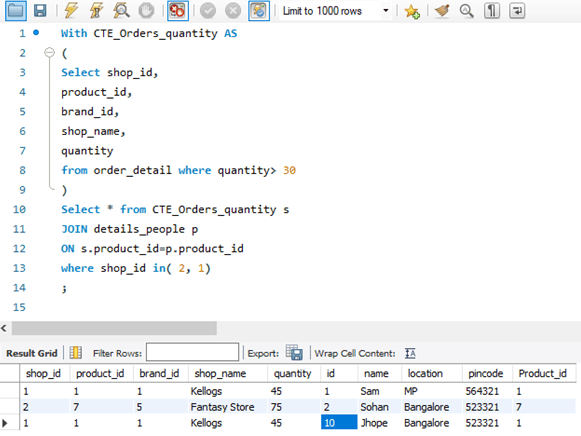
Query:
With CTE_Orders_quantity AS
(
Select shop_id,
product_id,
brand_id,
shop_name,
quantity
from order_detail where quantity> 30
)
Select * from CTE_Orders_quantity s
JOIN details_people p
ON s.product_id=p.product_id
where shop_idin( 2, 1);Output:
Explanation: Here we are finding the shops which have a quantity sold > 30, and then we filter the rest and bring only the shop_id that are (2, 1), then join it with the “details_people” table.
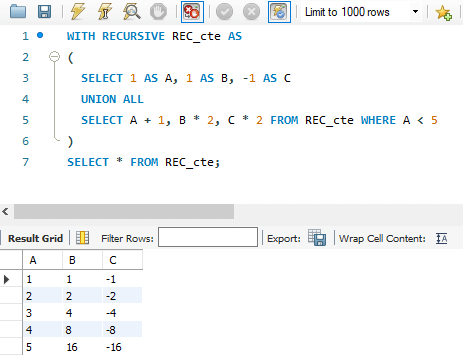
9. Now let us see the RECURSIVE CTE
Query:
WITH RECURSIVE REC_cte AS
(
SELECT 1 AS A, 1 AS B, -1 AS C
UNION ALL
SELECT A + 1, B * 2, C * 2 FROM REC_cte WHERE A < 5
)
SELECT * FROM REC_cte;Output:
Conclusion
- MySQL WITH clause defines the CTE (Common table expressions). A common table expression is a named temporary result set that can be used multiple times.
- You can define the CTE using the WITH clause, which allows for one or more sub-clauses separated by a comma in active voice.
- Each sub-clause in the CTE defines a result set and associates it with a name. You can use CTEs within other CTEs. Additionally, recursive CTEs refer to themselves.
- The result set exists only within the scope of the single statement as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, or DELETE
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL WITH” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.