Updated May 26, 2023
Introduction to MySQL GROUP BY month
MySQL GROUP BY is a MySQL clause for grouping a set of table rows into subgroups based on values of expressions or columns. Thus, the GROUP BY clause reduces the number of table rows in the output set. The clause returns a single row for every group specified in the query. The GROUP BY clause is a non-compulsory clause of the SELECT statement in MySQL, used together in the query. In addition, the GROUP BY CLAUSE can be defined by applying certain functions like aggregate functions or date functions. With this implementation, we can group the table rows using month or year by applying DATE_FORMAT() in MySQL, adding to the GROUP BY clause to display the result set grouping according to the month part of the DATE function.
Syntax
Syntax structure for using the GROUP BY Month clause in MySQL:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(ColumnName, '%m-%Y') FROM TableName
GROUP BY MONTH (ColumnName) , YEAR (ColumnName) DESC;To display the result set using the GROUP BY Month clause, you can use the following syntax, which is described as follows:
- The MySQL operator DATE_FORMAT() is used here to be easy enough to group the timestamp, date, or datetime table column implementing any format your result needs to show in the query section.
- TableName denotes the particular database table involved in the GROUP BY Month clause.
- ColumnName defines the table column you want to group using the month or year formats. The column data type should have either DATETIME, TIMESTAMP, or DATE so that while using the GROUP BY Month clause, the month part can be properly extracted based on the column from the table data in the database.
- We can even sort the result set or date column values using ASC or DESC options.
How GROUP BY month works in MySQL?
- In MySQL, the SELECT statement is often applied to fetch all the records that match each other from the database tables based on several clauses used in the query statements.
- It helps summarize the type of data we want to retrieve from the tables based on any table field, column values, or aggregate functions used, like AVG, SUM, MIN, MAX, etc., in MySQL. Other functions like the DATE function with their respective formats are also used.
- The GROUP BY clause and SELECT query display the result rows in grouping order with the help of column and data type in MySQL. Generally, the GROUP BY clause should appear in MySQL query after the two clauses, FROM and WHERE, to specify the grouping column with function.
- Usually, the MONTH() function is defined to identify every month, and aggregate functions help to show the calculative values of sum, average, minimum, maximum, and so on.
- Thus, we will use GROUP BY Month to fetch the table records in the output set by grouping the column with the month part of the Date function provided in the DATE_FORMAT() structure.
Examples of MySQL GROUP BY month
Given below are the examples mentioned :
Example #1
Simple Example using GROUP BY Month with DATE_FORMAT().
To recognize the above concept of the GROUP BY Month clause, let us build up a table to show the rows results from the table grouped by month part of the DATE_FORMAT().
Suppose we have the following query code to create a table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE DemoGroupMonth(Group_ID INT PRIMARY KEY, Due_Date DATE);Again, we will enter the sample records in the table using the following statement.
Code:
INSERT INTO DemoGroupMonth VALUES(1,NOW());
INSERT INTO DemoGroupMonth VALUES(2,DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 3 year));
INSERT INTO DemoGroupMonth VALUES(3,DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL -3 year));
INSERT INTO DemoGroupMonth VALUES(4,DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 2 year));
INSERT INTO DemoGroupMonth VALUES(5,DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL -2 year));
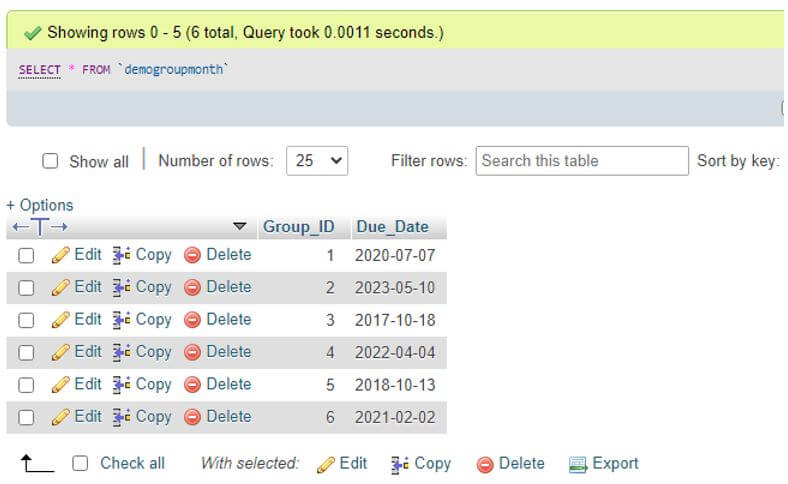
INSERT INTO DemoGroupMonth VALUES(6,DATE_ADD(NOW(), INTERVAL 1 year));Now, we will view all the records from this table DemoGroupMonth by applying the following SELECT statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM DemoGroupMonth;Output:
After this, we will code for retrieving the result set with GROUP BY Month.
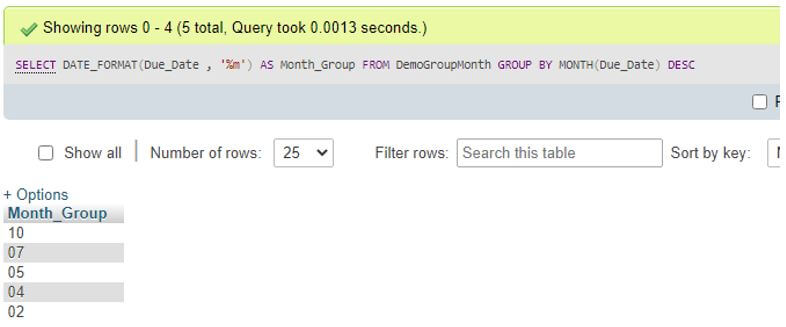
Code:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT(Due_Date , '%m') AS Month_Group FROM DemoGroupMonth GROUP BY MONTH(Due_Date) DESC;The succeeding output produces the month grouped by implementing GROUP BY.
Output:
As you can see, the result set displays the DATE column values by grouping them with the month and arranging them in descending order.
Suppose we want to count the number of records in the table by determining or calculating it using a specific period such as a Day, Month, or Year part of the DATE function. In this case, the column will have a DATETIME, DATE, or TIMESTAMP field data type. The simple query will be as follows.
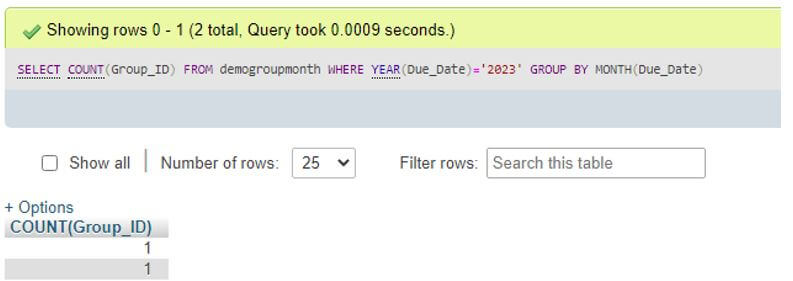
Code:
SELECT COUNT(Group_ID) FROM demogroupmonth WHERE YEAR(Due_Date)='2023' GROUP BY MONTH(Due_Date);Output:
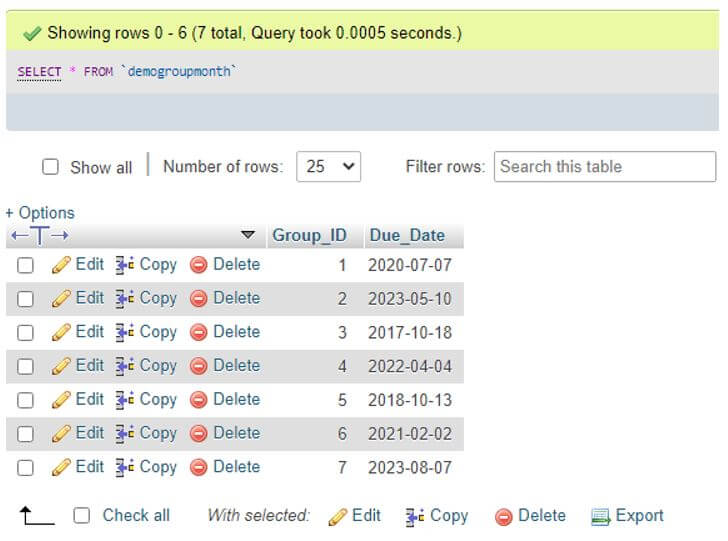
For this, we again inserted some rows in the table with a year equal to 2023 to make the result properly run as.
Code:
select * from demogroupmonth;Output:
Example #2
Example using GROUP BY Month with the same date.
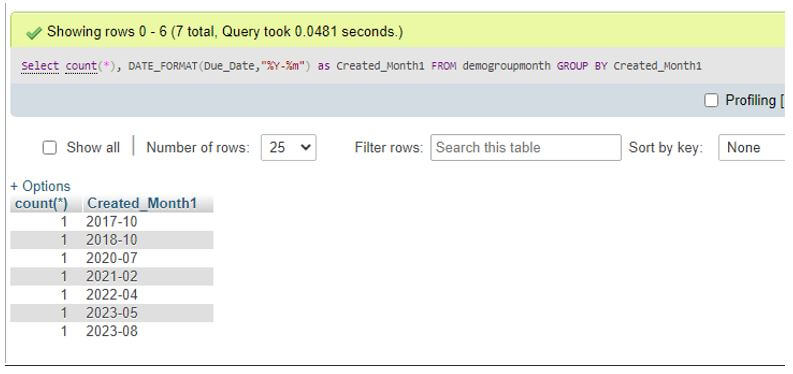
If we want group table rows added on the identical date or day, then we will query the count of such grouped rows as follows with GROUP BY Month.
Code:
Select COUNT(*), DATE_FORMAT(Due_Date,'%m') as Month_Created_At FROM demogroupmonth GROUP BY Month_Created_At;Output:
Example #3
Example using GROUP BY Month for Employee month-wise data.
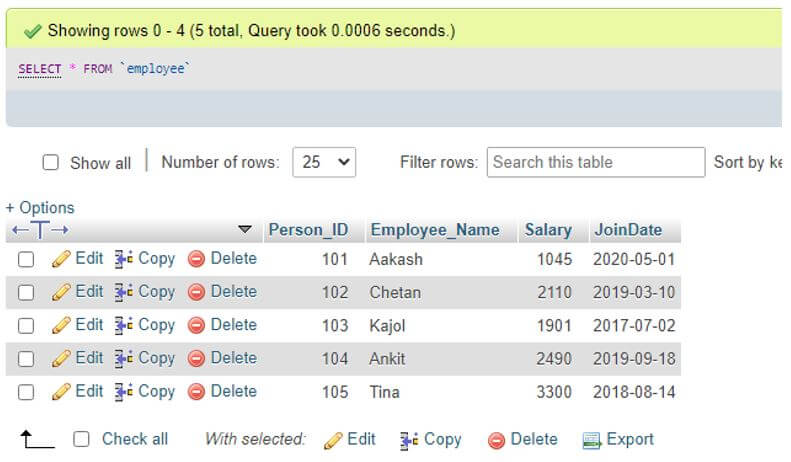
Assume that we have a table in our database as Employee, which includes fields such as Person_ID, Employee_Name, Salary, and JoinDate.
Code:
select * from employeeOutput:
Here the JoinDate column of the table contains DATE data type values to group rows by month.
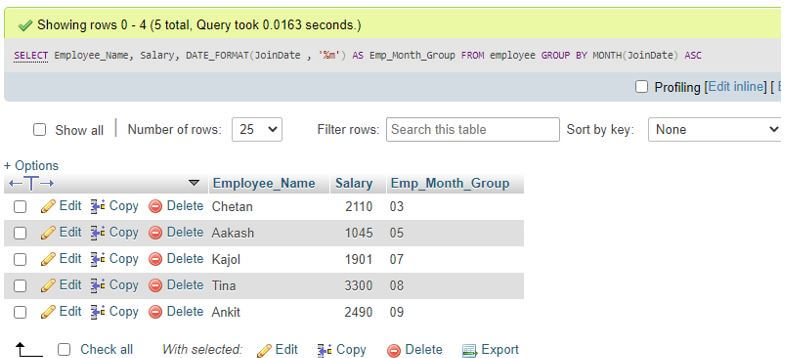
Code:
SELECT Employee_Name, Salary, DATE_FORMAT(JoinDate , '%m') AS Emp_Month_Group FROM employee GROUP BY MONTH(JoinDate) ASC;Output:
We can query any employee data to find month-wise records from the Employees table in the database implementing the MySQL GROUP BY month clause.
Conclusion
The MySQL GROUP BY month clause is responsible for grouping to provide a set of rows grouped by the EXTRACT function that permits abstracting parts of a date value like month, year, day, or time. The MySQL GROUP BY month clause helps find out the monthly report in sales database tables to produce the systematic data of the employees.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL GROUP BY month” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.